Collection of public datasets
To formulate an advert hoc tradition medium appropriate for in vitro cultivation of bacterial taxa which can be attribute of the toddler intestine microbiota, a meta-analysis was carried out geared toward defining the taxonomic composition of the toddler intestinal microbial ecosystem primarily based on publicly out there shotgun metagenomic datasets. For this goal, an in-depth literature search was carried out to retrieve shotgun metagenomic datasets primarily based on Illumina sequencing know-how similar to fecal samples from wholesome, full-term infants that ranged in age from one month to 36 months, for the reason that transition from an infant- to an adult-like intestine microbiota is assumed to have occurred by the point the toddler reaches three years of age4,9,17,24,25. Furthermore, in case of longitudinal research, just one pattern per toddler was thought of to keep away from redundant samples, whereas for research involving the administration of medicine, prebiotics and/or probiotics, solely toddler fecal samples belonging to the management group had been chosen. This allowed for a group of 2411 publicly out there samples, chosen from 17 cohorts, and protecting totally different geographical areas. Moreover, primarily based on the idea that the toddler intestine microbiota is very variable and dynamic in the course of the first three years of life, the chosen samples had been divided into three totally different age-based teams, i.e., group 1-6 M (from 30 days to six months of life), group 6-12 M (between 6 months and one yr of life), and group 12-36 M (from one to a few years of age), as beforehand described9,17. This grouping resulted in a complete of 1328, 372 and 711 samples similar to the 1-6 M, 6-12 M and 12-36 M teams, respectively. Particulars concerning the number of public datasets are mentioned in additional element within the supplementary textual content.
Meta-analysis of the toddler intestine bacterial neighborhood and identification of the dominant bacterial species
To offer an in-depth analysis of the bacterial species typical of the human intestine microbiota throughout infancy and to standardize the bioinformatic pipeline, 100,000 reads per every pattern of the chosen 2411 publicly out there samples had been re-analyzed by the use of the lately printed METAnnotatorX2 software program pipeline, which is particularly designed to course of shotgun metagenomics information units26. Particularly, 100,000 reads had been processed for every pattern as they correspond to the proposed default variety of reads required to attain a dependable taxonomic profile of bacterial species current at >0.5% relative abundance, which is a cut-off that was chosen to offer robustness to the taxonomical analyses to be able to remove bacterial species with severely decreased abundance, and appropriate with shallow shotgun metagenomics functions, as beforehand described26. Moreover, even if the NCBI-based RefSeq database doesn’t embrace Metagenome Assembled Genomes (MAGs) and that it’s not absolutely consultant of bacterial species typical of non-Westernized populations, the RefSeq was employed because the reference database for the METAnnotatorX2 pipeline-based evaluation26,27. Certainly, the usage of the RefSeq database allowed us to solely use whole-genome shotgun assemblies with prime quality annotations making the evaluation extra correct and strong26,28.
Based mostly on the obtained species-level taxonomic profiles, a β-diversity evaluation was carried out by a Principal Coordinate Evaluation (PCoA) illustration to remove any outliers. Based mostly on the latter evaluation and the above-mentioned exclusion standards, a complete of 1669 samples had been retained to outline the principal bacterial gamers of the toddler intestine microbiota (Desk 1 and Supplementary Desk 1). After high quality checks and eradicating Homo sapiens reads, a complete of 106,519,353 reads had been taxonomically labeled with a median of 63,822 ± 15,018 reads per pattern (Supplementary Desk 2). Taxonomic reconstruction of the bacterial neighborhood of every analyzed pattern is reported in Supplementary Materials (Supplementary Desk 3).
