Think about n phenotypically distinct species competing for a restricted useful resource, C, and uncovered to a drug, A, equipped at focus Ae (0) = A0, solid as the next mannequin:
$$dot S_j = overbrace {G_jleft( C proper)S_j}^{{{{{{{{mathrm{Progress}}}}}}}}} cdot overbrace {I_jleft( A proper)}^{{{{{{{{mathrm{Inhibition}}}}}}}}},$$
(1a)
$$dot A_j = overbrace { – dA_j}^{{{{{{{{mathrm{Decay}}}}}}}}} + overbrace {varphi _jleft( {A_e – A_j} proper)S_j}^{{{{{{{{mathrm{Fick}}}}}}}}^prime {{{{{{{mathrm{s}}}}}}}};{{{{{{{mathrm{Diffusion}}}}}}}}},$$
(1b)
$$dot A_e = – dA_e – mathop {sum}limits_{j = 1}^n {varphi _jleft( {A_e – A_j} proper)S_j} ,$$
(1c)
$$dot C = – mathop {sum}limits_{j = 1}^n {overbrace {U_jleft( C proper)S_j}^{{{{{{{{mathrm{C}}}}}}}} – {{{{{{{mathrm{Uptake}}}}}}}}}} ,$$
(1d)
right here (dot S_j) and (dot A_j) signify the density of people per unit quantity from species j and their content material of drug A over time, respectively, with preliminary circumstances Sj(0) = Sj0, Aj(0) = 0, and C(0) = C0 > 0. The uptake of useful resource C by people of species j may be modelled as a saturating Monod perform provided that carbon transport is mediated by enzymes in nature [17, 18]. This perform is proportional to the maximal uptake price (overline {mu _j}),
$$U_jleft( C proper): = bar mu _jfrac{C}{{K_j + C}},$$
(2)
the place Okj is the half‐saturation parameter—the affinity of people from species j for the restricted useful resource C is due to this fact given by 1/Okj. The expansion price of every species, at a given useful resource focus is denoted by Gj(C): = Uj(C) · yj, the place yj is the biomass yield per unit of useful resource in people from species j. Be aware that, for simplicity, I assume that yj doesn’t range between pure and combined tradition circumstances. Biomass yield is dependent upon useful resource availability [19] and competitors for a typical carbon supply will seemingly change yj in all competing species, albeit these adjustments may be troublesome to measure [20]. Their progress inhibition by drug A is described qualitatively by the Hill perform [21].
$$I_jleft( A proper): = frac{1}{{1 + left( {A_j/kappa _j} proper)^alpha }},;{{{{{{{mathrm{the place}}}}}}}};0; le ;I_jleft( A proper) le 1$$
(3)
Scaling the expansion perform Gj(S) equally to bacteriostatic medication [22]. This perform is dimensionless and has two parameters. First, α is a dimensionless Hill coefficient which characterises the co‐operativity of the inhibition. And second, κj is the affinity of drug A for its goal. It may be derived from the drug focus required to halve the maximal progress price, in order that A50 = 1/κj → κj = 1/A50 [21]. For the sake of simplicity, I assumed that drug A diffuses from the surroundings into cells of species j, and vice versa, following Fick’s first diffusion regulation [23] with a diffusion coefficient (varphi _j); and a part of A being misplaced to chemical stability [24] at a price d. This isn’t an unreasonable assumption provided that antimicrobial molecules can certainly diffuse by way of cell membranes facilitated by membrane proteins [25]. Consequently, drug A is launched in energetic kind following the demise of goal and non‐goal species.
