Research topics
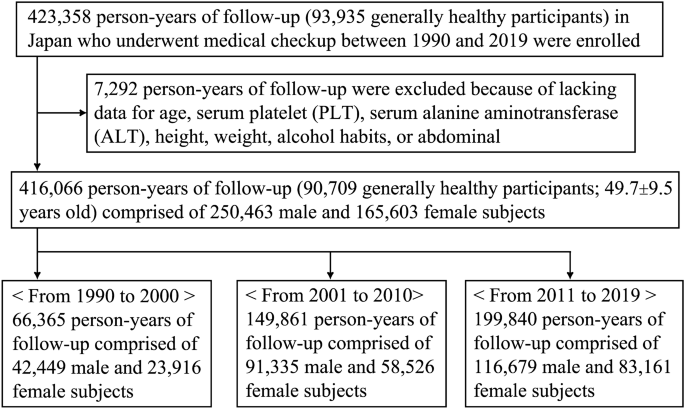
After excluding topics missing important knowledge (Fig. 1), a consecutive 416,066 person-years of follow-up (90,709 typically wholesome individuals) from 1990 to 2019 have been analyzed (imply age, 49.7 ± 9.5 years; vary 20–93 years). The typical variety of follow-ups was 5.5 ± 4.8 and the common length of follow-ups was 4.8 ± 6.1 years. The examine consisted of 66,365 topics (42,449 males and 23,916 ladies) between 1990–2000, 149,861 topics (91,335 males and 58,526 ladies) between 2001–2010, and 199,840 topics (116,679 males and 83,161 ladies) between 2011–2019. The info on fatty liver, FIB-4 index, BMI, and alcohol consumption of every age group are proven in Desk 1 (complete 416,066 topics), Supplementary Desk S1 (250,463 males), and Supplementary Desk S2 (165,603 ladies).
Thirty-year traits of fatty liver, FIB-4 index, and physique mass index in Japan
As proven in Desk 1, in contrast with that within the Nineties (roughly 22%), the prevalence of fatty liver enormously elevated within the 2000s (greater than 35%); nevertheless, there was no outstanding change between 2001–2010 (39.2%) and 2011–2019 (35.5%). Alternatively, the speed of excessive FIB-4 index (≥ 2.67) didn’t markedly change through the 30 years (0.9% in 1990–2000, 0.6% in 2001–2010, and 1.1% in 2011–2019). Additional, though BMI didn’t change notably (imply BMI: 23.1 in 1990–2000, 23.0 in 2001–2010, and 23.1 in 2011–2019), the prevalence of weight problems (BMI ≥ 30) constantly elevated from 1990 to 2019 (1.9% in 1990–2000, 2.7% in 2001–2010, and three.8% in 2011–2019).
Though comparable traits have been noticed for each males (Supplementary Desk S1) and ladies (Supplementary Desk S2), there was a substantial distinction of their prevalence between sexes. The charges of fatty liver, excessive FIB-4 index (≥ 2.67), and weight problems in males have been greater than these in ladies in all three intervals (1990–2000, 2001–2010, and 2011–2019) and all age teams (< 40, 40–49, 50–59, 60–69, and > 70 years). In all female and male topics through the 30 years, the charges of fatty liver have been 42.9% and 22.2%, charges of excessive FIB-4 index (≥ 2.67) have been 1.1% and 0.6%, charges of weight problems have been 3.5% and a couple of.6%, and charges of heavy consuming have been 18.4% and 5.4%, respectively.
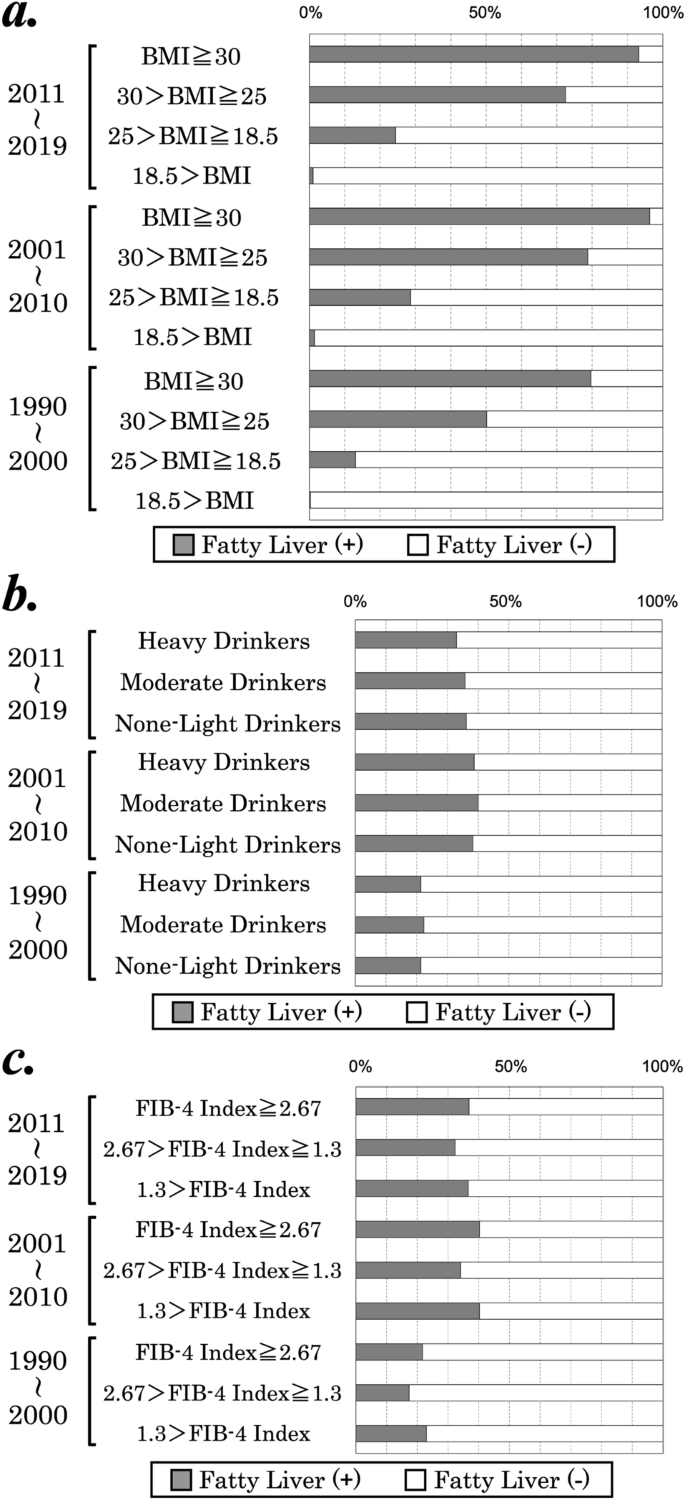
The presence of fatty liver is considerably related to a better BMI however not with alcohol consumption or FIB-4 index