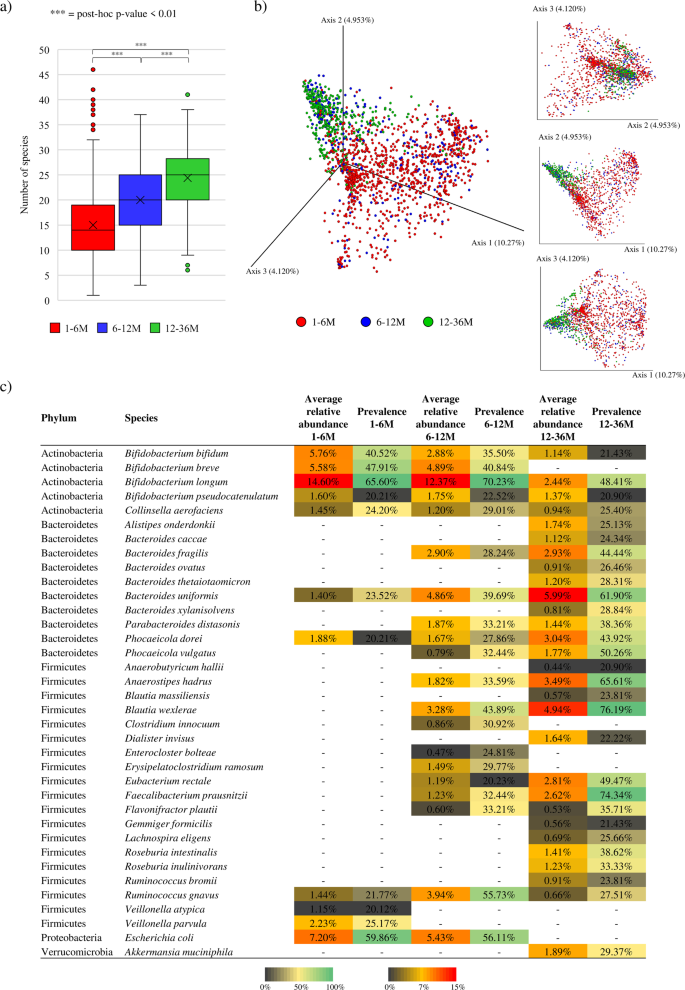
As anticipated from already printed single cohort-based and/or longitudinally research, species richness evaluation revealed a progressive and statistically important increment within the common variety of species throughout teams that positively correlated with age (ANOVA post-hoc p worth < 0.01) (Fig. 1)29. Furthermore, a Bray-Curtis dissimilarity-based beta-diversity evaluation, represented by PCoA, highlighted clear compositional variations between samples belonging to 1-6 M or 6-12 M, when in comparison with these of the 12-36 M group (Fig. 1). On this context, ANOSIM statistics revealed statistically important variations between the fecal microbiota composition of infants belonging to the 1-6 M and 6-12 M teams with respect to the already weaned group (p-value <0.01 in each circumstances), emphasizing the pivotal function performed by the transition to an solely strong weight loss program on influencing the taxonomic composition of the toddler intestine microbiota. As well as, beta-diversity evaluation revealed a extremely variable bacterial composition throughout the 1-6 M group, whereas the intestinal neighborhood throughout the 6-12 M and 12-36 M appeared to steadily stabilize (Fig. 1), an statement that correlates with the already demonstrated excessive instability and inter-individual variability of intestine microbiota in the course of the very early levels of life29,30. Extra particulars may be discovered within the Supplementary Textual content.
Panel a exhibits the field and whisker plot of the calculated species-richness primarily based on the variety of bacterial species noticed within the three age group. The x-axis stories the three thought of age teams, whereas the y-axis exhibits the variety of bacterial species. Packing containers are decided by the 25th and 75th percentiles. The whiskers are decided by the utmost and minimal values and correspond to the field excessive values. Traces contained in the containers signify the common, whereas crosses correspond to the median. Panel b shows each the two- and three-dimensional Bray-Curtis dissimilarity index-based PCoA of the 1669 chosen toddler fecal samples subdivided by age teams. Panel c stories the common relative abundance and prevalence of bacterial species similar to the core and accent intestine microbiota of every age group.