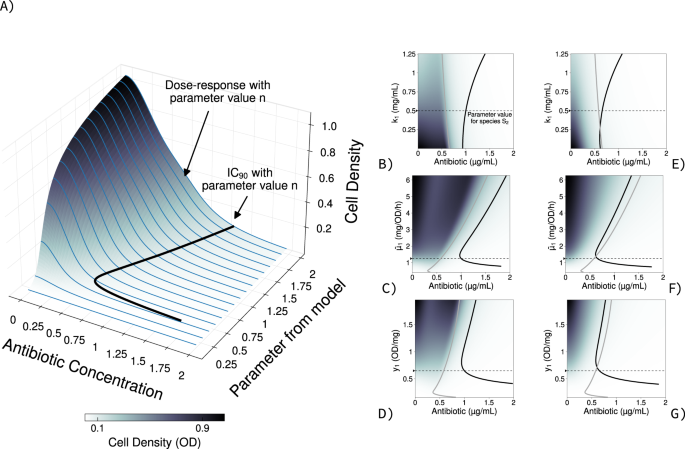
For my first computation I set the variety of species j = 2, to facilitate later experimental validation, the place I1(A) = I2(A) and G1(C) = G2(C). Thus, people from each species are delicate to A and phenotypically equivalent. Given Eq. 3, the density of people from both species as pure cultures, after 24 h of incubation, declines with greater drug concentrations constantly with normal medical protocols [26] (Fig. 1A). To permit experimental validation, I calculated the focus of A inhibiting the expansion of the pure cultures by 90% (IC90) as generally utilized in clinic laboratories [27,28,29]. The drug sensitivity of every species is dependent upon the values for the parameters Ok, (bar mu), and y of Eq. 2 (Fig. 1B–D, gray), with values that enhance the density of people leading to greater IC90 (particulars concerning the parameter values used may be present in Desk 1). That is per the inoculum impact [30] (Fig. S1), whereby sensitivity exams that use bigger inocula additionally report greater minimal inhibitory concentrations, therefore the standardisation of those medical assays.
A Progress of species S1, with completely different parameter values (okay1 (bar mu)1, and y1), after 24 h of progress within the presence of various antibiotic concentrations. I aggregated the ensuing dose‐response profiles (blue) to create a density map from low predicted cell density (white) to excessive predicted cell density (black). B–D IC90, antibiotic focus inhibiting 90% (IC90) the expansion predicted with out drug, ensuing with completely different parameters values for the half‐saturation parameter okay1 (B), maximal carbon up‐take (bar mu)1 (C), or biomass yield y1 (D) in eq. 1 when species S2 is drug‐delicate. The IC90 for species S1 rising as pure cultures is proven in gray, and rising in combined tradition with S2 are proven in black. The parameter values for species S2 have been mounted at a worth famous by a black arrow on the y‐axis, adopted by a dotted black line. E–G Change in IC90, as in Fig. (B–C), when the competing species S2 just isn’t drug‐delicate (resistant or tolerant). Parameter values used may be present in Desk 1.
Determine S1 reveals explicitly the theoretical relationship between IC90 and cell density of species S1 on the IC90 in pure tradition, direct and non‐linear constantly with prior knowledge [30,31,32]. For parameters (bar mu) and y, for instance, the ensuing change in IC90 with respect to the parameter values is nonmonotone, which suggests sure values for these parameters can maximise susceptibility for drug A. The neighbouring species reveals comparable, albeit not equivalent, adjustments in sensitivity (Fig. S2). This non‐linearity is brought on by cultures not reaching the equilibrium, for all drug concentrations and parameter values examined, inside the usual 24 h incubation instances. If, within the mannequin, cultures are allowed to develop for longer and attain equilibrium, the IC90–cell density profile can change (Fig. S1B). This phenomenon is exacerbated if each species develop in combined tradition circumstances, the place each grow to be phenotypically extra tolerant to drug A (Fig. 1B–D, black). If I have been to focus on, say, people from species S1, doing so when the species is surrounded by S2 would require extra drug. That is the case, for instance, of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma handled with gemcitabine when micro organism develop inside the tumour’s microenvironment [33]. Extra usually, genotypes analog to S1 ought to enhance their drug tolerance when they’re surrounded by equally delicate species. Regardless of the liberty in parameter values within the mannequin, this prediction is powerful to adjustments in biomass yield (yj) or maximal carbon uptake ((overline {mu _j})) of species S2 (Fig. S3).
