A latest examine posted to the medRxiv* preprint server examined hostile reactions after administration of a bivalent BNT162b2 coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine booster.
Vaccination is vital towards extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), however rising mutant variants of the virus impair the effectiveness of vaccines primarily based on the unique/wildtype SARS-CoV-2. Consequently, bivalent vaccines with spike messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) of wildtype and Omicron BA.1 or BA.4/5 variant have been developed.
Studies recommend that the bivalent mRNA-1273.214 vaccine primarily based on the Wuhan-Hu-1 and Omicron BA.1 spike mRNA has a barely increased charge of hostile reactions. Furthermore, no proof of hostile reactions after bivalent COVID-19 vaccination is obtainable resulting from approval with out further scientific research.
 Research: Bivalent BNT162b2mRNA authentic/Omicron BA.4-5 booster vaccination: hostile reactions and lack of ability to work in comparison with the monovalent COVID-19 booster. Picture Credit score: Akash Sain / Shutterstock
Research: Bivalent BNT162b2mRNA authentic/Omicron BA.4-5 booster vaccination: hostile reactions and lack of ability to work in comparison with the monovalent COVID-19 booster. Picture Credit score: Akash Sain / Shutterstock
The examine and findings
Within the current examine, researchers in Germany and the UK evaluated hostile reactions, professional re nata (PRN) treatment consumption, and the power to work after the second booster vaccination (fourth dose) amongst healthcare employees (HCWs). All contributors had been beforehand administered European Medicines Company (EMA)-approved major COVID-19 immunization, adopted by subsequent mRNA vaccine-based booster dose.
The second booster vaccine was both the monovalent BNT162b2 vaccine or the bivalent BNT162b2 vaccine with spike mRNA of wildtype and Omicron BA.4/5 variant. Members who obtained a distinct vaccine because the second booster dose and those that obtained a concurrent influenza vaccination have been excluded from the examine.
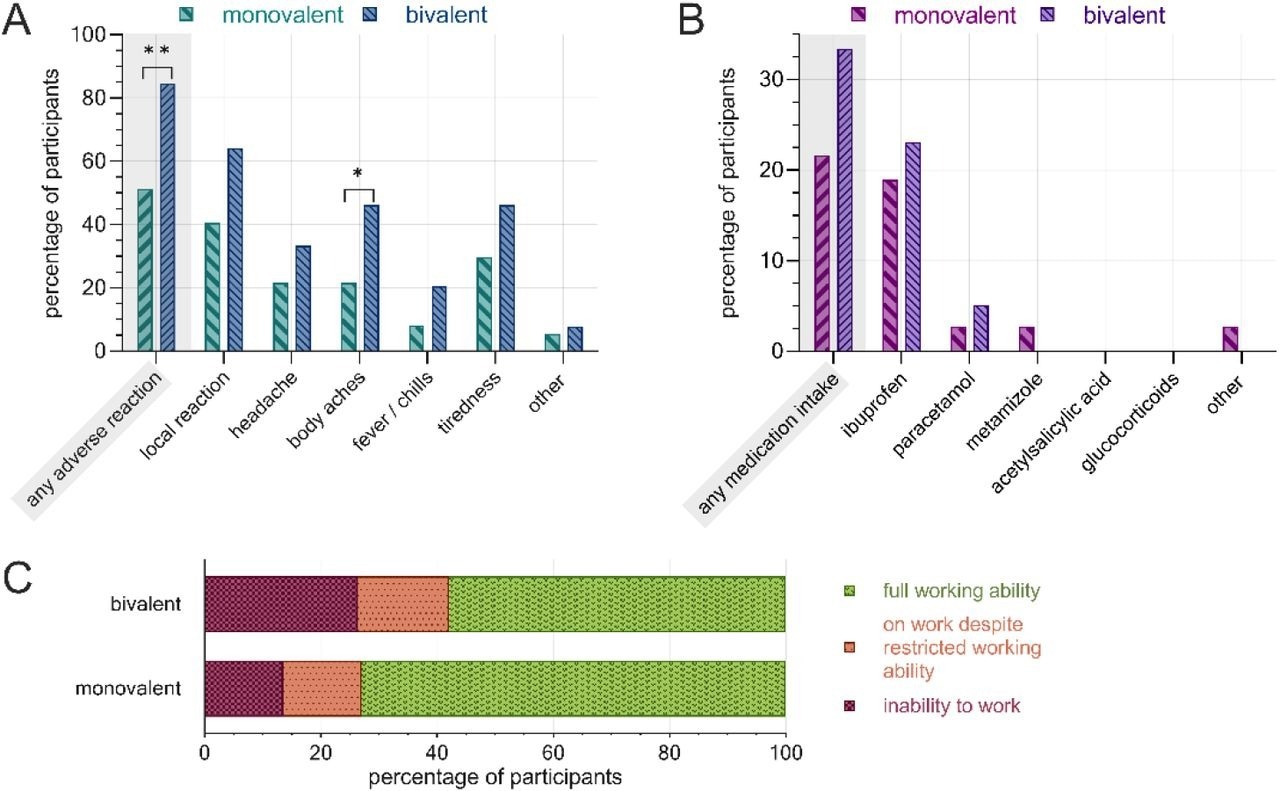 Publish-vaccination hostile reactions, PRN treatment and lack of ability to work following the second COVID-19 booster administration, separated by vaccine. A) charge of hostile reactions by subcategory, B) charge of PRN treatment, C) work skill restrictions. Monovalent: BNT162b2mRNA (n=37), bivalent: BNT162b2mRNA authentic/Omicron BA.4-5 (n=39). **: p<0.01, *: p<0.05.
