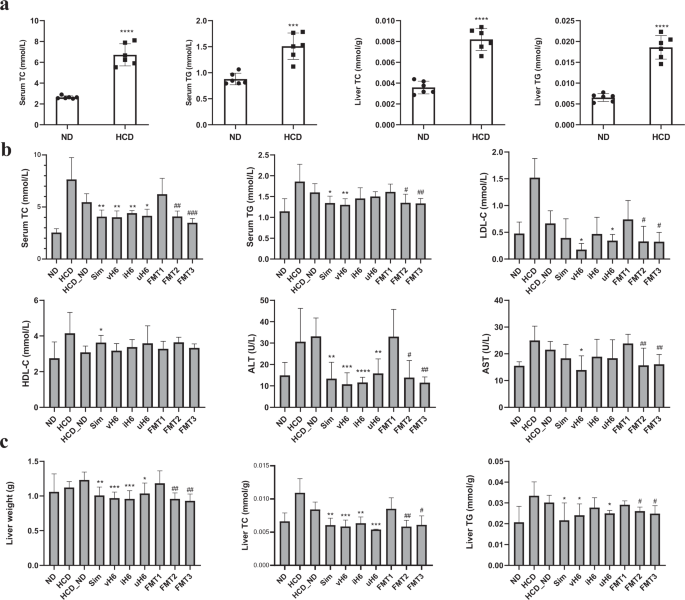
Results of v/i/uH6 on serum and liver physicochemical indexes of mice
In contrast with the ND group, the HCD group had no important variations in meals consumption and weight achieve (Supplementary fig. 1a), whereas, TC and Triglyceride (TG)in serum and liver of mice within the HCD group elevated considerably, and the content material was ~2–3 occasions that of the ND group (Fig. 1a), indicating that the hypercholesterolemia mice mannequin has been efficiently established.
a Serum TC and TG and liver TC and TG ranges in hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice. Information are represented because the imply ± SEM (n = 6). ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. management ND. b Serum TC, TG, LDL-C, high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (HDL-C), ALT, and AST ranges after 12 weeks. c Liver weight, TC, and TG ranges. Information are represented because the imply ± SEM (n = 8). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. management HCD_ND; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. management FMT1. HCD_ND refers back to the group of hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice; v/i/uH6 refers to viable (vH6), heat-inactivated (iH6), and ultrasonically-lysed (uH6) micro organism cells; FMT1/2/3 refers to utilizing feces from HCD_ND, Sim, and vH6 teams, respectively.
In contrast with the HCD_ND group, after 12 weeks of therapy with v/i/uH6 and FMT3, the physicochemical indexes associated to lipid metabolism in mice serum had been improved (Fig. 1b), TC was considerably decreased, particularly the serum TC within the FMT3 group, which decreased by 43.98% (P < 0.05). The serum TG ranges of mice given vH6 and FMT3 had been considerably decreased by 18.69% and 17.17%, respectively (P < 0.05). In contrast with the HCD group, low-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (LDL-C) ranges had been considerably decrease when given vH6, uH6 and FMT3 (0.18–0.34 mmol/L vs 1.5 mmoL). Furthermore, v/i/uH6 and FMT3 considerably diminished the serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ranges of mice, particularly these given vH6 and iH6 (10.76 U/L and 11.58 U/L, respectively). vH6 and FMT3 considerably decreased serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) ranges (P < 0.05).
v/i/uH6 and FMT3 equally improved the liver weight, TC and TG (apart from iH6) contents of mice (Fig. 1c). For instance, when given vH6 and iH6, liver weight decreased by 21.27% and 22.10%, respectively (P < 0.05). v/i/uH6 decreased TC by 30.44%, 24.49%, and 35.67%, respectively (P < 0.05). General, v/i/uH6 and FMT3 improved serum and liver physicochemical properties, together with decrease TC, TG, LDL-C, ALT, AST within the serum, and TC, TG within the liver at varied ranges.