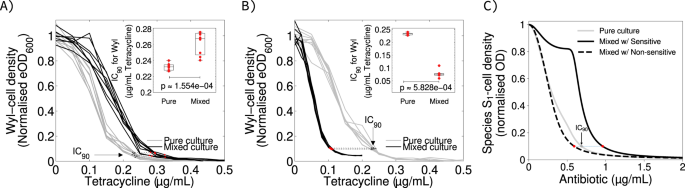
To check this speculation, I combined equal proportions (cell/cell) of Escherichia coli Wyl and Salmonella typhimurium SL1344 in minimal media supplemented with completely different concentrations of tetracycline (see Strategies). Be aware that the inoculum impact just isn’t linear with respect to the dimensions of inocula [31, 32] except the distinction between inocula is tenfold or extra, which isn’t the case right here. Tetracycline can diffuse passively into cells of each gram‐destructive species [34], who even have comparable sensitivity to this antibiotic: 0.232 ± 0.003 and 0.276 ± 0.016 μg/mL of tetracycline (imply IC90 ± 95% confidence, with n = 8 replicates, see Figs. S2 and S4). This approximates to I1(A) ≈ I2(A), as laid out by the idea above. The chromosome of E. coli Wyl carries yfp, gene encoding a yellow fluorescence protein (YFP), so I tracked its density in combined tradition circumstances. Persistently with Eq. 1a–d, the bacterium was round 23% extra tolerant to tetracycline when it grew in combined tradition with S. typhimurium (Mann–Whitney U‐take a look at p = 1.554 × 10−4, ranksum = 36 with n = 8 replicates, Fig. 2A).
A, B Change in normalised density of Escherichia coli Wyl as a perform of tetracycline focus, when Wyl grows in combined tradition with tetracycline-sensitive Salmonella typhimurium (A) and tetracycline-resistant Escherichia coli GB(c) (B). The change in density of Wyl rising in combined tradition is proven in black, with gray exhibiting the change in density in pure tradition. The IC90 in every situation is proven as dots, crimson for combined tradition circumstances and darkish gray for pure tradition, related by a dotted line. Non-parametric, Mann–Whitney U-test between IC90s is proven within the inset. Uncooked knowledge is proven as dots, whereas the packing containers signify median (centre of the field), twenty fifth, and seventy fifth percentile of the dataset. The whiskers present probably the most excessive knowledge factors that aren’t outliers. C Theoretical change in S1-cell density with growing antibiotic focus in pure (gray) and combined (black) tradition circumstances with neighbours which have completely different drug sensitivity. The plot represents the case the place each species have completely different carbon uptake ((bar mu)j), and variations in IC90 are represented as proven in (A, B) for consistency. Insets in (A and B), and uncooked knowledge for relative drug content material may be present in Fig. S4.
Subsequent, I explored within the mannequin the case the place people from each species have completely different sensitivities to drug A (I1(A) ≠ I2(A)). This situation is akin to pathogens corresponding to C. difficile rising alongside human cells [35] the place the latter are unaffected by the drug (I2(A) ≈ 1). The mannequin now predicts a subset of values for Ok, y, and (bar mu) that make S1 extra delicate to the drug within the presence of people from species S2 (Fig. 1E–G), whether or not S2 just isn’t affected by drug A or is immune to it for instance by way of efflux pumps [36] (see Supplementary Textual content). To check this prediction, I combined equal proportions (cell/cell) of two constructs of Escherichia coli with completely different sensitivities to tetracycline. One assemble is Wyl, used above, who’s delicate to the antibiotic. The opposite assemble is GB(c), harbouring a non‐transmissible plasmid carrying the gene tet(36) [37] and, due to this fact, immune to the drug. Tetracycline binds to the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting protein synthesis [38], and tet(36) offers ribosomal safety towards tetracycline [37] with out degrading the antibiotic. The IC90 for this assemble was 6.106 ± 0.272 μg/mL of tetracycline (imply IC90 ± 95% confidence with n = 8 replicates). Now, I1(A) « I2(A) satisfies the idea above. The IC90 for E. coli Wyl was 0.232 ± 0.003 μg/mL of tetracycline as pure tradition. Rising alongside drug‐resistant GB(c), nevertheless, it was 0.112 ± 0.003 μg/mL (Fig. 2B).
