When the primary people moved out of Africa, they carried their intestine microbes with them. Seems, these microbes additionally advanced together with them.
The human intestine microbiome is made up of a whole bunch to 1000’s of species of micro organism and archaea. Inside a given species of microbe, completely different strains carry completely different genes that may have an effect on your well being and the illnesses you’re prone to.
There may be pronounced variation within the microbial composition and variety of the intestine microbiome between individuals dwelling in several international locations world wide. Though researchers are beginning to perceive what elements have an effect on microbiome composition, similar to food regimen, there may be nonetheless restricted understanding on why completely different teams have completely different strains of the identical species of microbes of their guts.
We’re researchers who examine microbial evolution and microbiomes. Our not too long ago revealed examine discovered that not solely did microbes diversify with their early trendy human hosts as they traveled throughout the globe, they adopted human evolution by proscribing themselves to life within the intestine.
Microbes share evolutionary historical past with people
We hypothesized that as people fanned out throughout the globe and diversified genetically, so did the microbial species of their guts. In different phrases, intestine microbes and their human hosts “codiversified” and advanced collectively – simply as human beings diversified so that folks in Asia look completely different from individuals in Europe, so too did their microbiomes.
To evaluate this, we wanted to pair human genome and microbiome information from individuals world wide. Nonetheless, information units that supplied each the microbiome information and genome info for people had been restricted once we began this examine. Most publicly obtainable information was from North America and Western Europe, and we wanted information that was extra consultant of populations world wide.
So our analysis staff used current information from Cameroon, South Korea and the UK, and moreover recruited moms and their younger youngsters in Gabon, Vietnam and Germany. We collected saliva samples from the adults to determine their genotype, or genetic traits, and fecal samples to sequence the genomes of their intestine microbes.
For our evaluation, we used information from 839 adults and 386 youngsters. To evaluate the evolutionary histories of people and intestine microbes, we created phylogenetic bushes for every particular person and in addition to for 59 strains of probably the most generally shared microbial species.
After we in contrast the human bushes to the microbial bushes, we found a gradient of how nicely they matched. Some bacterial bushes didn’t match the human bushes in any respect, whereas some matched very nicely, indicating that these species codiversified with people. Some microbial species, in reality, have been alongside for the evolutionary journey for over a whole bunch of 1000’s of years.
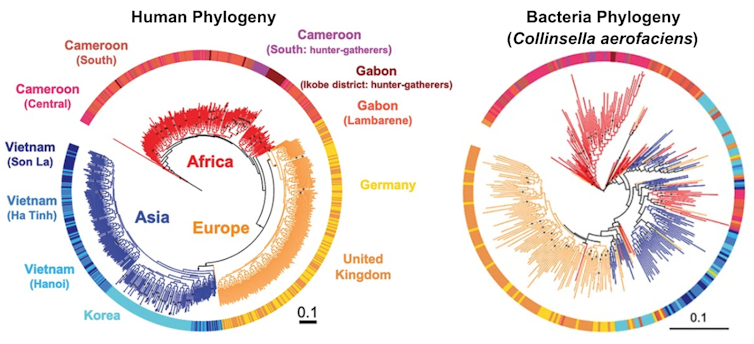
Reprinted with permission from Suzuki et al., Science Quantity 377, abm7759 (2022), CC BY-NC-ND
We additionally discovered that microbes that advanced in tandem with individuals have a novel set of genes and traits in contrast with microbes that had not codiversified with individuals. Microbes that partnered up with people have smaller genomes and better oxygen and temperature sensitivity, largely unable to tolerate situations beneath human physique temperature.
In distinction, intestine microbes with weaker ties to human evolution have traits and genes attribute of free-living micro organism within the exterior surroundings. This discovering means that codiversified microbes are very a lot depending on the environmental situations of the human physique and should be transmitted shortly from one particular person to the subsequent, both handed down generationally or between individuals dwelling in the identical communities.
Confirming this mode of transmission, we discovered that moms and their youngsters had the identical strains of microbes of their guts. Microbes that weren’t codiversified, in distinction, had been extra prone to survive nicely exterior of the physique and could also be transmitted extra broadly via water and soil.
Intestine microbes and personalised medication
Our discovery that intestine microbes advanced proper together with their human hosts presents one other technique to view the human intestine microbiome. Intestine microbes have handed between individuals over a whole bunch to 1000’s of generations, such that as people modified, so did their intestine microbes. Consequently, some intestine microbes behave as if they’re a part of the human genome: They’re packages of genes which might be handed between generations and shared by associated people.
Customized medication and genetic testing are beginning to make remedies extra particular and efficient for the person. Figuring out which microbes have had long-term partnerships with individuals might assist researchers develop microbiome-based remedies particular to every inhabitants. Clinicians are already utilizing regionally sourced probiotics derived from the intestine microbes of neighborhood members to deal with malnutrition.
Artur Plawgo/iStock through Getty Photos Plus
Our findings additionally assist scientists higher perceive how microbes transition ecologically and evolutionarily from “free-living” within the surroundings to depending on the situations of the human intestine. Codiversified microbes have traits and genes harking back to bacterial symbionts that reside inside insect hosts. These shared options recommend that different animal hosts can also have intestine microbes that codiversified with them over evolution.
Paying particular consideration to the microbes that share human evolutionary historical past can assist enhance understanding of the position they play in human well-being.

