The function of intestine microbial group (microbiome) in sustaining host well being has gained a number of consideration within the current previous1. Scientific research point out hyperlinks between dysbiosis or disturbance in microbiome and ailments that not solely have an effect on the intestine, but in addition organs like mind, liver, lung, kidneys, and many others. The pathophysiology of ailments effecting distal organs has usually been related to gastrointestinal discomfort or problems. The crosstalk between the intestine microbiome and distal organs is being more and more acknowledged and host-microbiome interactions are being delineated piece by piece2,3. The rising socio-economic burden of varied ailments related to modifications in intestine microbiome recommend the significance of understanding the molecular occasions facilitating such interactions.
Illnesses affecting distal organ like liver (e.g., non-alcoholic/alcoholic fatty liver, non-alcoholic/alcoholic steatohepatitis, liver fibrosis/cirrhosis) are sometimes seen to be related to dysbiosis in intestine microbiome4,5,6. Improve in fats cells in liver results in a state often called fatty liver illness. Fatty liver could happen because of extreme consumption of alcohol termed as ‘alcoholic fatty liver’ or may be noticed in people with no or negligible consumption of alcohol termed as non-alcoholic fatty liver7. In each circumstances the noticed pathological spectra could vary from easy hepatic steatosis, steatohepatitis to liver cirrhosis7. In circumstances the place an accumulation of fats results in irritation and harm, a complicated type of non-alcoholic fatty liver illness (NAFLD) referred to as as Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is noticed. Equally, alcoholic steatohepatitis is the inflammatory state of Alcoholic liver illness (ALD)8. Since, these liver related ailments are linked with dysbiosis in intestine microbiome, you will need to perceive the mechanisms concerned within the cross-talk between intestine and liver.
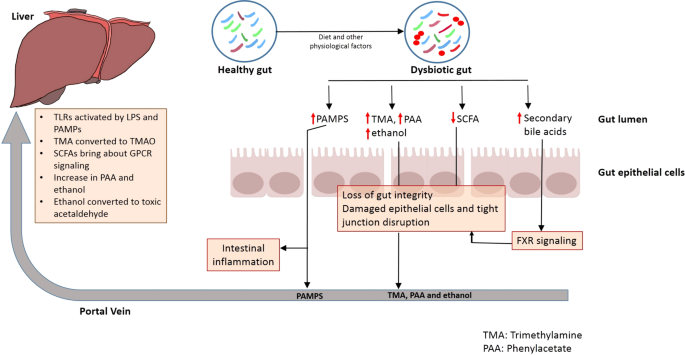
Sure mechanisms govern the tight bidirectional communication between the intestine and liver (Fig. 1). For instance, metabolic equipment of the host and resident intestine microbiome metabolize a number of exogenous dietary and environmental parts in addition to endogenous substrates like amino acids and bile acid. The merchandise generated throughout this course of are carried to liver by portal vein, thereby influencing hepatic physiology9. Equally, the immune cells activated by a number of dietary compounds in addition to metabolites from intestine microbiome can enter lymphatic system and modulate immune responses in distal organ just like the liver9. Then again, the liver communicates with the intestine by the discharge of bile acids and different metabolites into biliary tract of the systemic circulation9. The discharge of bile salts by liver additionally helps to manage unrestricted intestine microbial progress9.
Liver dysfunction influences immunity and metabolism of not solely the intestine, but in addition different organs. For instance, mind malfunction because of Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in addition to kidney problems are sometimes noticed in folks with liver illnesses10. Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) results in an impaired mind operate usually noticed in sufferers with superior liver ailments. The elements like decreased metabolism of ammonia related to liver failure have usually been related to incidence of HE11. Equally, cardiovascular ailments effecting coronary heart and blood vessels (CVD) are seen to be related to fatty liver and different liver problems12. Thus, you will need to perceive the mechanisms concerned within the interplay of Intestine–Liver axis with distal organs. The useful results of sure probiotics and Fecal Microbial Switch (FMT) in liver ailments in addition to illnesses (like HE and CVDs) that are linked to Intestine-Liver interplay with different organs additional spotlight the significance of the close-knit interplay of intestine microbiome with host physiology.