Moreover, taxonomic profiles similar to the 1669 chosen shotgun metagenomic samples had been scrutinized to determine probably the most consultant bacterial species of the 1-6 M, 6-12 M and 12-36 M age teams, permitting the reconstruction of dominant bacterial species of the toddler intestine microbiota, i.e., the “core” toddler intestine microbiota31. Particularly, this “core” neighborhood was outlined by deciding on these bacterial species occurring with a prevalence of >40% among the many assessed samples of a particular age group, whereas bacterial taxa displaying a prevalence starting from 20% to 40% had been used to determine toddler intestine accent bacterial taxa. These cut-off values had been adjusted from these steered in earlier literature primarily based on genus-level information to acquire extra permissive prevalence ranges, contemplating the excessive variability of the toddler intestine microbiota, the big selection of geographical areas from which the thought of samples derived, and the upper decision supplied by species-level accuracy17,32,33,34,35. Based mostly on these parameters, the “core” intestine microbiota of the 1-6 M group was discovered to include solely 4 totally different species, i.e., Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium longum, and Escherichia coli. The identical taxa, aside from Bifidobacterium bifidum, had been additionally noticed to be a part of the “core” intestine microbiota of the 6-12 M group along with different two further species, i.e., Blautia wexlerae and Ruminococcus gnavus. Conversely, the core intestinal neighborhood of the already weaned infants (12-36 M group) was characterised by the next microbial complexity, typical of an adult-like intestine microbiota (Fig. 1)9,18, together with Anaerostipes hadrus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides uniformis, Bifidobacterium longum, Blautia wexlerae, Eubacterium rectale, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, coupled with two different species previously belonging to the genus Bacteroides, however lately reclassified as members of the genus Phocaeicola, i.e. Phocaeicola dorei and Phocaeicola vulgatus (Fig. 1)36. Moreover, this evaluation revealed that the rising variety of “core” species throughout the 12-36 M age group corresponds to a progressive increment within the variety of species forming the so-called toddler accent intestine microbiota. Certainly, whereas solely seven taxonomically annotated species had been included within the accent microbiota of the 1-6 M group, 15 and 20 bacterial species represented the accent intestine microbial neighborhood of the 6-12 M and 12-36 M teams, respectively (Fig. 1). This reinforces the notion that weaning alerts the diversification of the toddler intestine microbiota in the direction of an adult-like intestine microbiota with a gradual growth of the species quantity.
The “core” microbiota assessed per every age group allowed the identification of probably the most prevalent species throughout all samples belonging to a single age group no matter weight loss program or geographical origin. On this context, to make the evaluation extra correct, since weight loss program and geographical origin have been indicated as two major elements deeply concerned in influencing intestine microbiota composition, the “core” microbiota for every age group was additionally assessed introducing the geographical areas of infants to which fecal samples belong as variable (Supplementary Desk 4). Extra info is mentioned intimately within the supplementary textual content.
Identification of species-level Toddler Intestine Neighborhood State Sorts (sIGCSTs)
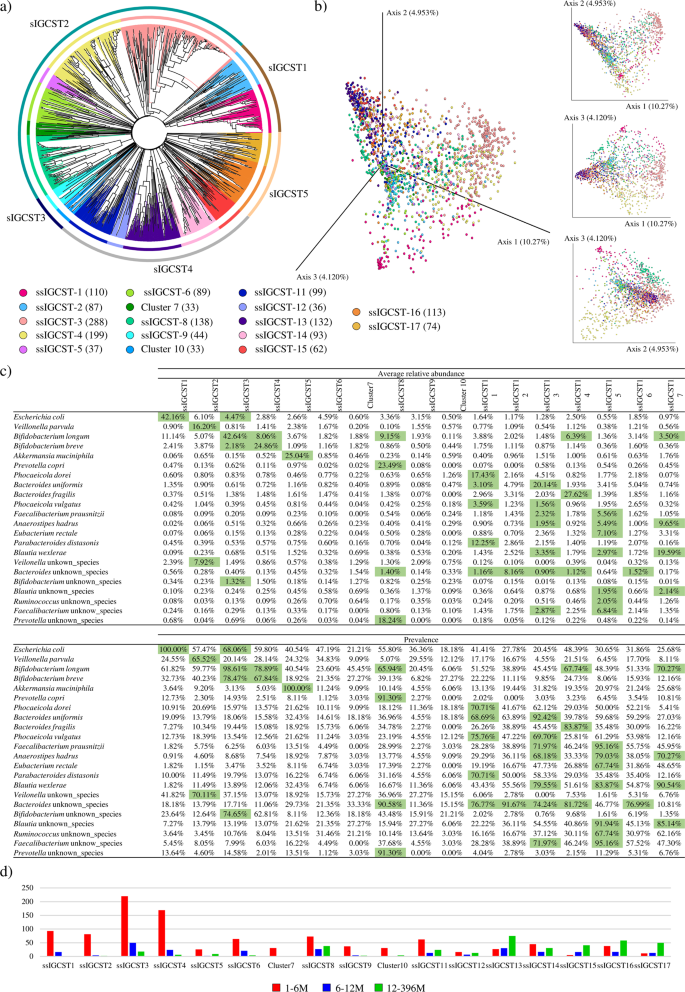
