Evaluation of PEVs measurement distribution
On this examine, we characterised and in contrast two totally different populations of PEVs, named as follows:
-
(1)
PEVs-THR, launched by platelets in response to the physiological stimulus thrombin;
-
(2)
PEVs-BCC, launched by platelets in response to the incubation with the triple damaging, extremely aggressive breast most cancers cell line MDA-MB-231.
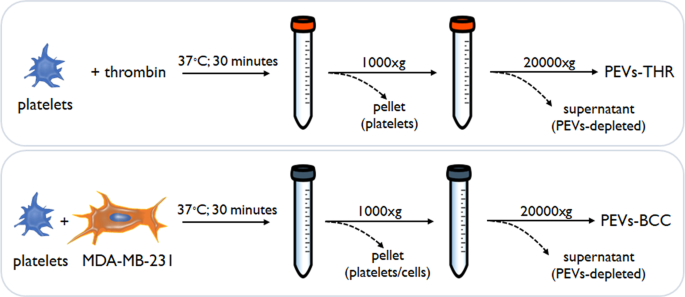
The process for PEVs isolation (Fig. 1) was primarily based on the technique adopted in our earlier investigations [6, 7, 12], and is detailed within the supplies and strategies part. The 2 populations of PEVs have been beforehand analyzed for his or her potential to stimulate the intrinsic aggressiveness of MDA-MB-231 cells [6, 7, 12] however they haven’t been characterised for his or her distinctive molecular signature.
The NTA evaluation revealed that platelet stimulation with thrombin or with MDA-MB-231 cells resulted within the launch of 6.20 ± 1.54 × 109 and seven.94 ± 5.0 × 109 particles per pattern, respectively. PEVs purified from every pattern contained a median of about 70 µg of proteins (PEVs-THR: 72.6 ± 4.4 µg; PEVs-BCC: 67.55 ± 5.93 µg).
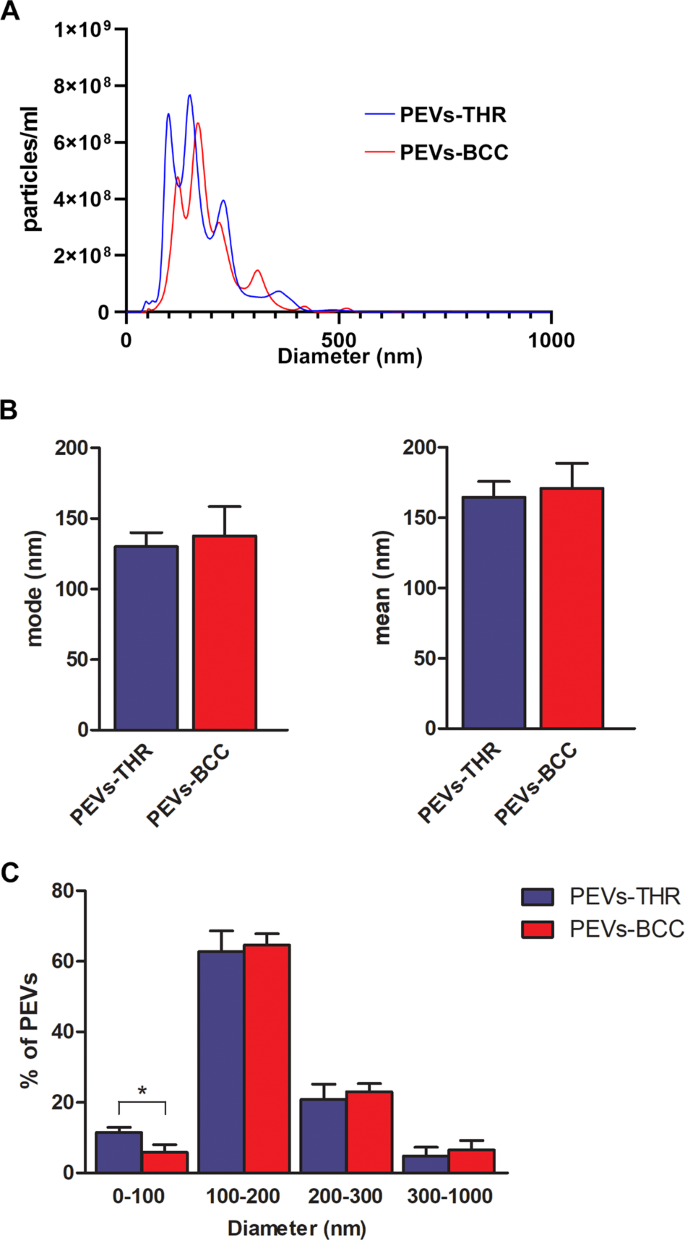
The measurement of the scale distribution of PEVs confirmed that each preparations contained heterogenous populations of vesicles with measurement starting from 50 to 500 nm (Fig. 2A). Knowledge evaluation revealed that each the mode and imply measurement of PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC have been related (Fig. 2B). In each PEVs preparations a lot of the particles (about 60%) have been within the 100–200 nm diameter vary, whereas about 20% of PEVs had a measurement within the 200–300 nm vary (Fig. 2C). The proportion of vesicles with a diameter larger than 300 nm was beneath 10% in each samples. Curiously, a statistically important distinction between the 2 preparations of PEVs was noticed for the smallest vesicles, with a diameter beneath 100 nm: the share of PEVs-THR falling on this subpopulation was clearly larger than that of PEVs-BCC (11.5% ± 1.49 vs 5.80% ± 2.25).
