Soil carbon, nitrogen, and SOM contents
The nitrogen, carbon, and SOM content material in soils had been completely different in these six sampling websites (Desk 1). WN1 and DF had considerably decrease nitrogen, carbon, and SOM content material than different websites (P < 0.05). The nitrogen content material in numerous soils ranged from 0.06 to 0.21% and the carbon content material was from 0.59 to three.86%. The SOM contents in six websites had been considerably completely different. QX had the very best SOM content material (55.17 g/kg), whereas WN1 had the least (17.72 g/kg). These two sampling websites had been positioned within the west (WN1) and east (QX) of Bijie Metropolis (Fig. 1). Not solely did they differ in altitude, however in addition they shew important variations in pH values. WN1 and WN2, positioned in the identical county, had comparable elevation and pH (Desk S1), however they introduced considerably completely different SOM contents.
Tobacco leaves chemical composition.
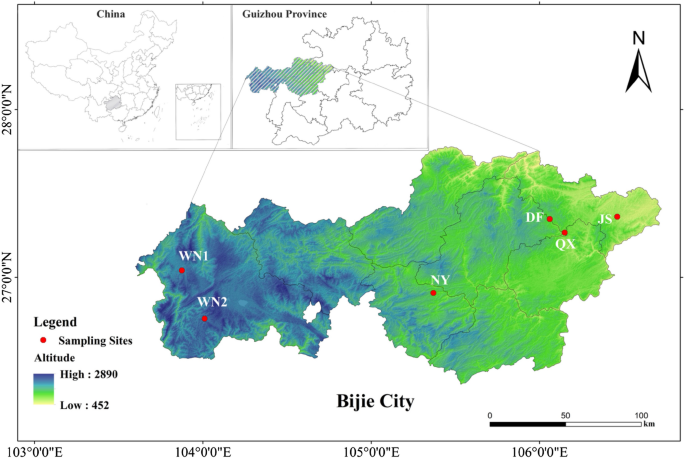
Pattern WN1, NY and DF had average nicotine contents that close to the suitable vary (Fig. 2). The nicotine contents of JS and WN2 had been far blow the usual worth vary. The nitrogen (N) and decreasing sugar contents might have an effect on the style and scent of tobacco as properly and Pattern WN1, DF, JS had acceptable N and decreasing sugar contents. The combustibility of flue-cured might improve with increased potassium (Okay) content material and Pattern NY had the very best content material. Excessive-quality flue-cured tobacco requires a starch content material of lower than 5% and solely the Pattern QX exceeded this vary (Fig. 2).
The ratio of decreasing sugar to nicotine, nitrogen to nicotine, and potassium to chlorine can replicate the connection between completely different chemical compositions and have an effect on the style and scent of tobacco. WN1, NY, DF had increased factors of those ratios than others. Nevertheless, all of the websites didn’t completely meet the usual of decreasing sugar to nicotine and nitrogen to nicotine. Basically, after combining all indicators within the analysis system of chemical elements of flue-cured tobacco, the result confirmed that the Pattern WN1, NY, DF might be categorised as high-quality tobaccos whereas Pattern JS, QX, and WN2 had been thought of low-quality ones (Fig. S1).
The variety of peaks extracted by the three solvents
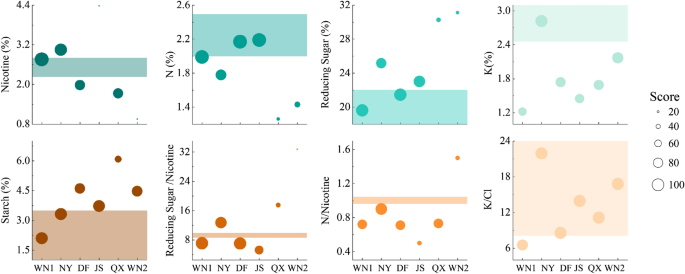
The variety of whole peaks amongst completely different samples ranged from 3783 to 7558 and WN1 and WN2 had probably the most peaks (Fig. 3). These two samples had been collected from Wei Ning County with completely different tobacco qualities (Fig. 2). Usually, MeOH and CHCl3 can extract extra compounds than H2O in every SOM pattern (Fig. 3), accounting for over 70% of whole peaks. Within the water extract, WN2 had probably the most peaks (2055) and QX had the bottom ones (842). Nevertheless, the share of peaks extracted by H2O ranged from 21.20 to 27.19%, displaying comparable developments in numerous samples. For the MeOH extract, WN1 had probably the most peaks (2930), adopted by DF (2391) and WN2 (2072), whereas NY had the minimal peaks (1313). The compounds extracted by MeOH in WN1 accounted for 41.95% of whole peaks. Within the CHCl3 extracts, solely NY accounted for over 45% of whole peaks.