Subsequent, we evaluated the prevalence of fatty liver in all three intervals by evaluating the frequency distribution of BMI, alcohol consumption, and the FIB-4 index (Fig. 2). As proven in Fig. 2a, an affiliation between fatty liver and BMI was noticed in all teams. Nonetheless, the affiliation of fatty liver with alcohol consumption or the FIB-4 index couldn’t be detected (Fig. 2b,c). Our outcomes indicated that the presence of fatty liver considerably mirrored BMI and weight problems however not alcohol consumption or FIB-4 index.
FIB-4 index is a extra helpful indicator of power hepatitis improvement compared with fatty liver
To judge the predictive means of FIB-4 index and fatty liver for power hepatitis or liver cirrhosis, we excluded 161,696 person-years of follow-up (48,407 individuals) earlier than April 2008 which didn’t have detailed data of comorbidities. We additional excluded 209 person-years of follow-up (63 individuals) which recognized with power hepatitis or liver cirrhosis at baseline. We additional excluded 2,161 person-years of follow-up (441 individuals) which recognized with liver, collagen, and hematological ailments.
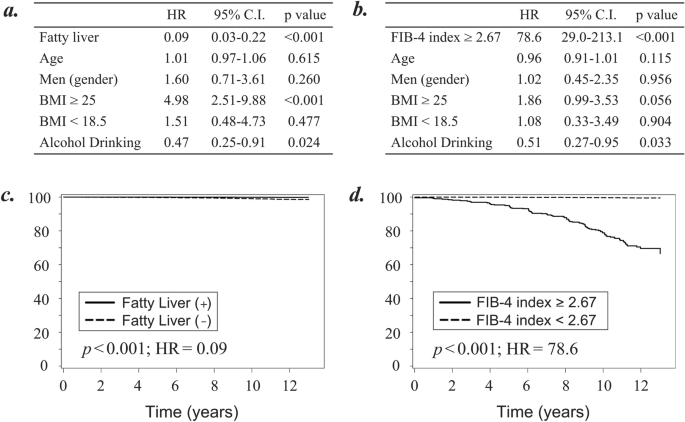
Of the 252,000 topics (61,857 individuals), 114 developed power hepatitis. Two fashions of cox regression analyses have been carried out to determine the contributing issue specializing in fatty liver (Fig. 3a) or FIB-4 index (Fig. 3b) for improvement of power hepatitis. Moreover, utilizing the time-to-event knowledge, the adjusted survival curves for Cox proportional hazards regression have been plotted to judge the usefulness of fatty liver (Fig. 3c) or FIB-4 index (Fig. 3d) for predicting the danger of power hepatitis.
Cox regression analyses to judge the usefulness of fatty liver and FIB-4 index for prediction of power hepatitis improvement. (a) Cox regression evaluation to judge power hepatitis improvement specializing in the presence of fatty liver. (b) Cox regression evaluation to judge power hepatitis improvement specializing in the worth of FIB-4 index. (c) Adjusted survival curves to judge the incidence of power hepatitis primarily based on the Cox proportional hazards regression categorized by the presence of fatty liver. (d) Adjusted survival curves to judge the incidence of power hepatitis primarily based on the Cox proportional hazards regression categorized by the worth of FIB-4 index. All analyses have been carried out on the examine individuals after excluding these with power hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and different ailments regarding liver, collagen, and hematological ailments on the time of entry. A p-value < 0.05 was thought-about statistically important. HR hazard ratio; C.I. confidence interval.