Publish-vaccination hostile reactions, PRN treatment and lack of ability to work following the second COVID-19 booster administration, separated by vaccine. A) charge of hostile reactions by subcategory, B) charge of PRN treatment, C) work skill restrictions. Monovalent: BNT162b2mRNA (n=37), bivalent: BNT162b2mRNA authentic/Omicron BA.4-5 (n=39). **: p<0.01, *: p<0.05.
Information on hostile reactions, sociodemographic components, PRN treatment, and the power to work have been obtained by a questionary utilizing Analysis Digital Information Seize (REDCap) software. As well as, the null speculation was examined utilizing the Mann-Whitney U and Fisher’s precise checks. Seventy-six HCWs obtained the second COVID-19 booster from August 13, 2021, to October 14, 2022.
Thirty-seven HCWs obtained the monovalent BNT162b2 vaccine, and 39 obtained the bivalent vaccine (wildtype/Omicron BA.4/5). Most HCWs (80%) have been feminine; the median age of feminine and male HCWs was 47 and 51, respectively. The speed of hostile reactions following the second booster administration was considerably increased amongst HCWs immunized with the bivalent vaccine (84%) than these receiving the monovalent vaccine (51%).
Particularly, the charges of headache, physique aches, tiredness, fever, chills, and native reactions have been considerably increased in HCWs receiving the bivalent vaccine. Bivalent vaccine-administered HCWs reported a extra frequent PRN treatment use and had elevated charges of workability restrictions than monovalent vaccine-administered restrictions.
Conclusions
The researchers noticed that HCWs receiving the bivalent BNT162b2 wildtype/Omicron BA.4/5 vaccine because the second booster shot confirmed a better prevalence of hostile reactions than monovalent vaccine-boosted HCWs. Notably, the interval between the primary and second booster administration was 193 days for monovalent vaccine recipients and 322 days for bivalent vaccine recipients.
Moreover, HCWs reported elevated PRN treatment consumption and lack of ability to work following bivalent booster dose administration. The examine’s limitations embody its retrospective questionnaire-based design and the shortage of blinding and randomization. General, these findings could assist inform scientific choices concerning monovalent and bivalent vaccination.
*Necessary discover
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reviews that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established data.