The magnitude-weighted parameters of SOM formulation extracted by completely different solvents
The magnitude-weighted parameters had been calculated based mostly on the formulation and relative depth (Desk S2). To begin with, we in contrast these parameters extracted by completely different solvents. For the (H/C)w, (N/C)w, (O/C)w, and C#w, it was clear that (H/C)w and C#w in water extracts had been decrease than these in MeOH and CHCl3 whereas the (N/C)w and (O/C)w had reverse outcomes. In another way, MeOH extracts had the next diploma of unsaturation than the opposite two extracts, which was determined by DBE. Water extracts had increased (DBE/C)w and DBE/C ratios, representing a excessive density of C=C double bonds and revealing fragrant or condensed fragrant buildings. Additionally, the Ai-mod can distinguish non-aromatic, fragrant, and condensed fragrant compounds. The Ai-mod in H2O extracts was increased than in different extracts. Because of this, the share of condensed fragrant in water extracts was increased than these in different extracts in all samples. The non-aromatic accounted for the overwhelming majority of whole formulation (45.3–86.86%) whereas fragrant for the least (4.49–15.53%).
Variations in SOM compounds sort
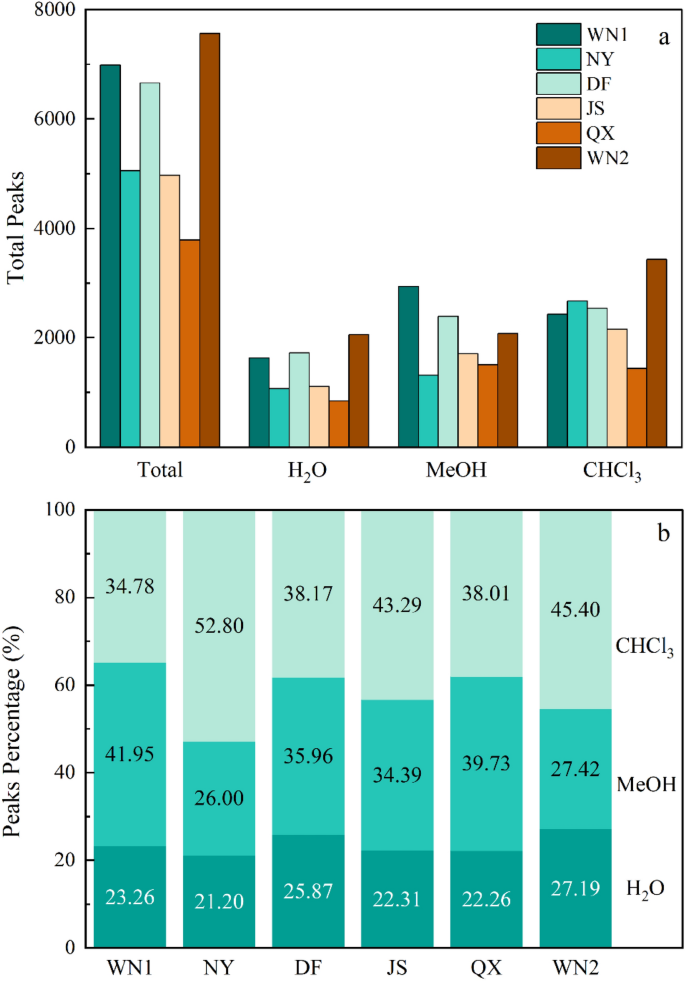
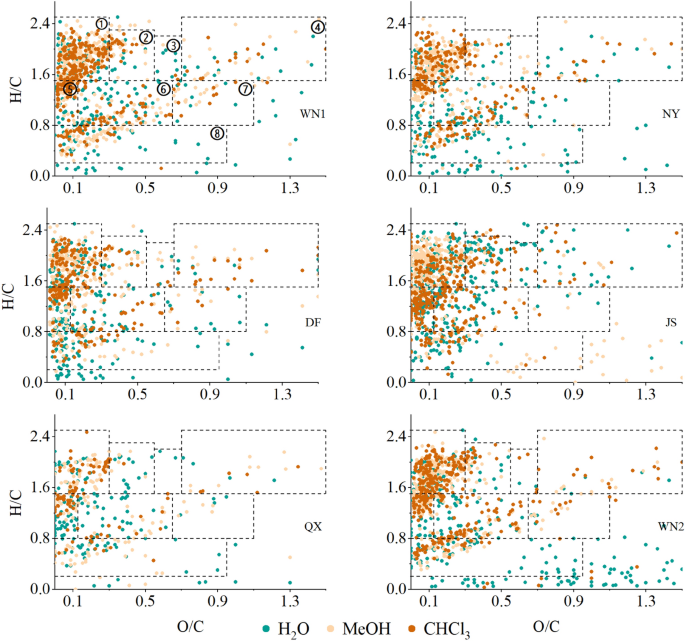
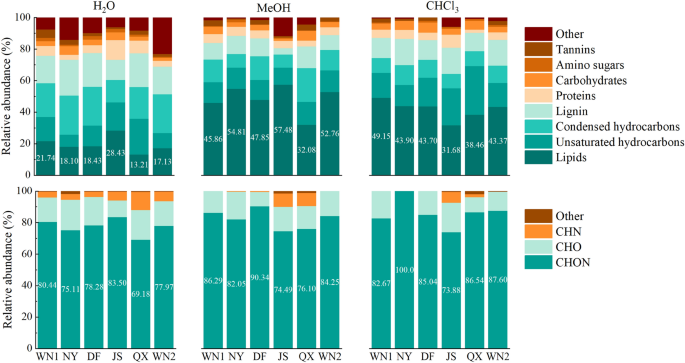
The SOM compounds could be categorised into eight differing kinds in line with their O/C and H/C ratio, together with amino sugars, carbohydrates, condensed hydrocarbons, lignin, lipids, proteins, tannins, and unsaturated hydrocarbons19, which is proven within the Van Krevelen diagram (Fig. 4). Usually, all of the compounds extracted by three solvents had been primarily composed of lipids, unsaturated hydrocarbons, condensed hydrocarbons, and lignin, accounting for a median of 85% in polar extracts and 75% in