A Consultant measurement distribution of PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC obtained by NanoSight evaluation. B Quantification of the evaluation of PEVs measurement expressed as mode (i) and imply (ii) diameter. Outcomes are reported because the imply ± SD of three unbiased experiments. C Measurement distribution expressed as the chances of particles detected within the totally different dimension ranges (0–100, 100–200, 200–300, 300–1000 nm). The outcomes are reported because the imply ± SD of three experiments. Statistical significance of the variations was calculated between PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC inside the identical measurement vary. *p < 0.05.
Comparative proteomic profiling of PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC
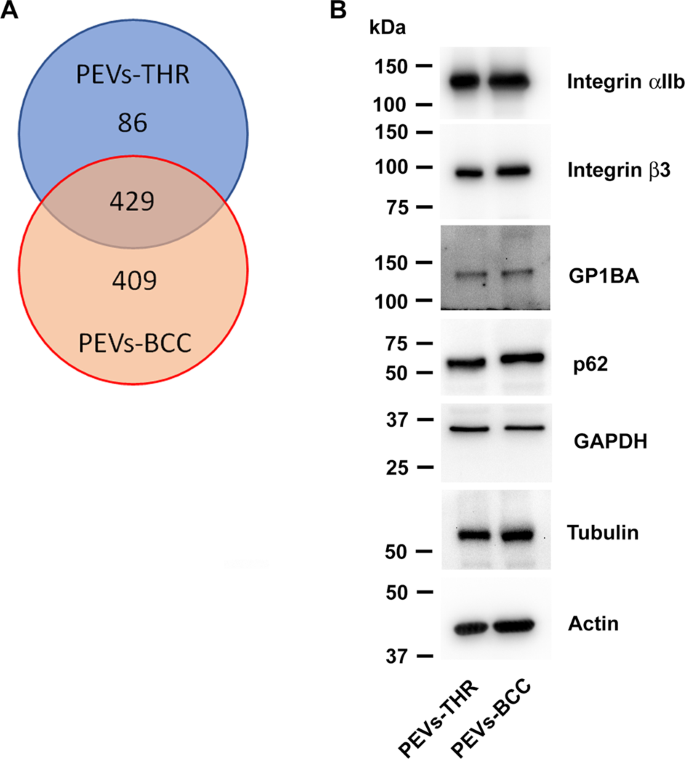
The protein content material of the 2 populations of PEVs was analyzed upon in-solution digestion by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The listing of proteins recognized within the two PEVs samples analyzed is reported as supplementary materials (Desk S1). As proven within the Venn diagram reported in Fig. 3A, a complete of 924 proteins have been recognized by this strategy, of which 429 proteins present in each samples, 86 proteins completely current within the PEVs-THR, and 409 proteins detected solely within the PEVs-BCC. It seems subsequently that PEVs-BCC are extra heterogeneous in protein composition than PEVs-THR. Platelet-derived proteins, comparable to integrin αIIb (ITA2B), integrin β3 (ITB3), and GPIbα (GP1BA), in addition to the cytoskeletal proteins actin (ACTB) and tubulin (TBA1), have been present in each PEVs preparations and their presence was confirmed by immunoblotting evaluation. Additionally typical EVs markers such because the enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and the autophagosome part p62 [15, 16], have been present in each PEV-THR and PEV-BCC as additionally confirmed by immunoblotting (Fig. 3B). The presence of a number of proteins selectively present in one of many two PEVs preparations (marked in blue in Desk S1) means that the mechanism of cargo choice for PEVs-THR and PEVs-BBC could also be considerably totally different and should underlie radically totally different practical skills.