Though the reconstruction of a “core” toddler intestine microbiota permits the identification of probably the most prevalent bacterial species throughout a pattern cohort, it doesn’t determine doable distinct motifs within the general neighborhood composition profile, thereby ignoring the presence of extremely plentiful and consultant bacterial species in a subset of samples37,38,39,40. Due to this fact, to be able to present stratification of the chosen samples into compositional patterns, the 1669 shotgun-based microbial profiles had been subjected to 2 unsupervised analyses, i.e., Prediction Energy and Silhouette Width41, permitting the prediction of the minimal variety of clusters essential to divide samples into distinct neighborhood state varieties. Particularly, the unsupervised Prediction Energy evaluation and the Silhouette-based methodology recognized an optimum variety of 4 and 5 clusters, respectively (Supplementary Determine 1). Based mostly on these information, pre-setting the variety of clusters to be recognized to 5, a Hierarchical CLustering evaluation (HCL) primarily based on taxonomic profiles at species stage of every enrolled pattern was carried out, permitting the division of samples into 5 totally different teams, right here referred as species-level Toddler Intestine Neighborhood State Sorts (sIGCSTs) (Fig. 2). In depth insights into the recognized sIGCSTs revealed that 4 clusters are dominated by a single bacterial species with a excessive prevalence (>65%), i.e., E. coli (sIGCST1), B. longum (sIGCST2), B. uniformis (sIGCST4), and B. wexlerae (sIGCST5), whereas sIGCST3 didn’t present any dominant bacterial taxon (Supplementary Desk 5). On this context, though the sIGCSTs prevalent species corresponded to a few of the bacterial taxa above-defined as “core” intestine microbiota-characterizing species, a lot of the latter did not be represented by the recognized sIGCSTs. Due to this fact, a supervised cluster evaluation primarily based on a Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrix-related Hierarchical Clustering (Supplementary Desk 6) and supported by 3D Bray-Curtis PCoA (Fig. 2) was carried out to implement and biologically confirm the outcomes of the unsupervised approaches, as beforehand described42, and to determine putative sub-sIGCSTs (ssIGCSTs) representing a steady spectrum of variability throughout the 5 main sIGCSTs. Intimately, to be thought of as a putative ssIGST, every cluster needed to embrace no less than 20 samples (roughly 1% of whole samples), whereas the ssIGCST consultant bacterial species needed to possess a prevalence greater than 65%. Curiously, this evaluation allowed the subdivision of the 5 sIGCSTs into 17 putative sub-clusters with sIGCST1, sIGCST3, and sIGCST5 break up into two sub-clusters every, whereas sIGCST2 and sIGCST4 had been divided into six and 5 sub-clusters, respectively (Fig. 2). Nevertheless, the descriptive evaluation primarily based on two-way frequency tables revealed that greater than 90% of clusters 7 and 10 had been from a single geographic origin/dataset (Supplementary Desk 7), thus these clusters weren’t thought of as actual ssIGCSTs. Additional details about the outcomes obtained for cluster validation primarily based on two-way frequency tables has been reported in Supplementary textual content. In accordance with these parameters, solely 13 out of the 17 recognized sub-clusters had been proven to be successfully dominated by a minimal of 1 to a most of six predominant bacterial species (Fig. 2). Curiously, a lot of the latter correspond to the abovementioned “core” toddler intestine microbiota-characterizing taxa, thus confirming the evolutionary adaptation of those species to the toddler gut. Nevertheless, the HCL evaluation additionally allowed the identification of an extra annotated species, beforehand not labeled as “core” taxa, i.e., Prevotella copri, as consultant of particular sub-cluster (Fig. 2), suggesting its ecological relevance within the meeting and growth of the toddler intestine microbiota.