Intestine microbiome and liver ailments
‘Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Illness’ (NAFLD) and ‘Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis’ (NASH) are liver illnesses which were related to dysbiosis in intestine microbiome and ‘Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth’ (SIBO)13,14. Comparable signs have additionally been noticed in people affected by ‘Alcoholic Liver Illness’ (ALD) because of extreme abuse of alcohol. The non- progressive type of these ailments (e.g. NAFLD) usually entails fats accumulation in liver or steatosis, whereas the progressive kind (e.g. NASH) is recognized by liver harm and irritation (steatohepatitis)9. Evaluation of stool samples of 57 sufferers confirmed decrease ranges of Prevotella and better Bacteroides in addition to Ruminococcus are seen within the intestine of sufferers with NASH at stage 2 fibrosis or larger as in comparison with these in management topics with fibrosis stage 115. This means that intestine microbiome modifications are related to severity of illness (fibrosis stage 1 vs. stage 2 on this case). Entire genome sequencing of intestine microbial group obtained utilizing stool samples signifies larger abundances of Escherichia coli and Bacteroides vulgatus within the intestine of NAFLD sufferers in early (72 sufferers) in addition to superior levels of fibrosis (14 sufferers)16. Equally, pediatric topics struggling with NASH are seen to have larger incidence of genus Escherichia as in comparison with overweight non-NASH topics9. A number of research on intestine samples (stool in addition to biopsy) of human in addition to animal methods have indicated that whereas sufferers with ALD have an elevated variety of micro organism belonging to the household Enterobacteriaceae of their intestine, they’ve decrease abundances of genera Lactobacillus and Bacteroidetes17,18. Alterations in intestine microbial group have additionally been noticed in cirrhosis sufferers. Apparently, evaluation of stool samples of 95 liver cirrhosis sufferers and 47 wholesome controls indicated an invasion of oral microbes like Streptococcus and Veillonella into the small gut is noticed in cirrhosis sufferers19,20. Bacterial genera like Veillonella, Megasphaera, Dialister, Atopobium, and Prevotella are additionally present in larger abundances in biopsies of distal duodenum from 30 cirrhosis sufferers as in comparison with 28 wholesome controls used within the examine21.
Along with ascertaining the function of intestine microbiome in liver ailments sure research have indicated potential use of probiotics as a remedy for continual liver ailments. The outcomes of those therapeutic methods differ when it comes to their efficacy and long-term impacts in addition to results on host-microbiome stability have but to be elucidated. a few of these research have been talked about in Supplementary Desk 1. Whereas most of those research point out a lower in pro-inflammatory markers like cytokines, Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and many others. in addition to enchancment in liver lesions, few research additionally point out that no important change is noticed with the consumption of probiotics in liver illness (Supplementary Desk 1). The efficacy of a synbiotic (mixture of a prebiotic (fructo-oligosaccharides and a probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12) administered for 10–14 months on the intestine microbiome, liver fats and fibrosis was studied as part of a placebo managed examine referred to as Insyte. The examine recruited 55 NAFLD sufferers with symbiotic administration whereas 49 have been administered a placebo. The outcomes indicated that though a intestine microbiome change was noticed, no important modifications in liver pathophysiology may very well be noticed22. Thus, long-term randomized managed trials with bigger variety of members are wanted to obviously perceive the efficacy of probiotics/prebiotics or symbiotics in amelioration of liver illness.
Intestine–Liver axis
Mechanisms of communication
Intestinal barrier integrity
The intestinal barrier, comprising of tightly certain cells, ensures selective switch of vitamins and restricts the motion of pathogenic organisms from the intestine lumen into the host system23. The intestine microbiome influences intestine barrier integrity by both sustaining immune signaling mechanisms or by producing metabolites like brief chain fatty acids (SCFAs)23. Thus, disturbances in any of those elements can result in a rise in intestine permeability. For instance, dysbiosis in intestine microbiome in circumstances of inflammatory ailments or because of consumption of excessive fats food plan, alcohol and antibiotics can result in lack of intestine barrier integrity24,25.
A compromised intestine barrier integrity is prone to result in translocation of microorganisms and microbes- derived molecules into the portal system26. Underneath such situation, these microbes in addition to their biosynthesized metabolites can translocate to the liver from the place they are often carried by the portal system to distal organs, thereby inflicting their irritation and harm (Fig. 1)26. Sure metabolites fashioned within the gut may instantly work together with host elements so as to result in exacerbation of liver illness27,28.
Switch of microbes and microbes-derived metabolites by portal circulation
The intestinal dysbiosis is accompanied by lack of intestine barrier integrity and switch of pathogen related molecular patterns (PAMPS) to the portal circulation29 (Fig. 1). This results in induction of sample recognition receptors (PRR) like TOLL-like receptors and NOD-like receptors in liver cells, which ends up in activation of pro-inflammatory signaling cascades, which in flip result in native inflammatory responses29. Toll-like receptors are one class of PRRs that are suppressed in wholesome liver circumstances30 (Fig. 1). The supply of pathogens or/and the molecules biosynthesized by them to the liver results in activation of toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling. This results in a rise within the manufacturing of cytokines like Tumor Necrosis Issue α (TNF α) and Interleukin-1β, each of that are identified to behave on micro organism and viruses. An elevated TLR signaling and expression of those cytokines because of extended stimulation can worsen hepatic harm in a number of liver ailments31. For instance, NASH is thought to have an effect on the degrees of TLR2 (lipopolysaccharide), TLR4 (peptidoglycan), TLR5 (flagellin), and TLR9 (bacterial DNA), all of that are activated by microbial antigens, thereby resulting in inflammatory signaling cascades31.
Systemic ranges of LPS, a part of Gram-negative micro organism, are larger in circumstances of liver ailments like NAFLD and NASH. Injecting LPS in mice mannequin for NAFLD enhances liver harm in addition to elevates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines32,33. Wild sort mice fed with excessive fats food plan develop steatohepatitis with an elevated TLR4 expression and proinflammatory cytokines32,33. Additional, TLR4 mutants are proof against LPS induced launch of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus confirming function of TLR4 signaling in NAFLD and NASH30. Presence of bacterial DNA (which is larger in NASH sufferers) results in elevated expression of TLR9 in NASH fashions30. Experiments with TLR9-deficient fashions fed with choline-deficient amino acid-defined (CDAA) food plan present lesser irritation, steatosis or fibrosis as in comparison with these in wild sort mannequin30. TLR9 signaling impacts expression of inflammasome in macrophages, thereby leading to formation of proinflammatory IL-1β and enhancement of the development of hepatic harm in NASH30.