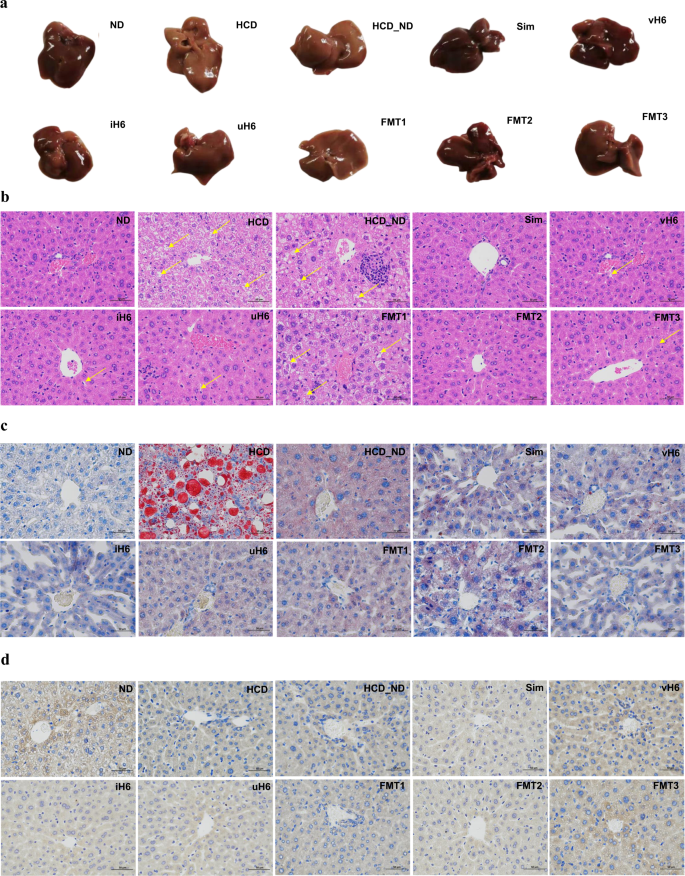
Impact of v/i/uH6 on liver degeneration in hypercholesterolemic mice
Mice fed with HCD confirmed hepatomegaly with a grayish-yellow hue. Nonetheless, v/i/uH6 and FMT3 inhibited hepatomegaly, the colour (reddish-brown) and comfortable texture of liver had been near regular. (Fig. 2a). HE staining confirmed that within the HCD group, the association of liver cells was unfastened and disordered, a lot of fats vacuoles of various sizes and numbers appeared, the liver cells had been enlarged, partially necrotic, and the liver cells had been severely broken. (Fig. 2b). When mice had been handled with v/i/uH6 and FMT3, the harm of liver cells was clearly diminished, the fats droplets within the cytoplasm had been diminished, and the liver cells had been organized neatly.
a Photos of mice livers after totally different remedies. b, c Consultant photos of H/E staining and Oil Pink O staining of liver sections (400×, scale bar = 50 μm). Some native broken parts of hepatocyte are indicated by yellow arrows in H/E staining. d Consultant photos of immunofluorescent staining of liver sections utilizing anti-UCP1 (400×, scale bar = 50 μm). HCD_ND refers back to the group of hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice; v/i/uH6 refers to viable (vH6), heat-inactivated (iH6), and ultrasonically-lysed (uH6) micro organism cells; FMT1/2/3 refers to utilizing feces from HCD_ND, Sim and vH6 teams, respectively.
Oil crimson O staining confirmed that liver lipid droplets in hepatocytes of HCD mice confirmed particle accumulation and fusion into flakes (Fig. 2c). Nonetheless, when mice had been handled with vH6, iH6 and FMT3, the lipid droplets had been considerably much less, the scale was smaller, and the distribution was irregular and uneven.
The expression of UCP1 in liver tissues was detected by immunohistochemical staining (Fig. second). In contrast with HCD_ND and FMT1, UCP1 expression was considerably enhanced in mice given vH6, iH6 and FMT3, and there was a big space of optimistic brown particles within the liver tissues. In conclusion, v/i/u H6 and FMT3 may be noticed to enhance liver degeneration to various levels by staining liver sections.