As a comparability, vesicles instantly launched by cultured MDA-MB-231 cells (henceforth named EVs-MDA-MB-231) have been additionally subjected to proteomic profiling. To this objective, MDA-MB-231 cells have been incubated below the identical experimental situations used to generate PEVs-BCC, however within the absence of platelets. A restricted quantity of EVs was recovered within the supernatant of those samples (0.47 ± 0.21 µg). LC-MS evaluation recognized 566 proteins in EVs-MDA-MB-231. Solely a comparatively small fraction (135 proteins out of 566) was shared by EVs-MDA-MB-231 and PEVs-BCC, whereas 166 proteins have been present in all of the EVs populations. As anticipated, only a few proteins, particularly 4, have been recognized in each EVs-MDA-MB-231 and PEVs-THR (Supplementary Fig. 1).
Quantitative MS evaluation of PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC
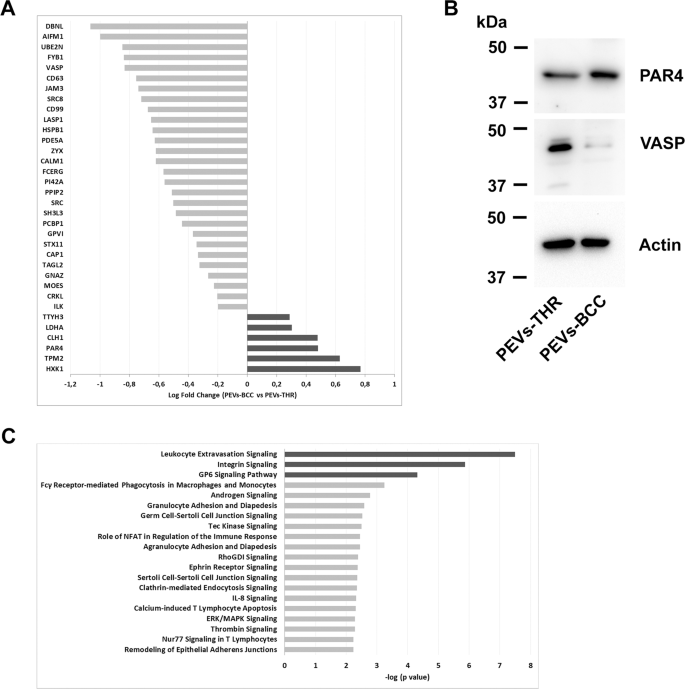
The flexibility of PEVs to control particular processes in goal cells has been broadly documented [6,7,8,9, 12, 17,18,19]. It’s affordable to hypothesize that the capability of PEVs to regulate organic responses might rely on the supply of proteins concerned within the regulation of particular pathways. Since PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC are remarkably totally different in protein composition, we additional investigated their protein cargo by quantitative proteomic evaluation. Whereas qualitative evaluation can present a listing of proteins recognized in PEVs samples, label-free quantitative proteomics yields details about the practical variations between two organic samples. This strategy allowed the comparability of the degrees of proteins expressed in PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC. A complete of 34 proteins have been discovered to be differentially expressed between the 2 PEVs samples (fold change > 1.3 and p-value < 0.05) (Fig. 4A). Mild grey bars point out proteins which might be expressed at larger ranges in PEVs-THR slightly than PEVs-BCC, conversely darkish grey bars point out proteins which might be extra plentiful in PEVs-BCC. The outcomes from quantitative MS evaluation have been validated by immunoblotting, specializing in the proteins VASP and PAR4, that are detectable in each samples, however expressed at larger ranges in PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC, respectively (Fig. 4B).
