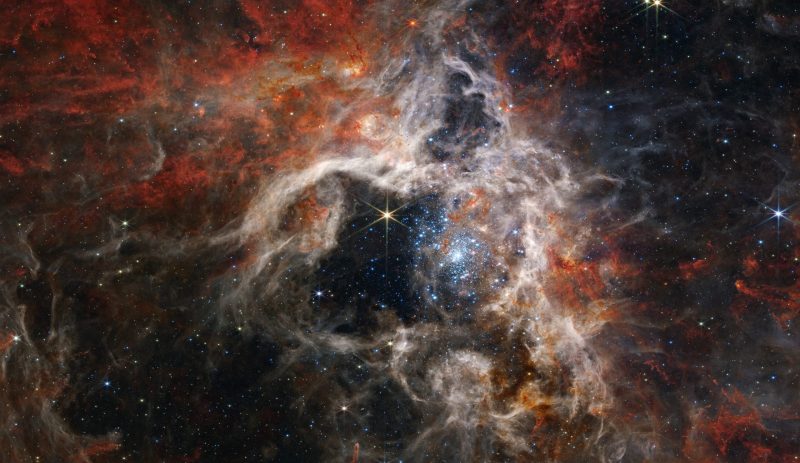

Webb catches the Tarantula Nebula
The Webb has caught an excellent picture of the Tarantula Nebula. On September 6, 2022, NASA and ESA launched new photographs of the Tarantula Nebula, also called 30 Doradus, and its star-forming area. The James Webb Area Telescope has turned three of its devices, NIRCam, NIRSpec and MIRI, on this cloudy and starry area that lies within the Massive Magellanic Cloud, a satellite tv for pc galaxy of the Milky Method.
Within the new photographs, we will see glowing star-forming areas that have been beforehand hidden behind mud. And the gasoline and dirt tendrils present totally different construction within the near-infrared of NIRCam and the mid-infrared of MIRI. Plus, we will even see distant background galaxies.
The Tarantula Nebula
The Tarantula Nebula lies 161,000 light-years distant within the LMC, which is within the Southern Hemisphere constellation of Dorado the Goldfish. In truth, this cloudy, dusty stellar nursery is dwelling to the most well liked, most large stars identified. By the way in which, the Tarantula Nebula will not be solely dwelling to the biggest and brightest star-forming area within the Massive Magellanic Cloud but additionally within the Native Group, our regional assortment of galaxies.
NIRCam’s view of the Tarantula
The picture on the high of this text is NIRCam’s near-infrared view of the Tarantula. The hollowed-out area at middle reveals the place fierce radiation from younger stars have cleared the world. In addition to large, younger stars glowing in pale blue. ESA stated:
Solely the densest surrounding areas of the nebula resist erosion by these stars’ highly effective stellar winds, forming pillars that seem to level again towards the cluster. These pillars include forming protostars, which is able to ultimately emerge from their dusty cocoons and take their flip shaping the nebula.
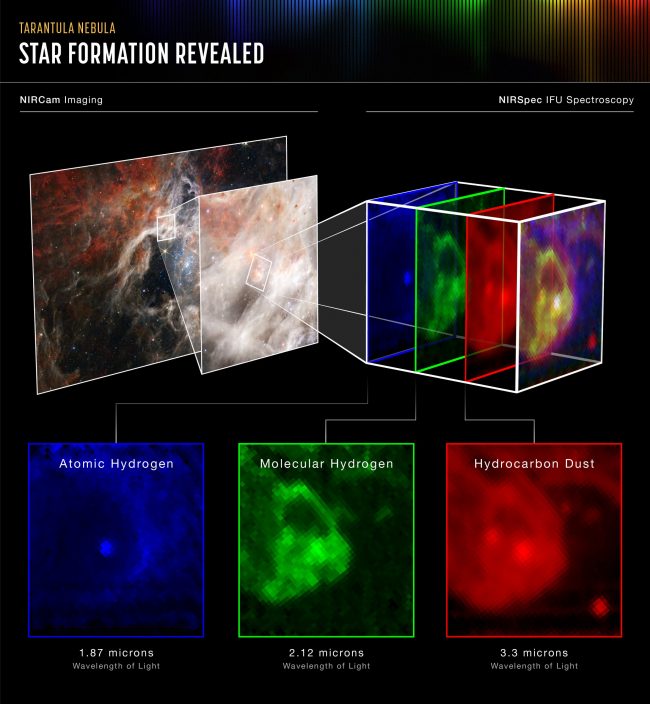
NIRSpec’s view of the Tarantula
NIRSpec is Webb’s Close to InfraRed Spectrograph. And the spectrograph spreads gentle right into a spectrum, which permits astronomers to research the article’s temperature, mass and chemical composition, for instance. So, the younger star NIRSpec centered on within the Tarantula Nebula will not be but on the stage the place it’s clearing out the area round itself.