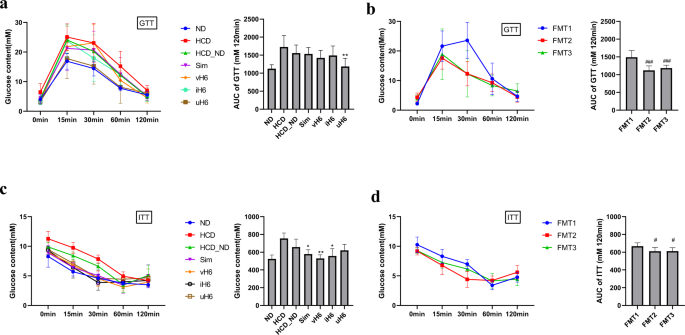
Impact of v/i/uH6 on glucose tolerance take a look at and insulin tolerance take a look at in hypercholesterolemic mice
Within the HCD group, the glucose ranges of mice had been disturbed and the blood glucose ranges elevated sharply. v/i/uH6 and FMT3 decreased the realm below curve (AUC) values akin to glucose tolerance in mice, which had been considerably decreased by 23.89% and 20.50% within the uH6 and FMT3 teams, respectively (P < 0.05, Fig. 3a, b). Equally, v/i/uH6 and FMT3 improved insulin tolerance of mice, as evidenced by diminished glucose and decrease AUC values within the insulin tolerance take a look at, which had been a considerably decreased by 19.53%, 15.10%, and eight.35% within the vH6, iH6, and FMT3 teams, respectively (P < 0.05, Fig. 3c, d). These outcomes point out that v/i/uH6 and FMT3 can enhance glucose and insulin tolerance in hypercholesterolemic mice.
a, b GTT: mice fasted in a single day had been injected with glucose (2 mg/kg) intraperitoneally. Blood glucose was decided at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min then. c, d ITT: mice fasted for 4 h had been injected with insulin (0.75 U/kg). Blood glucose was decided at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min then. AUC worth was calculated. Information are introduced because the imply ± SEM (n = 8). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01vs. management HCD_ND; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. management FMT1. HCD_ND refers back to the group of hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice; v/i/uH6 refers to viable (vH6), heat-inactivated (iH6), and ultrasonically-lysed (uH6) micro organism cells; FMT1/2/3 refers to utilizing feces from HCD_ND, Sim and vH6 teams, respectively.
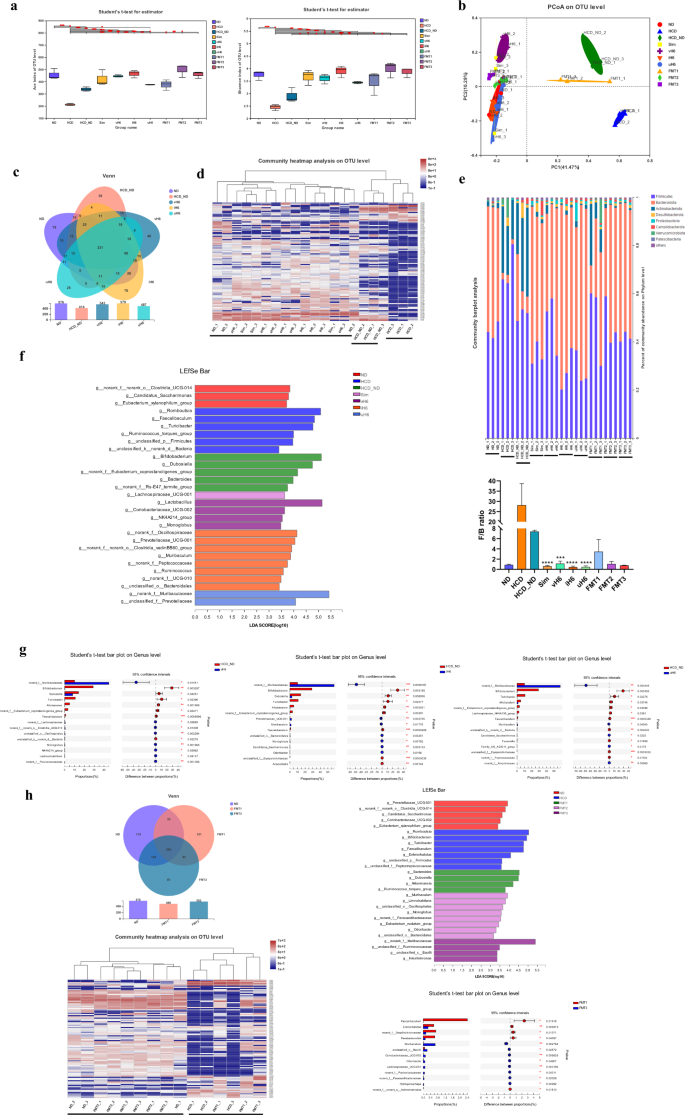
Impact of v/i/uH6 on intestinal microbiota construction of hypercholesterolemic mice
A complete of 1061 OTUs, together with 18 phyla, 33 lessons, 78 orders, 112 households, 196 genera, and 305 species, had been recognized in mice intestinal microbiota by 16S rRNA sequencing know-how. The α variety of intestinal microbiota of various handled mice was evaluated based mostly on OTU ranges. The Ace, Shannon, and Shannoneven indexes of the intestinal microbiota of mice given v/i/uH6 and FMT3 had been considerably greater than these of