TLR2 interacts with such Gram-positive bacterial cell wall parts like lipoteichoic acids and peptidoglycan. Based mostly on the experimental observations on mice fashions, insulin resistance induced by excessive fats food plan might be prevented by inhibition of TLR2 signaling34. Additional, TLR2-deficient mice are seen to be proof against ‘Choline Poor Amino Acid’ (CDAA) induced steatohepatitis and have decreased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines35. In distinction, TLR2-deficient mice on ‘Methionine-Choline Poor’ (MCD) food plan show related or extreme steatohepatitis as in comparison with wild sort mice30. Though, MCD food plan could result in options of steatohepatitis, it helps in rising the insulin sensitivity and promotes weight discount. Then again, excessive fats and CDAA diets result in weight acquire and insulin resistance36.
TLR5 binds to bacterial flagellin and performs a protecting function for the gut. TLR5-knockouts develop not solely weight problems and steatosis, but in addition show an imbalance within the intestine microbiome30. Additional, switch of intestine microbial communities from TLR5 knockout mice to WT germ-free mice provides rise to metabolic syndrome30. Thus, an interaction of intestine microbiome and TLR5 in all probability contribute in direction of metabolic syndrome pathophysiology.
Metabolites transferred from intestine by systemic and portal circulation
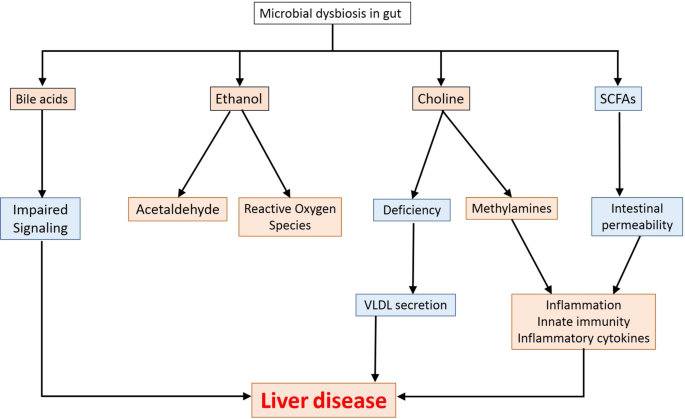
A number of metabolites biosynthesised within the intestine exert a number of results in liver (depicted in Fig. 2).
Trimethylamine and trimethylamine oxide
Choline, a dietary macronutrient, is concerned in a number of physiological processes in liver, which embrace phospholipid biosynthesis (phosphatidyl choline and different membrane lipids), ldl cholesterol metabolism and enterohepatic circulation of bile and lipids9. Deficiency of choline within the food plan results in impairment in liver and mind operate in addition to metabolic processes and muscle motion. Free choline is absorbed by small gut which then both will get built-in into the membrane or is transferred to liver the place it’s prone to get transformed to betaine, lecithin, and many others37. Lesser availability of choline results in accumulation of triglycerides (because of decrease formation of phosphatidyl choline by the host) in liver, an element which has been related to NASH and in addition within the manifestation of NAFLD38. Whereas a choline-deficient food plan induces steatohepatitis, extra choline in food plan (exceeding the absorptive capability of host) strikes to the massive gut to get assimilated to Trimethylamine (TMA) by intestine microbes (Supplementary File 1–1.1)39. One other route for biosynthesis of TMA entails degradation of carnitine obtained from dietary sources like pink meat and dairy merchandise (Supplementary File 1–1.1). The TMA thus fashioned is transferred to liver by portal circulation and will get transformed to Trimethylamine Oxide (TMAO), a part which has been implicated in a number of cardiometabolic problems, hepatic ailments, and many others39.
Quick-chain fatty acids
Metabolites like brief chain fatty acids (SCFAs) primarily embrace butyrate, propionate and acetate and are fashioned within the giant gut because of dietary assimilation of polysaccharides, resistant starch, fiber, and many others40. The SCFAs work as nutrient and power supply for intestinal epithelium and act as precursors for lipogenesis and gluconeogenesis41. The butyrate stage within the intestine helps in sustaining the intestinal integrity in addition to permeability42. A lower in butyrate is noticed in a number of liver illnesses and alcohol influenced liver accidents43.
SCFAs bind and activate G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) GPR41 and GPR4344. This activation influences peptide-YY secretion in addition to causes inhibition of intestine motility, thereby rising the nutrient utilization and yielding of power. The signaling throughout GPR41 and GPR43 results in secretion of GLP1 which in flip reduces the meals consumption in addition to emptying of gastric tract44. Additional, GPCR signaling additionally impacts regulation of fatty acid oxidation and insulin sensitivity by hepatocytes. Aside from this, GPR43 activation additionally results in inhibition of lipolysis and decreased plasma fatty acids44.