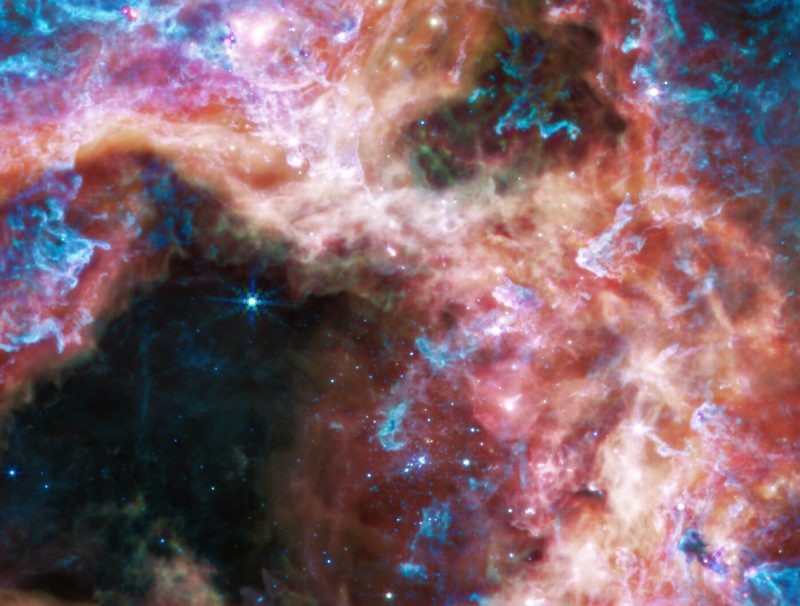
MIRI’s view of the Tarantula
The longer infrared wavelengths that MIRI sees allow us to look deeper into the Tarantula Nebula. So now we will see cooler areas, the place protostars are nonetheless gaining mass.

Why Webb focused the Tarantula Nebula
The Tarantula Nebula not solely tells us a couple of large star-forming area within the close by universe, nevertheless it’s additionally an instance of what was taking place in the course of the universe’ cosmic midday. As a result of this was a time when our universe was a number of billion years outdated and star formation peaked. Moreover, our Milky Method doesn’t have a comparable area of livid star formation.
Finally, astronomers will be capable of examine Webb’s photographs of the Tarantula Nebula with photographs of star-forming areas it sees within the earlier universe.
Two area telescopes, twice the star energy.
This #TransformationalTuesday, watch as @NASAHubble’s view of the Tarantula Nebula fades into Webb’s NIRCam, then MIRI instrument views. Hubble and Webb will work collectively to showcase the universe throughout a number of wavelengths of sunshine. pic.twitter.com/GDIRSWWFQV
— NASA Webb Telescope (@NASAWebb) September 6, 2022
Backside line: The James Webb Area Telescope has captured photographs of the Tarantula Nebula, revealing stellar nurseries and protostars. This star-forming area lies within the Massive Magellanic Cloud, a satellite tv for pc galaxy of the Milky Method.