the HCD_ND and FMT1 teams (Fig. 4a and Supplementary fig. 2b). The β-diversity principal coordinate evaluation (PCoA) confirmed that the intestinal microbiota of mice given v/i/uH6 and FMT3 teams was much like that of the ND group however considerably totally different from that of the HCD, HCD_ND and FMT1 teams (Fig. 4b). In comparison with HCD_ND, v/i/uH6 elevated the abundance of intestinal microbiota in mice, and the variety of OTUs elevated by 31.16%, 39.86%, and 17.63%, respectively (Fig. 4c). Warmth maps based mostly on OTU ranges confirmed that the intestinal microflora construction of the HCD, HCD_ND teams and different therapy teams had been clearly divided into three elements, and the neighborhood abundance of v/i/uH6 was extra much like that of the ND and Sim teams (Fig. 4d). Additional evaluation of intestinal microbiota composition on the phylum stage (Fig. 4e) confirmed that in HCD group, the Firmicutes elevated and the Bacteroidota decreased within the gut, which led to a rise of F/B ratio. Whereas v/i/uH6 diminished the relative abundance of Firmicutes by 5.94%, 44.96%, and 44.64% respectively, it elevated the relative abundance of Bacteroidota by 234.85%, 377.05%, and 362.53% respectively, and diminished the F/B ratio considerably in comparison with the HCD_ND group.
a Alpha-diversity assessed by richness (ACE) and variety (Shannon). b Beta variety calculated utilizing weighted UniFrac by PCoA. c Venn diagram of OTUs in mice given v/i/uH6. d Heatmap of the relative abundance of the highest 100 OTUs in mice given v/i/uH6. e Relative abundance of microbiota on the phylum stage and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio. f LDA rating (LDA > 2.5) in mice given v/i/uH6. g Two teams comparability utilizing a Scholar’s t take a look at. h Venn diagram of OTUs, heatmap of the relative abundance of the highest 100 OTUs, LDA rating and two teams comparability utilizing a Scholar’s t take a look at in fecal microbiota transplantation teams. Information are introduced because the imply ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. HCD_ND refers back to the group of hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice; v/i/uH6 refers to viable (vH6), heat-inactivated (iH6), and ultrasonically-lysed (uH6) micro organism cells; FMT1/2/3 refers to utilizing feces from HCD_ND, Sim and vH6 teams, respectively.