A Protein quantification in PEVs populations by LC-MS. The Log Fold Change signifies the distinction of single protein expression in PEVs-BCC vs PEVs-THR. The darkish grey bars point out proteins extra represented in PEVs-BCC, conversely gentle grey bars proven proteins extra enriched in PEVs-THR. B Immunoblotting evaluation of PAR4 and VASP in PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC. Actin staining was carried out as management for equal loading. C Gene ontology enrichment evaluation of the PEVs proteins concerned within the regulation of particular organic processes. The 20 pathways that, in keeping with the bioinformatic analyses, displayed essentially the most important protein enrichment are reported. The darkish grey bars point out pathways that have been predicted to be inhibited by PEVs-BCC in comparison with PEVs-THR, whereas gentle grey bars point out processes which might be more likely to be modulated though no prediction was attainable.
Bioinformatic evaluation of the expression profiles allowed us to affiliate particular teams of otherwise expressed proteins to foretell practical pathways. Proteins concerned within the regulation of leukocyte extravasation, integrin, and GPVI signaling, have been discovered to be extra plentiful in PEVs-THR than in PEVs-BCC. Accordingly, these pathways have been additionally predicted to be negatively regulated in PEVs-BCC versus PEV-THR (Fig. 4C, darkish grey bars). On the identical time, different pathways (gentle grey bars in Fig. 4C), comparable to ERK/MAPK signaling and Calcium-induced T Lymphocyte Apoptosis, have been recognized as considerably altered by PEVs, however right here a prediction of regulation, inhibition or activation, was not attainable primarily based on the proteomic quantitative profile (Fig. 4C). A whole listing of all the anticipated pathways, doubtlessly related to the proteins quantified in PEVs, is reported in Supplementary Desk S2.
PEVs within the regulation of leukocyte features
Looking for novel practical results of PEVs, we selected to deal with their attainable potential to control leukocyte perform. Specifically, the results of PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC on the regulation of leukocyte extravasation and calcium-induced T-cell apoptosis have been investigated. As experimental mobile mannequin, the immortalized human T-cell line Jurkat was chosen, since these cells have been beforehand used to analyze leukocyte migration [20, 21] and Ca2+-induced apoptosis [22, 23].
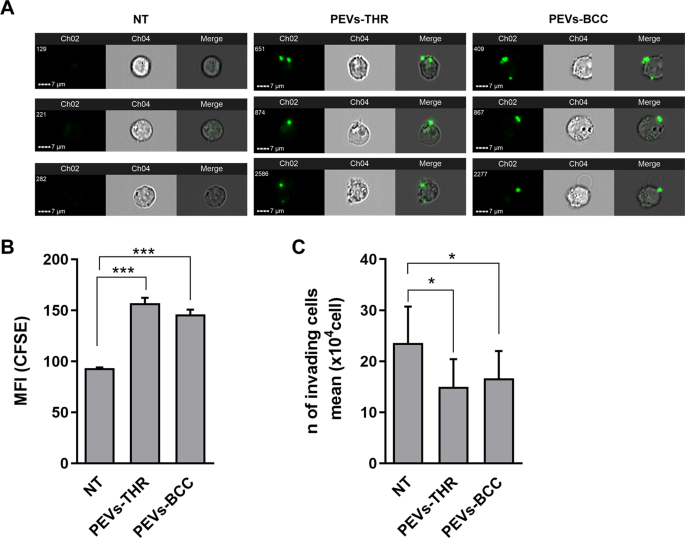
By imaging circulation cytometry experiments, we discovered that Jurkat cells effectively interacted with PEVs upon 16 h incubation (Fig. 5A). Quantitative evaluation revealed that PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC displayed a comparable potential to bind to Jurkat cells (Fig. 5B).
A Consultant pictures of CFSE-loaded PEVs interacting with Jurkat cells. For Jurkat cells handled with PEVs-THR or PEVs-BCC and untreated cells (NT), three consultant examples together with green-fluorescence pictures of Channel 2 (Ch2), brightfield pictures of Channel 4 (Ch4) and Merge of Ch2 and Ch4 are proven. B Evaluation of PEVs-Jurkat cells interplay by circulation cytometry. Jurkat cells have been co-cultured for twenty-four h with PEVs obtained from CFSE-labeled platelets upon stimulation with thrombin or MDA-MB-231 cells. The green-fluorescent sign of PEVs related to Jurkat cells was quantified as Median Fluorescence Depth (MFI). The plot reviews the imply ± SD of three unbiased experiments. ***p < 0.0001 (pattern vs NT). C Jurkat cells migration evaluated by transwell assay. Cells that moved within the backside chamber have been collected and counted utilizing a hemocytometer. The info are expressed as variety of migrated cells and the graph proven the imply ± SD of 4 unbiased experiments with *p < 0.05.