It’s noteworthy to focus on the 2 processes at play. On the one hand, the expansion of every species is proscribed attributable to competitors for a similar useful resource—also called aggressive suppression [16]. It may very well be conjectured that the noticed variations in IC90 are brought on by variations in progress, with respect to pure tradition circumstances, brought on by aggressive suppression. Certainly, E. coli Wyl grows much less, with respect to pure tradition circumstances, within the presence of both competitor as Fig. S5 illustrates. Inside this distinction, Wyl grows extra within the presence of tetracycline‐resistant E. coli GB(c), and but, drug efficacy towards Wyl was highest within the presence of this competitor. Now, the relative abundance of every species throughout the competitors determines the stream and distribution of antimicrobial molecules given they diffuse passively following Fick’s regulation. Since glucose is actively transported into the cytoplasm, even towards focus gradients [17, 18], the mannequin predicts just about no impact on the carbon uptaken by every species as Fig. S6 illustrates. In different phrases, the carbon supply C is depleted extra quickly when extra species use it, limiting the expansion of every competing species with respect to pure tradition circumstances.
Then again, the sensitivity to drug A determines the fraction of carbon that will get utilized by every species. When I1(A) ≈ I2(A), Eq. 1a–d recommend that people from each species accumulate comparable quantities of drug A (Fig. S7A–C). Because of this, analog to the carbon, drug A is depleted extra quickly, limiting the publicity of the goal species S1. When combining each processes for carbon and drug molecules, the result’s comparatively fewer drug molecules per cell in each species with respect to that predicted in pure tradition. Nonetheless, when I1(A) ≠ I2(A), by advantage of various affinities of drug A for every species (κ1 ≠ κ2), the buildup of drug molecules is uneven (Fig. S7D–I). Quickly after the publicity to drug A, the species S2, with the least affinity for it, and the surroundings are in equilibrium. In different phrases, the variety of drug molecules that diffuse into S2‐cells are the identical that diffuse from these cells again to the surroundings. These molecules, in turns, are collected by the species with probably the most affinity for the drug. Right here, integrating each processes ends in extra molecules per cell within the species with highest drug‐sensitivity (S1).
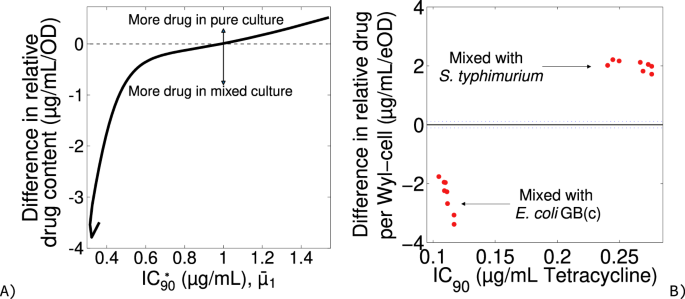
To confirm this speculation, I estimated the content material of tetracycline in E. coli Wyl by dividing the bacterium’s tradition density, measured in relative fluorescence items to permit monitoring in combined tradition circumstances, by the focus of tetracycline defining its IC90. The estimates intently resemble the theoretical predictions in Fig. 2C: E. coli Wyl incorporates ~20% much less tetracycline rising subsequent to Salmonella typhimurium and 65% extra tetracycline rising alongside drug‐resistant GB(c) (Fig. 3).
A Distinction in drug content material per S1-cell on the IC90 between pure tradition and combined tradition circumstances. Optimistic and destructive values denote extra drug in S1-cells in pure and combined tradition circumstances, respectively. Lack of distinction is proven as a horizontal, dotted line. B Experimental estimation of the distinction in relative cell content material within the bacterium Escherichia coli Wyl. Uncooked knowledge for Wyl is proven as crimson dots. Lack of distinction is proven as a horizontal, black line and the 95% confidence of the dearth of distinction as a horizontal, dotted line.