LEfSe evaluation confirmed important variations in intestinal microbiota construction between the totally different therapy teams (Supplementary fig. 2f), and linear discriminant evaluation (LDA) was used to judge the predominant micro organism within the totally different teams. The dominant micro organism of mice given vH6 had been Lactobacillus, Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002, and norank_f__Oscillospiraceae, Muribaculum, unclassified_o__Bacteroidales, and Ruminococcus when given iH6, and norank_f__Muribaculaceae when given uH6 (Fig. 4f). Scholar’s t take a look at confirmed that within the HCD_ND group, the abundance of Faecalibaculum, Allobaculum and Turicibacter elevated considerably in comparison with that of the v/i/uH6 handled group during which the abundance of norank_f__Muribaculaceae elevated considerably in comparison with that of the HCD_ND group (Fig. 4g). As well as, in comparison with the HCD_ND group, i/uH6 elevated unclassified_o__Oscillospirales and Lachnoclostridium, and vH6 elevated Muribaculum considerably, so these dominant micro organism might be potential biomarkers for efficient ldl cholesterol discount by L.p.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) utilizing feces from mice handled by vH6 additionally improved the intestinal microbial composition induced by HCD (Fig. 4h). In comparison with the FMT1 therapy, the variety of intestinal microbes OTUs of FMT3 handled mice elevated by 15%, and the warmth map of neighborhood distribution was extra much like that of the conventional and FMT2 handled mice. Equally, the quantity of Firmicutes decreased by 15.45% and that of Bacteroidota elevated by 79.3% in FMT3 handled mice. The dominant micro organism of FMT3 handled mice had been norank_f__Muribaculaceae, unclassified_f__Ruminococcaceae, unclassified_c__Bacilli, and Intestinimonas, of which norank_f__Muribaculaceae was additionally probably the most plentiful dominant micro organism of uH6 handled mice. In contrast with FMT1 therapy, FMT3 elevated the abundance of Enterorhabdus, Muribaculum, unclassified_c__Bacilli, Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002 and norank_f__Paracaedibacteraceae elevated. As well as, FMT3 decreased Faecalibaculum ranges, which was per the v/i/uH6 handled group. These outcomes indicated that v/i/uH6 and FMT3 can alleviate the dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota of hypercholesterolemic mice by regulating intestinal microbes.
Impact of v/i/uH6 on fecal metabolites in hypercholesterolemic mice
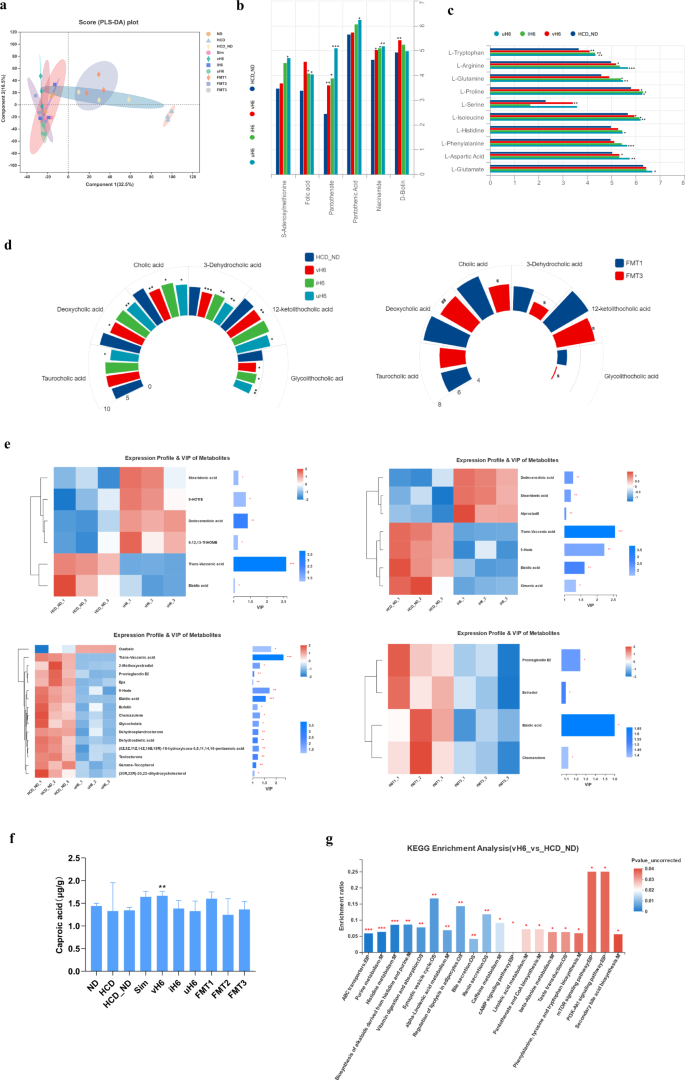
Non-targeted detection of mice fecal metabolites was performed based mostly on UPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS. MS and MS/MS info was matched with the metabolic public databases HMDB (http://www.hmdb.ca/) and Metlin (https://metlin.scripps.edu/). A complete of 1114 fecal metabolites had been recognized. PLS-DA evaluation confirmed that the teams of HCD, HCD_ND, and FMT3 had been clearly separated from the opposite therapy teams (Fig. 5a), and the substitution take a look at mannequin confirmed that the PLS-DA mannequin was dependable (Supplementary fig. 3a). In accordance with the warmth map, the fecal metabolites of mice given v/i/uH6 and FMT3 had been extra much like the ND group, however had been clearly separated from the HCD, HCD_ND, and FMT1 teams (Supplementary fig. 3b). All metabolites had been categorised as vitamins-cofactors, amino acids, bile acids and lipids. In contrast with the HCD_ND group, v/i/uH6 elevated relative content material of six vitamins-cofactors, amongst which pantothenate and niacinamide had been considerably elevated (Fig. 5b). Nonetheless, FMT3 didn’t change the extent of vitamins-cofactors considerably (Supplementary determine 3c). In comparison with HCD_ND group, v/i/uH6 considerably elevated the content material of amino acids (Fig. 5c), equivalent to l-Tryptophan, l-Proline, l-Phenylalanine, and l-Glutamate, and the