Unexpectedly, the danger of creating power hepatitis was greater in topics with out fatty liver than in these with fatty liver (Fig. 3a,c; Hazard ratio [HR] = 0.09; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03–0.22, p < 0.001). Alternatively, the danger of creating power hepatitis was a lot greater in topics with a excessive FIB-4 index (≥ 2.67) than in these with out it; (Fig. 3b,d; HR = 78.6; 95% CI, 29.0–213.1, p < 0.001). Assuming the state of affairs with inadequate data of present or earlier medical historical past, we carried out the identical analyses utilizing all of the 416,066 individuals. Then, comparable survival curves have been plotted for power hepatitis improvement concerning fatty liver (Supplementary Fig. S1a; HR = 16.0, p < 0.001) and FIB-4 index (Supplementary Fig. S1b; HR = 58.6, p < 0.001).
As for different contributing elements, our knowledge indicated that those that drink alcohol have the decrease threat of creating power hepatitis (Fig. 3a,b; HR = 0.47 and HR = 0.51, p = 0.024 and p = 0.033).
FIB-4 index is a extra helpful indicator of liver cirrhosis improvement compared with fatty liver
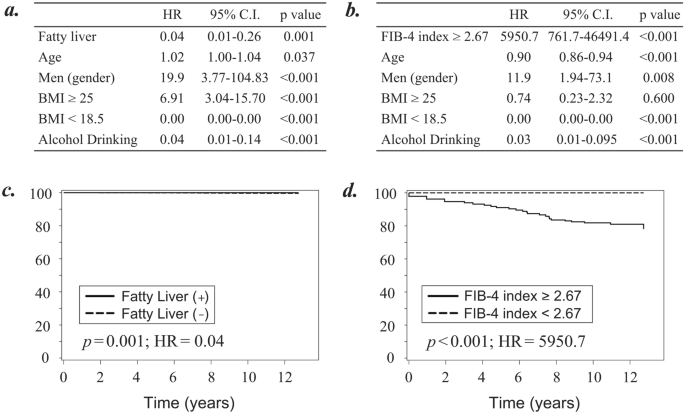
Of the 252,000 topics, 23 developed liver cirrhosis. Two fashions of cox regression analyses have been carried out to determine the contributing issue specializing in fatty liver (Fig. 3a) or FIB-4 index (Fig. 3b) for improvement of liver cirrhosis. Moreover, utilizing the time-to-event knowledge, the adjusted survival curves for Cox proportional hazards regression have been plotted to judge the usefulness of fatty liver (Fig. 4c) and the FIB-4 index (Fig. 4d) for predicting the danger of liver cirrhosis.
Cox regression analyses to judge the usefulness of fatty liver and FIB-4 index for prediction of liver cirrhosis improvement. (a) Cox regression evaluation to judge liver cirrhosis improvement specializing in the presence of fatty liver. (b) Cox regression evaluation to judge liver cirrhosis improvement specializing in the worth of FIB-4 index. (c) Adjusted survival curves to judge the incidence of liver cirrhosis primarily based on the Cox proportional hazards regression categorized by the presence of fatty liver. (d) Adjusted survival curves to judge the incidence of liver cirrhosis primarily based on the Cox proportional hazards regression categorized by the worth of FIB-4 index. All analyses have been carried out on the examine individuals after excluding these with liver cirrhosis, liver cirrhosis, and regarding liver, collagen, and hematological ailments on the time of entry. A p-value < 0.05 was thought-about statistically important. HR hazard ratio; C.I. confidence interval.
Much like power hepatitis (Fig. 3), the danger of creating liver cirrhosis was greater in topics with out fatty liver than in these with fatty liver (Fig. 4a,c, HR = 0.04; 95% CI, 0.01–0.26, p = 0.001). The chance of creating liver cirrhosis was a lot greater in topics with a excessive FIB-4 index (≥ 2.67) than in these with out it (Fig. 4b,d; HR = 5950.7; 95% CI, 761.7–46,491.4, p < 0.001). Determine 4 confirmed that categorization primarily based on the worth of the FIB-4 index was extra helpful than categorization primarily based on the presence of a fatty liver to foretell improvement of liver cirrhosis. Assuming the state of affairs with inadequate data of present or earlier medical historical past, we carried out the identical analyses utilizing all of the 416,066 individuals. Then, comparable survival curves have been plotted for power hepatitis improvement concerning fatty liver (Supplementary Fig. S2a; HR = 32.1, p < 0.001) and FIB-4 index (Supplementary Fig. S2b; HR = 532.4, p < 0.001).
As for different contributing elements, our knowledge indicated that those that drink alcohol have the decrease threat of creating liver cirrhosis (Fig. 3a,b; HR = 0.04 and HR = 0.03, p < 0.001 and p < 0.001).