non-polar extracts of whole compounds, respectively (Fig. 5). Within the H2O extracts, lipids, unsaturated hydrocarbons, and condensed hydrocarbons accounted for about 60% of the overall compounds, and every of them had the same proportion. Nevertheless, the lipids alone accounted for over 40% in most MeOH and CHCl3 extracts (Fig. 5). For the completely different high quality of tobacco, the distinction was a lot smaller amongst high-quality ones than decrease ones.
The chemical composition of SOM compounds of various soil samples. Colours point out completely different extracts. Completely different numbers on dotted field in WN1 signify completely different compounds which might be acceptable for all of the figures: ① Lipids, ② Proteins, ③ Amino Sugars, ④ Carbohydrates, ⑤ Unsaturated hydrocarbons, ⑥ Lignin, ⑦ Tannins, ⑧ Condensed hydrocarbons.
Additionally, we grouped the formulation based mostly on their elemental composition, together with CHNO, CHN, CHO and others. All of the extracts had been primarily composed of CHNO, starting from 69 to 100% (Fig. 5). The compounds extracted by H2O had been extra complicated than these of MeOH and CHCl3. Among the many fractions extracted by water, every pattern contained “others” elements, and the relative abundance of CHN was increased than that of the opposite two solvent-extracted fractions. Amongst them, pattern JS contained the very best CHON substance content material of 83.5%. In distinction, DF had the very best CHON content material (90.34%) within the MeOH-extracted fractions, and WN14 and WN2 didn’t comprise CHN and different substances.The relative abundance of CHON compounds was increased within the NY, QX and WN2 areas obtained within the fractions extracted utilizing CHCl3. Samples WN, NY and DF contained solely CHO and CHON fractions, which had been additionally areas of higher tobacco high quality.