content material of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), equivalent to l-Isoleucine. By way of bile acids, in comparison with the HCD_ND group, v/i/uH6 diminished the content material of main bile acids by 18.10%, 13.31%, and 21.00% respectively, and diminished the content material of secondary bile acids, equivalent to Deoxycholic acid, 3-Dehydrocholic acid, 12-ketolithocholic acid, Glycolithocholic acid. FMT3 had the identical pattern in bile acids regulation (Fig. 5d). The differential metabolites between totally different therapy teams had been screened by a cluster warmth map and VIP bar graph (Fig. 5e). v/i/uH6 and FMT3 handled mice had been recognized for 7, 7, 16, and 4 notable lipid metabolites, respectively. In comparison with the HCD_ND group, vH6 considerably upregulated 4 lipids metalolites, particularly 9,12,13-TriHOME, 9-HOTrE, stearidonic acid and dodecanedioic acid. iH6 considerably upregulated stearidonic acid, dodecanedioic acid and alprostadil. uH6 considerably upregulated ouabain one. FMT3 diminished all differential metabolites in comparison with FMT1. On the entire, there are similarities within the differential metabolites of v/i/uH6 and FMT3, equivalent to elaidic acid, trans-vaccenic acid, stearidonic acid, and so on.
a Partial least squares-discriminant evaluation (PLS-DA) based mostly on the microbial metabolites. b–d The relative content material of vitamins-cofactors, amino acids and bile acids detected by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS based mostly non-targeted metabolomics method. e The clustering heatmap and VIP bar map of the differential lipids had been in contrast between the 2 teams. f The content material of caproic acid. g KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation of differential metabolites in HCD_ND vs. vH6. Information are introduced because the imply ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. HCD_ND refers back to the group of hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice; v/i/uH6 refers to viable (vH6), heat-inactivated (iH6), and ultrasonically-lysed (uH6) micro organism cells; FMT1/2/3 refers to utilizing feces from HCD_ND, Sim and vH6 teams, respectively.
For focused detection of SCFAs, a Thermo TRACE1310-ISQ LT gasoline chromatograph outfitted with an Agilent HP-INNOWAX capillary column was used. In comparison with the HCD_ND group (Fig. 5f), vH6 elevated the content material of caproic acid (P < 0.05), acetic acid, propionic acid, isobutyric acid, butyric acid, valeric acid, and complete SCFAs; uH6 elevated the content material of acetic acid, propionic acid and valeric acid. In comparison with the FMT1 group FMT3 elevated the content material of Acetic acid and Propionic acid, though none of those variations had been statistically important (Supplementary fig. 3e).
The organic processes of fecal metabolites had been predicted utilizing KEGG pathway evaluation. Evaluation of differential metabolites between vH6 and HCD_ND teams revealed that vH6 regulated hypercholesterolemia in mice by many pathways, together with vitamin digestion and absorption, lipolysis regulation, cAMP signaling pathway, linoleic acid metabolism, phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, mTOR signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and secondary bile acid biosynthesis. Just like vH6, iH6, and uH6 are concerned in regulating metabolic pathways, such because the cAMP signaling pathway, bile secretion, lipolysis regulation, or mTOR signaling pathway (Fig. 5g and Supplementary fig. 3f). Relative to FMT1, FMT3 might regulate metabolism through bile secretion and secondary bile acid biosynthesis. In conclusion, v/i/uH6 all improved intestinal metabolites in hypercholesterolemia mice to totally different levels. Specifically, the v/i/uH6 cells elevated the intestinal flora metabolism of vitamins-cofactors, in addition to amino acids, whereas reducing the relative content material of main bile acids.