Along with GPCR-based signaling, SCFAs can attain the liver by the portal circulation and might have both useful or deleterious results on the liver. For instance, elevated acetate might be channeled to fatty acid biosynthesis pathway, thereby resulting in triglyceride accumulation which has usually been correlated to liver illnesses41,45. Equally, propionate which acts as a precursor for gluconeogenesis has additionally been related to NAFLD41,46. Then again, butyrate could make the most of a number of mechanisms to scale back the pathophysiology related to liver ailments. As an illustration, butyrate can activate ‘AMP activated Protein Kinase’ (AMPK), which in flip reduces irritation and influences glucose in addition to lipid metabolism. AMPK additional suppresses lipogenic genes41. AMPK expression in liver (regulated by butyrate) reduces insulin resistance and weight problems. Butyrate also can operate as inhibitors of ‘Histone deacetylases’ (HDACs) which might forestall improvement of liver ailments like NASH and NAFLD at epigenetic stage41.
Administration of SCFAs has useful results like discount in hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance47. Quite the opposite, whereas enrichment of formate and acetate are present in grownup topics at superior levels of NAFLD, butyrate and propionate are seen to be larger in gentle NAFLD16. These variations in general functioning of SCFAs in liver ailments could also be affected by elements like food plan and surroundings.
Ethanol and acetaldehyde
Ethanol is absorbed largely in abdomen and small gut by way of diffusion by gastrointestinal mucosa48. Majority of ethanol in giant gut is obtained from systemic circulation. Among the intestine microbes can convert ethanol to acetaldehyde and to lesser extent acetate utilizing alcohol metabolizing enzymes akin to alcohol dehydrogenase49. Liver additionally expresses enzymes for ethanol metabolism in response to systemic ethanol content material50.
Apparently, whereas sure small quantities of ethanol are noticed within the bloodstream of topics who don’t devour alcohols, pediatric topics with NASH are seen to own larger serum ethanol ranges as in comparison with overweight kids with out NASH51. These ranges of ethanol may very well be contributed by metabolism by the intestine microbiome52. Consumption of ethanol is probably going so as to add to the pathophysiology of liver ailments (NASH, NAFLD, and many others.) since it might trigger not solely a rise in intestinal permeability, but in addition could help in manufacturing of inflammatory cytokines25. Endogenous ethanol can enhance availability of acetate, a precursor of triglyceride formation by mechanisms involving inhibition of TCA cycle53. Ethanol oxidation by CYP2E1 can result in manufacturing of free radicals which is prone to elevate irritation54. Aside from this, ethanol might be metabolized to acetaldehyde which can both disrupt the tight junctions within the intestinal epithelium55 or could have oxidant-dependent cytotoxic and metabolic impact on intestinal goblet like cells56.
Bile aids
Oxidation of ldl cholesterol to kind main bile acids, cholic acid, and chenodeoxycholic acid takes place within the hepatocytes by a multi-step course of57. These bile acids are additional conjugated to glycine or taurine which operate as fats emulsifiers within the duodenum for solubilizing fat57. The launched bile acids enter canaliculi by an export pump and transfer to the gallbladder the place they get saved58. The bile acids are launched into the duodenum upon consumption of meals as a response to extend in manufacturing of cholecystokinin57. The intestinal microbiome converts these main bile acids to secondary bile acids akin to deoxycholic, lithocholic, and ursodeoxycholic acids59.
Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) prompts FXR signaling, which in flip helps in not solely regulating glucose ranges and metabolism (enhance insulin sensitivity, glycogen synthesis and inhibit gluconeogenic genes), but in addition influences ldl cholesterol transport, inhibits lipogenesis and enhances fatty acid oxidation60. Bile acids additionally result in discount in expression of lipogenic genes in addition to assist in decreasing triglyceride ranges by activating FXR and the pathway involving small heterodimer companion (SHP) and the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1)61. FXR additionally will increase the proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) expression which in flip exerts anti-inflammatory results and regulates lipid in addition to glucose metabolism62.
Whereas most (95%) of the bile acids are reabsorbed within the distal a part of ileum and transported again to liver by portal vein, the remaining will get deconjugated by intestine microbes and excreted out within the feces57. A small fraction of reabsorbed bile acids is prone to escape uptake into liver and attain the peripheral tissues by systemic circulation. The modifications noticed in bile acids in liver illness have been detailed in Supplementary File 1–1.2.
Immune surveillance by liver impacts distal organs
Liver performs an essential function in immune regulation in addition to immunomodulation and possesses virtually 80% of all tissue-based macrophages63. It impacts the innate immunity in different organs and is chargeable for secretion of irritation mediators like serum IL-6 and the acute part protein CRP64,65 in. Thus, you will need to perceive the function of intestine microbiome, the biosynthesized metabolites in liver and the general results on distal organs.