Frequent compounds of tobacco planting soils of various qualities
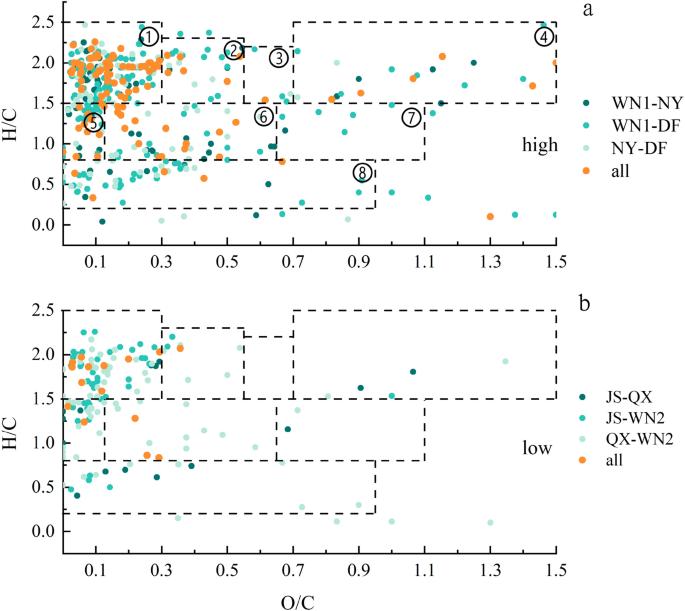
Van Krevelen plots had been used to point out widespread compounds, which suggests the identical formulation present in in excessive and low high quality soils based mostly on O/C and H/C ratios (Fig. 6a,b). Within the prime quality tobacco soils, 169, 267 and 186 widespread compounds had been discovered between WN1-NY, WN1-DF and NY-DF, representing 4.77%, 7.53% and 5.25% of the overall formulation, respectively (2992). Amongst three soils of high-quality tobacco, the variety of widespread compounds was 105, accounting for two.96% of the overall formulation (orange dots in Fig. 6a). Within the soils of low high quality vegetation, the variety of widespread compounds was a lot lower than within the prime quality ones, representing solely 0.56% (2549) of the overall formulation (Fig. 6b).
Van Krevelen diagrams of widespread SOM formulation. (a) Frequent formulation in high-quality soils. (b) Frequent formulation in low-quality soils. Completely different colours point out widespread fractions between two or three samples. Completely different numbers on dotted field in excessive signify completely different compounds which might be acceptable for each figures: ① Lipids, ② Proteins, ③ Amino Sugars, ④ Carbohydrates, ⑤ Unsaturated hydrocarbons, ⑥ Lignin, ⑦ Tannins, ⑧ Condensed hydrocarbons.
Among the many three widespread elements of high-quality tobacco soils, aside from tannins, all compound sorts had been noticed, together with lipids, proteins, amino sugars, carbohydrates, unsaturated hydrocarbons, lignin, and condensed hydrocarbons. Amongst them, lipids account for about 50%, unsaturated hydrocarbons, lignin and condensed hydrocarbons for 10%, and proteins and carbohydrates for five%. Within the low high quality soils, solely lipids, proteins, Unsaturated hydrocarbons and Lignin had been discovered to be widespread in all three samples, and lipids constituted the bulk (66.67%).