Correlation of microbial neighborhood, physicochemical indicators, and metabolites in v/i/uH6 handled mice
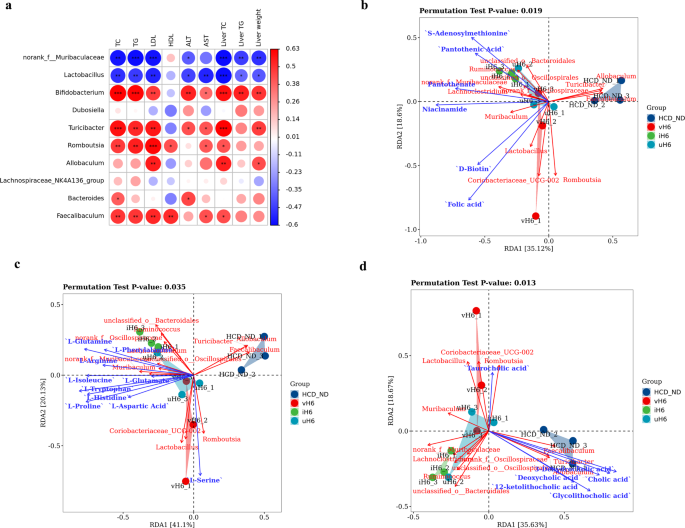
Additional evaluation of Pearson correlations between intestine microbiota (high 10 genera on the genus stage) and physicochemical indicators of hypercholesterolemia confirmed that norank_f__Muribaculaceae and Lactobacillus had important unfavourable correlations with TC, TG, LDL, ALT, AST, and liver weight. Turicibacter, Romboutsia, and Faecalibaculum all had important optimistic correlations with these indices (Fig. 6a). Allobaculum additionally had a major optimistic relationship with LDL, liver TC and liver weight. The correlation between fecal metabolites and microbial neighborhood construction was assessed by redundancy evaluation (RDA), as proven in Fig. 6b–d and Supplementary fig. 4a, b. Within the v/i/uH6 handled group, Faecalibaculum, Allobaculum, and Turicibacter confirmed a major unfavourable relationship with different micro organism, confirming earlier findings. D-biotin and folic acid had a robust optimistic correlation with Lactobacillus, Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002 and Muribaculum, whereas vitamins-cofactors had a optimistic correlation with the dominant micro organism of v/i/uH6 handled mice (Fig. 6b). l-serine correlated strongly with Lactobacillus and Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002, whereas the remaining amino acids correlated with v/i/uH6 dominant micro organism (Fig. 6c). For bile acids, glycolithocholic acid had no correlation with unclassified_o__Bacteroidales and Turicibacter. Romboutsia and Faecalibaculum confirmed important optimistic correlations with most bile acids (Fig. 6d). These outcomes indicated a robust correlation between the manufacturing and abundance of fecal metabolites and intestinal microbes in hypercholesterolemic mice given v/i/uH6. Equally, within the FMT3 group, a correlation between microbial communities and physicochemical indicators and metabolites was found, however there was no statistical significance (Supplementary fig. 4c–g). Briefly, the Pearson correlation evaluation confirmed that norank_f__Muribaculaceae and Lactobacillus had a unfavourable correlation with blood lipid ranges. RDA indicated a robust optimistic correlation between the manufacturing and abundance of fecal metabolites and intestinal microbes in hypercholesterolemic mice given v/i/uH6.
a Correlation evaluation between high 10 richest micro organism and physicochemical indices of hypercholesterolemia by Spearman technique. b–d Redundancy evaluation (RDA) of the correlation between v/i/uH6 microbial neighborhood and fecal metabolites (vitamins-cofactors, amino acids, bile acids). Information are introduced because the imply ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. HCD_ND refers back to the group of hypercholesterolemia mannequin mice; v/i/uH6 refers to viable (vH6), heat-inactivated (iH6), and ultrasonically lysed (uH6) micro organism cells.