Intestine–Liver–Mind axis
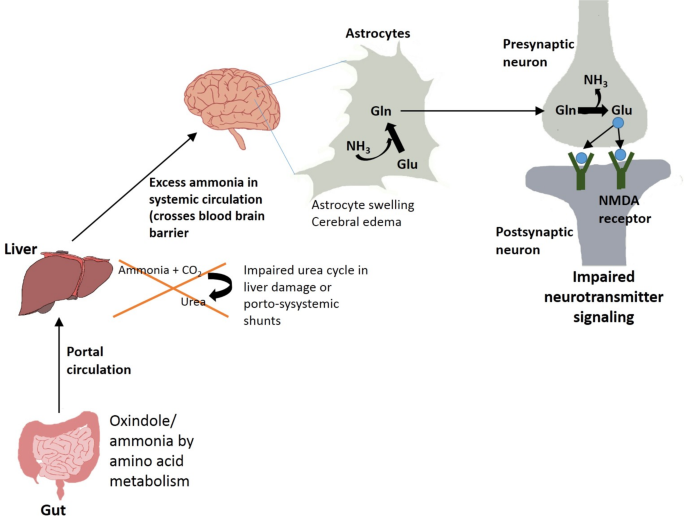
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE), linking mind operate with liver ailments, entails an unlimited vary of neurological and psychiatric abnormalities, starting from subclinical alterations to coma11. HE has usually been noticed as one of many main problems in people with hepatic insufficiency which incorporates ailments like liver cirrhosis and fibrosis10. HE is noticed in virtually 30–45% of sufferers with liver cirrhosis and 24–53% of sufferers with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)66. Having seen the hyperlink between the intestine and liver, you will need to view this reference to respect to mind pathophysiology as noticed in HE, i.e. Intestine–Liver–Mind axis
Intestine microbial merchandise like ammonia and oxindole, obtained after metabolism of amino acids, are deleterious for mind12 (Fig. 3). Oxindole capabilities as a sedative by performing as a ligand for voltage operated sodium channels within the mind. Ammonia capabilities by influencing neurotransmission, pH, membrane potential, astrocyte swelling, and many others. Liver ailments like cirrhosis are sometimes related to insufficiency in detoxing of ammonia and indole derivatives by the liver10,11. The discount in clearance of ammonia from portal vein in cirrhotic sufferers is accompanied by larger ammonia uptake by mind astrocytes which has been related to neurological signs (Fig. 3). Ammonia is primarily fashioned in gastrointestinal tract by the motion of glutaminase or urease enzymes in addition to metabolism of different nitrogen-rich compounds67. This ammonia will get into portal circulation and reaches the liver the place it’s additional detoxified by urea cycle. People with portosystemic shunts or liver failure usually have compromised liver detoxing skills which result in extreme accumulation of nitrogen wastes in systemic circulation (Fig. 3). Extra ammonia is prone to cross blood mind barrier and be absorbed into astrocytes the place it presumably will get transformed to glutamine12. Glutamine thus fashioned could trigger oxidative or osmotic stress and astrocyte swelling, additional manifesting as cerebral edema and elevated GABAergic exercise (Fig. 3)68.
Systemic irritation and sepsis have additionally been thought-about as elements that are concerned in exacerbation of HE69. HE sufferers usually present larger incidence of inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, IL-18 and TNFα11. The presence of systemic and native irritation has been proven to enhance the impact of hyperammonemia in HE. Proinflammatory cytokines might be produced in mind, thereby giving rise to neuroinflammation70. Systemic irritation can happen in case of liver cirrhosis because of a number of elements, one in every of them being enhance in intestinal permeability which might result in translocation of micro organism and their merchandise into systemic circulation68. These micro organism together with their PAMPs assist in activating the immune response with launch of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The loss in intestine barrier integrity in case of liver failure can occur because of elements like discount in formation of tight junction proteins, discount in SCFA ranges, dysbiosis in intestine, endotoxemia, and many others.71. Systemic irritation and hyperammonemia could result in activation of resident macrophages in central nervous system referred to as microglial cells72. This will likely lead to formation of mind derived proinflammatory cytokines and lead to neuronal loss of life.
Intestine–Liver–kidney axis
Hepatic failure is commonly linked to kidney dysfunction or continual kidney illness (CKD)73. A discount within the estimated glomerular filtration fee (eGFR) of <60 mL/min for greater than 3 months is taken into account because the prognosis of CKD in cirrhosis. A examine in 2019 confirmed that 46.8% of hospitalized sufferers with cirrhosis have been recognized with CKD74. Equally, there’s a correlation between lack of kidney operate and dyslipidemia75. NAFLD results in lipid accumulation, usually concerned in aggravating insulin resistance, irritation, hypertension and weight problems, which in flip could affect kidney dysfunction76. Improve in biosynthesis of pro-inflammatory, pro-thrombotic elements in NAFLD could contribute in direction of renal harm77. Additional, modifications within the expression of hepatic lipase result in excessive triglyceride ranges. Ranges of Apolipoprotein B-100 containing lipoproteins biosynthesized in liver additionally present abnormalities in CKD sufferers78. Systemic irritation throughout CKD may cause a number of results and contribute to NAFLD.