To review leukocyte extravasation, a transwell assay with matrigel-coated membranes was adopted. This strategy revealed that incubation with PEVs considerably lowered the chemotactic invasion of Jurkat cells by the extracellular matrix. Regardless of the totally different enrichment in proteins regulating the extravasation pathway, PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC displayed a really related impact on Jurkat cell migration (Fig. 5C). Conversely, EVs launched by most cancers cells within the absence of platelets (EVs-MDA-MB-231) didn’t affect Jurkat cell migration (Supplementary Fig. 2).
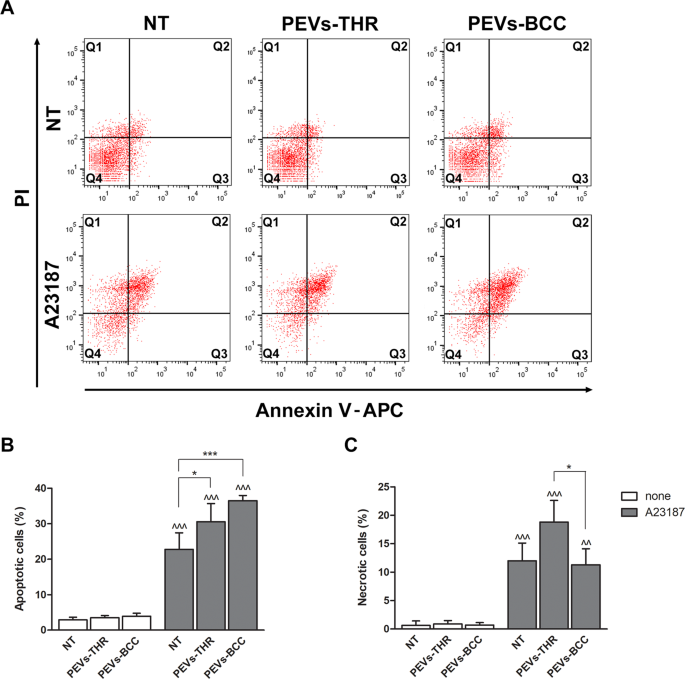
We subsequent investigated whether or not the interplay with PEVs may affect Ca2+-induced apoptosis in Jurkat T cells, as predictable from the informatic evaluation of PEVs cargo. As reported in Fig. 6, the incubation of Jurkat cells with PEVs-THR or PEVs-BCC alone didn’t trigger any important improve of the share of apoptotic cells. As anticipated, stimulation with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 induced a outstanding apoptosis in Jurkat cells. The proportion of apoptotic cells considerably elevated when stimulation of Jurkat cells with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 was carried out within the presence of PEVs (Fig. 6B). Though PEVs-BCC appeared to show a stronger stimulation of apoptosis than PEV-THR, the statistical evaluation revealed no important variations between the 2 samples. The remedy with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 brought on necrosis in about 10% of the Jurkat cells. Curiously, Ca2+-induced T-cell necrosis was considerably potentiated within the presence of PEVs-THR however was not affected by PEVs-BCC (Fig. 6C). Due to this fact, each PEVs-THR and PEVs-BCC have been capable of stimulate Ca2+-induced apoptosis of Jurkat cells, however solely PEVs-THR additionally potentiated cell necrosis.
A Consultant dot plots of Jurkat cell apoptosis analyzed by circulation cytometry. The sign related to propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin V-APC are reported on the y- and x-axis, respectively. B Quantification of apoptosis as the share of cells within the Q2 (late apoptosis) and Q3 (early apoptosis) quadrants. The info are consultant of the imply ± SD of 4 unbiased experiments. The outcomes of the statistical evaluation of the variations between samples handled with A23187 (grey bars) and respective controls (white bars) are indicated by ^^^ (p < 0.0001). The statistical significance of the variations between PEVs-treated samples and respective controls is indicated with the asterisks (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.0001). C Quantification of necrotic cells as the share of cells within the Q1 quadrant. The info are consultant of the imply ± SD of three unbiased experiments with *p < 0.05. The statistical significance between samples handled with A23187 (grey bars) and respective controls (white bars) are indicated by as ^ (p < 0.05) and ^^ (p < 0.001).