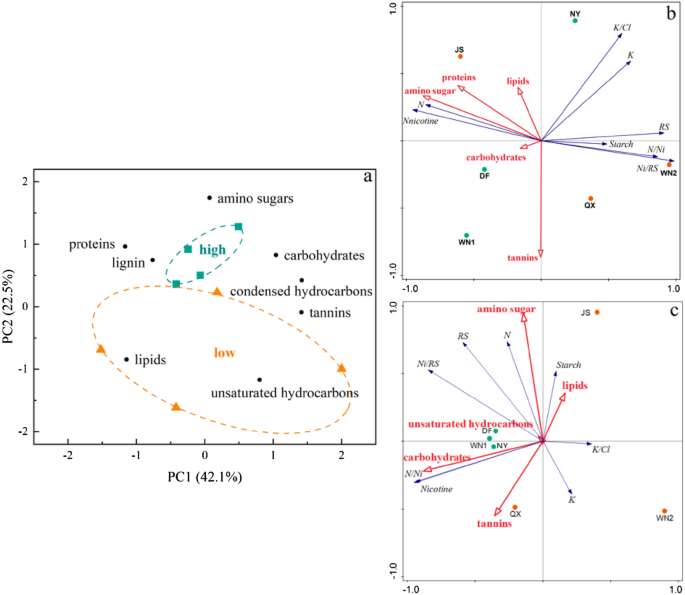
Principal part evaluation (PCA) was carried out to find out the important parameters affecting the widespread compounds. Determine 7 a confirmed inexperienced and orange knowledge factors had been scores for the samples, whereas the black knowledge factors had been the loadings from every variable. PC1 defined 42.1% of the overall variance and PC2 defined 22.5%. A transparent separation was noticed between widespread compounds of various high quality vegetation. The gap between every level decided the diploma of similarity and distinction of the assorted compounds between the factors. As proven, the rating of upper high quality compounds was constructive on the PC2 axis whereas the low-quality ones scattered in three quadrants, indicating that good-quality soil compounds had been extra comparable than low-quality ones.
PCA and RDA outcomes based mostly on tobacco chemical composition and SOM compounds. (a) PCA of widespread compounds and their sorts. (b) Ordination biplot based mostly on RDA of tobacco chemical composition and SOM compounds. Tannins and amino sugar had been recognized as important components and included within the mannequin. (c) Ordination biplot based mostly on RDA of tobacco chemical composition scores and SOM compounds. Amino sugar had been recognized as important components and included within the mannequin.
Relationship between SOM fractions and tobacco high quality
The RDA and Monte Carlo permutation exams had been carried out to investigate the connection between SOM compounds and the chemical composition of tobacco leaves (Fig. 7b,c). In response to the usual, scores based mostly on the tobacco high quality analysis degree system had been additionally included. Our outcomes recommended that chemical elements of tobacco leaves depended to a big diploma on SOM composition.
For the RDA based mostly on the chemical content material of tobacco leaves (Fig. 7b), lipids, proteins, amino sugar, carbohydrates, and tannins had collective results on tobacco high quality. Collectively they defined 89.86% of the overall variability. Amino sugar and tannins had a major impact on the chemical elements of tobacco leaves, explaining 59.2% and 22.5%, respectively. The content material of N and nicotine in tobacco leaves had been positively correlated to amino sugar whereas different contents had been detrimental. The tannins had been positively correlated with starch, nicotine content material and nitrogen/nicotine ratio solely. In response to the place of various samples projected on the arrow ray of DOM composition, we might work out their relationships. For the amino sugar, JS, DF, WN1, and NY had been positively correlated to it whereas QX and WN2 had a detrimental relationship. The tannins positively impacted WN1, QX, DF, WN2 and negatively influenced JS, NY.
For the RDA evaluation based mostly on the rating of every content material in tobacco leaves (Fig. c), carbohydrates, amino sugar, tannins, unsaturated hydrocarbons, and lipids differed in influence levels and solely carbohydrates had important results (P = 0.028). Each Axis 1 and a pair of defined 97.36% of whole variances. The scores of N, decreasing sugar and nicotine content material, nitrogen/nicotine and nicotine/decreasing sugar ratio had been positively associated to carbohydrates whereas starch, Okay, and Okay/Cl had detrimental relationships. DF, WN1, NY, and QX had been positively associated to carbohydrates whereas JS, WN2 had been reverse. Apparently, the place of high-quality samples, WN1, NY and DF had been nearer than different samples, indicating their decrease distinction than low-quality ones.