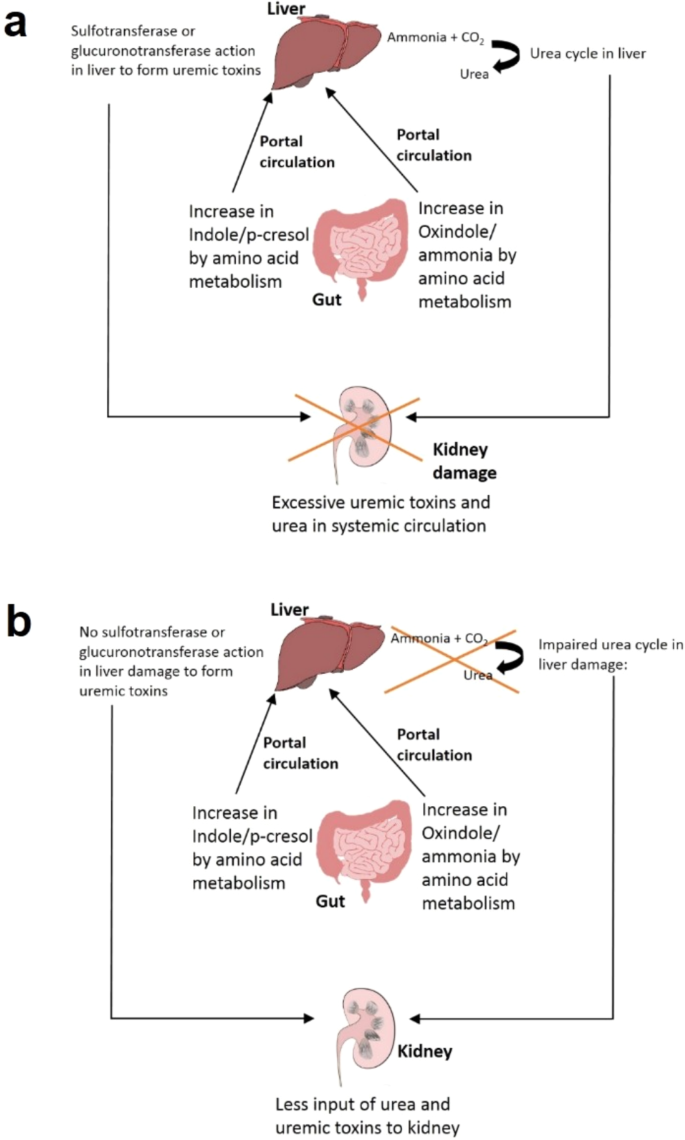
Intestine microbiome performs an essential function within the connection between liver and kidneys (‘Intestine–Liver–Kidney axis’) depicted in Fig. 4a. Dysbiosis in intestine microbiome or excessive stage of proteins in food plan result in excessive protein fermentation within the intestine, thereby giving rise to formation of ammonia, indole, p-cresol, and many others.79 (Fig. 4a). Whereas indole is fashioned by fermentation of tryptophan by intestinal micro organism, p-cresol is fashioned by decarboxylation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid which is a product of tyrosine degradation by host enzyme80,81. These merchandise are absorbed by intestinal mucosa and brought to the liver the place they’re additional modified by host sulfotransferases or glucoronotransferases to offer rise to indoxyl-sulfate, indoxyl glucuronate, p-cresyl-sulfate, and p-cresyl-glucuronate, all of that are uremic toxins82. These toxins transfer into systemic circulation and are cleared from the system by renal filtration. Such toxins additionally have an effect on the development of renal illnesses and are noticed to be elevated in sufferers with CKD and finish stage renal illness (ESRD)82 (Fig. 4a). The uremic toxins are anticipated to behave as agonists of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and affect launch of pro-inflammatory cytokines in addition to enhance irritation and oxidative stress83. The noticed alterations in expression of genes like hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) and drug transporter operate are anticipated since these genes have AhR websites on their promoters84. This results in modifications in drug metabolism in hepatocytes (Fig. 4a). In sufferers with CKD and superior liver illness or cirrhosis, the exercise of enzymes chargeable for modification in liver (sulfotransferases) is lowered and will contribute in direction of discount within the uremic toxin formation82 (Fig. 4b). Thus, the quantity of uremic toxins within the physique in case of kidney harm can also be influenced by the liver situation. Additional, uremic toxins might have regulatory results in liver (Fig. 4b).
a Intestine–Liver–kidney axis with out liver harm: Oxindole and cresol produced by intestine microbiome are transformed to uremic toxins in liver. The uremic toxins attain kidneys by portal circulation. b Intestine–Liver–Kidney axis with liver harm: Oxindole and cresol produced within the intestine usually are not transformed to uremic toxins in liver.
TMA produced by intestine microbiome from choline metabolism is transformed to TMAO in liver by flavin-like monooxygenases. The TMAO is carried to kidneys by systemic circulation and cleared by glomerular filtration85. TMA and TMAO ranges are elevated in people with renal ailments, CKD, ‘Finish Stage Renal Illness’ (ESRD), fibrosis, and many others86. Additional, the next presence of TMAO is related to liver illnesses like NAFLD, NASH, liver cirrhosis, and many others87. TMAO helps in suppression of bile acid mediated farnesoid X receptor signaling in liver, which in flip results in aggravation in liver steatosis87. This means that change in TMAO ranges throughout kidney dysfunction may affect the physiology of liver.
Intestine–Liver–Lung axis
A rise in innate immunity concomitant with a rise in inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) has been related to deterioration in lung operate and exacerbation of ailments like Power Obstructive Pulmonary Illness (COPD)88. COPD refers to a lung illness that causes airflow blockage to the lungs and results in breathing-related issues. The prevalence of steatosis, NASH and fibrosis in COPD sufferers have been reported to be 41.4%, 36.9% and 61.3%, respectively89. The upper innate immune response in addition to pro-inflammatory markers like IL-6 have been correlated to pathophysiology of lung illnesses88. The liver works as a web site of immunomodulation with the mevalonate pathway enjoying a significant function. Statins which inhibits the mevalonate pathway in liver is noticed to scale back the lung harm90. Lovastatin is seen to scale back deleterious results of macrophage activation in mouse fashions. Atorvastatin is proven to scale back not solely lung inflammatory cells by 30–60%, but in addition expression of pro-inflammatory genes together with discount in CRP and IL-691.
Along with mevalonate pathway, liver performs an important function in build up an innate immune response when it comes to recruitment of macrophages and the neutrophils on the web site of lung harm. Research on mouse mannequin point out its function in rising launch of IL-6 and acute part proteins by alveolar macrophages92. These proteins are prone to generate continual irritation resulting in activation of innate immunity in circulation in addition to in lungs (termed as innate immune hyper-responsiveness), particularly in circumstances of harm as seen in ailments inflicting lung harm. Thus, the “Liver–Lung axis” hyperlinks the innate immune responsiveness and lung harm with the innate immune response regulated by the liver and the mevalonate pathway88.
To evaluate attainable hyperlink between food plan and respiratory ailments, outcomes based mostly on a examine on ~120,000 topics point out important discount in incidence of COPD with consumption of high-fiber food plan comprising of complete meals grains93. Equally, consumption of complete grains reveals substantial enhancements in FEV1 (Pressured Expiratory Quantity in 1 s) of people who smoke (200 ml change throughout food plan quartiles) as in comparison with non-smokers (50 ml change throughout dietary quartiles)94. Evidences point out the impact of dietary fibers on immunomodulation of innate immune response. Comparability of results of dietary fiber consumption on particular causes of loss of life recommend dietary fiber’s function in discount in mortality in people affected by respiratory illnesses95. Equally, 50–60% discount in mortality because of consumption of high-fiber food plan comprising of complete grains (HR = 0.47 for males and 0.40 for girls) has been noticed in a European examine on >450,000 people96. A examine on a cohort of 35,339 Swedish girls confirmed {that a} long-term consumption of dietary fiber may very well be related to a 30% decrease threat of COPD97. Epidemiological and scientific research additionally recommend function of high-fiber diets in decreasing systemic irritation and resulting in lower markers of irritation like CRP and IL-698.
Trying into the ‘Intestine–Liver–Lung axis’, one of many attainable methods by which dietary fiber gives profit is by stimulating the expansion of useful micro organism in intestine which assist in biosynthesis of SCFAs by fermentation3. Some SCFAs get absorbed and enter portal circulation, thereby affecting organs like liver99. SCFAs operate by modulating innate immune activation. Excessive-fiber food plan is seen to scale back pulmonary irritation in murine fashions. SCFAs affect the migration of neutrophils and macrophages by way of GPCR activation which helps in decreasing pulmonary inflammatory response44. Moreover, SCFAs inhibit the HMG-CoA reductase which catalyzes the speed limiting step of mevalonate pathway41. This inhibition permits discount in inflammatory markers and decreasing of the innate immune response. HMG-CoA reductase inhibition within the liver ‘dampens’ the innate immune response and lowers serum ranges of IL-6 by the IL-6 trans-signaling pathway88. This results in a downstream inhibitory impact on the pro-inflammatory transcription elements NF-ĸB and sign transducer and activator of transcription88.
Intestine–Liver–Coronary heart axis
Liver ailments like NAFLD, NASH, and cirrhosis, which have been related to modifications in intestine microbiome, additionally correlate with the incidence cardiovascular (CV) illnesses comprising problems of coronary heart and blood vessels (‘Intestine–Liver–Coronary heart axis’)100. Non-alcoholic fatty liver illness (NAFLD) is related to the next threat of heart problems (CVD) which incorporates coronary coronary heart illness (CHD), coronary heart failure, stroke, and arrhythmia101. A comply with up examine on 285 people with biopsy confirmed NAFLD and no incidence of CVD confirmed an incidence of a cardiovascular occasion in 9.1% of those superior stage people inside 5 years of comply with up102. Publicity to lipopolysaccharide and its binding to TLR4 result in an inflammatory immune response with launch of pro-inflammatory cytokines103. This course of promotes LDL oxidation, formation of atherosclerotic plaques and thrombogenesis104.
Dietary consumption that are larger in choline, betaine or carnitine (e.g. pink meat) results in formation of TMA by intestine micro organism, which additional will get transformed to TMAO in liver39,87,105. The rise in TMAO ranges is related to liver in addition to CV occasions86. Thus, TMAO might be thought-about as marker for a deteriorating liver situation or Cardiovascular well being86. TMAO concentrations have been associated to atherosclerosis which is among the main causes of CVDs in addition to ‘Main antagonistic cardiovascular occasions’ (MACE) together with myocardial infarction, stroke, and many others.86. Greater TMAO ranges and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) are noticed to be accompanied with cardiac dysfunction in mouse fashions106. The inhibition of choline TMA lyase enzyme by chemical compounds like 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol (DMB) can forestall enhance in TMA ranges in addition to different outcomes107.
There exists a hyperlink between endothelial dysfunction and TMAO ranges. TMAO therapy carried out on human monocytic THP-1 cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) reveal a rise in monocyte adhesion which result in elevated expression of VCAM-1108. Moreover, lipid metabolism can also be regulated by TMAO which alters ldl cholesterol and sterol metabolism106. Catabolism of ldl cholesterol entails bile acid synthesizing enzyme Cyp7a1 catalyzing the speed limiting step. TMAO lowers the expression of this enzyme which has been related to atherosclerosis109. Supplementation of choline, carnitine or TMAO could lower reverse ldl cholesterol transport. Additional, TMAO influences the rise in expression of CD36 and SR-A1 (scavenger receptors) which results in lipid accumulation and foam cell formation106,110. These results are induced by oxidative modification of LDL in presence of TMAO. The inhibition of MAPK by inhibitors results in a discount in expression of CD36 in addition to foam cell formation, indicating motion of MAPK/JNK pathway in atherosclerosis induced by TMAO111.
Some inconsistencies concerning hyperlink of plasma TMAO ranges and CVDs nonetheless exist. For instance, short- and long-term larger plasma TMAO ranges are noticed in folks after bariatric surgical procedure. The result’s sudden as excessive TMAO concentrations enhance the CVD threat whereas the goal of bariatric surgical procedure is to scale back CVD threat39. Nonetheless, recording their food plan and intestine microbiome might have thrown some gentle on whether or not TMAO ranges have been discovered to be larger in topics because of a surgery-induced change in intestine microbiome or because of a higher ingestion of carnitine (a TMA precursor) which is commonly promoted as a weight reduction inducing complement.
There are additionally sure contrasting observations concerning function of TMAO in CVDs. Though, TMAO is proven to correlate with inflammatory markers and endothelial dysfunction, some research point out such associations solely in case of HIV and type-II diabetes39. Few research additionally point out no important correlation of TMAO ranges with inflammatory marker CRP. Protecting function of TMAO in CVDs have additionally been reported. After carnitine supplementation, enchancment is seen in some CVDs regardless of a rise in TMAO and TMA112. Meals gadgets like marine fish include excessive ranges of TMAO that are noticed in circulation after dietary consumption. Regardless of that, research on mice present that supplementation of fish oil together with a excessive fats food plan alleviate harm attributable to TMAO together with elevated glucose tolerance and irritation of adipose tissue113.
In abstract, the Intestine–Liver axis refers to bidirectional communication between intestine, its microbiome and the liver. The metabolites produced by intestine microbiome are linked with liver by systemic circulation, portal circulation and the bile duct. Whereas the metabolites produced within the intestine affect immunity, metabolism and bile acid manufacturing, the bile acids produced in liver in flip regulate the intestine microbial composition in addition to intestine epithelial barrier integrity. Subsequently, a dysbiosis in intestine microbiome not solely results in a change within the bile acid pool inside the host, but in addition usually been noticed in liver associated pathophysiologies like NAFLD, NASH, ALD, and many others. Additional, since some intestine micro organism are able to metabolizing bile acid, the bile acid pool determines and influences the composition of intestine microbiome. The shifting stage of bile acids impacts the intestinal integrity and metabolism by affecting FXR signaling. Publicity of liver immune cells to metabolites like TMAO produced by intestine micro organism can enhance liver irritation. Additional, the liver regulates the innate immunity in addition to metabolism of varied toxins and metabolites in different organs. In different phrases, a deterioration in liver situation also can affect the metabolism signaling and immunity in different essential host organs. Therefore, the Intestine–Liver axis might be prolonged to distal organs like Intestine–Liver–Mind, Intestine–Liver–Kidney, Intestine–Liver-Coronary heart and Intestine-Liver-Lung axes.
Findings from the Intestine-Liver-X (X being Mind or Kidney or Coronary heart or Lung) axes point out potential of using intestine microbiome as diagnostic and therapeutic technique for early detection and administration of not solely liver ailments, but in addition ailments effecting different organs (e.g., continual kidney illness, hepatic encephalopathy, cardiovascular illnesses, respiratory obstructions, and many others.). Figuring out microbiome signatures which might be indicative of various well being circumstances is an energetic space of analysis. An understanding of Intestine–Liver axis and interactions with distal organs can additional assist in figuring out probiotic and fecal transplant methods as preventive therapeutic regimes for liver illnesses. Though sure research have indicated potential use of probiotics as a remedy for continual liver ailments, long-term impacts in addition to results on host-microbiome stability have but to be elucidated (Supplementary Desk 1). Scientific trials with standardized dosage of probiotics and prolonged period of administration together with common follow-ups are mandatory to verify the efficacy of the probiotics in manipulating the Intestine–Liver axis in addition to understanding their impacts on different organs like mind, kidney, lung and coronary heart.