Panel a stories a round cladogram generated by a hierarchical clustering (HCL) evaluation primarily based on chosen publicly out there shotgun metagenomes associated to fecal samples of wholesome infants aged from just a few days to a few years. The outer circle across the cladogram divides samples in response to the recognized sIGCSTs, whereas the interior circles present a subdivision of fecal samples primarily based on the outlined sub-sIGCSTs. Panel b exhibits the three- and two-dimensional Principal Coordinate Evaluation (PCoA) primarily based on the identical samples used for the HCL by coloring samples in response to the ssIGCST they belong to. Shade legend for panel a and b stories the cluster identify and the variety of toddler fecal samples per every recognized ssIGCST. Panel c shows the common abundance and prevalence of micro organism specifying every recognized ssIGCSTs. Panel d depicts the distribution of samples for every ssIGCST divided by age teams.
In depth insights into the assessed ssIGCSTs revealed that 4 sub-clusters had been primarily represented by fecal samples of the 1-6 M, permitting the identification of E. coli, V. parvula, B. longum, and B. breve because the principal bacterial species that characterize the intestine microbiota of pre-weaning infants (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Desk 8). Conversely, ssIGCST13 and ssIGCST17 had been preponderant amongst fecal samples belonging to the 12-36 M toddler group, suggesting that A. hadrus, B. uniformis, F. prausnitzii, P. vulgatus, and B. wexlerae are 5 dominant species of an toddler intestinal neighborhood growing into an adult-like intestine microbiota (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Desk 8). On the identical time, nearly all of the remaining 12-36 M samples had been included in both of 4 clusters, all dominated by members of the phylum Bacteroidota, i.e., sIGCST8, 11, 14, and 16, in addition to in two clusters characterised by the next bacterial complexity with numerous dominant taxa, i.e., ssIGCST16 and 17. These findings underscore that, when growing and maturing into an adult-like intestine microbiota, the toddler intestine neighborhood undergoes a transition with a lower within the relative abundance of species belonging to bacterial genera typical of the pre-weaning section (i.e. Bifidobacterium and Escherichia) with a parallel improve in taxa belonging to bacterial genera typical of an grownup intestine neighborhood (Bacteroides/Phocaeicola and Prevotella)40,43. Moreover, these observations additionally spotlight that the toddler intestine microbiota experiences a rise in bacterial biodiversity with, in sure circumstances, a concomitant lower within the abundance of dominant species (Fig. 2).
Toddler fecal pattern development performances in numerous tradition media and prediction of macronutrient necessities for ssIGCST communities
In vitro cultivation fashions have been developed as cost- and time-efficient, but highly effective instruments to review the results of intrinsic and extrinsic elements on each composition and performance of the human intestine microbiota19,44. Notably, whereas in vitro batch cultures don’t contain human or animal hosts, thus stopping moral issues associated to in vivo research, they nonetheless require cautious consideration of tradition medium formulation to satisfy the dietary wants of intestinal microorganisms and protect/keep the microbial gamers19,21,45. Nevertheless, though at present used bacterial development media for in vitro cultivation of the human intestine microbial neighborhood are usually composed of complicated and chemically undefined parts, they differ in formulation and part concentrations21,46,47,48,49.
On this context, to be able to determine which parts are needed to acquire a profitable in vitro cultivation of the toddler intestine microbiota, 5 fecal samples of infants aged between 4 and 29 months and comprising the recognized ssIGCST-dominant species, had been grown for twenty-four h in duplicate on 18 totally different commercially out there tradition media usually used for human intestine microbiota cultivation, following the MiPro mannequin (Supplementary Desk 9 and Supplementary Desk 10)21. Taxonomic composition of every organic replicate at 24 h, coupled with two replicates obtained at 0 h (instantly after inoculation), was assessed by a shallow shotgun metagenomics strategy. DNA sequencing generated a complete of 15,198,683 reads with a median of 79,993 reads per pattern, decreased to 9,982,665 whole reads with a median of 52,540 reads per pattern after high quality filtering (Supplementary Desk 11). Moreover, to acquire a complete organic interpretation of the analyzed tradition microbiome complexity, a quantitative microbiome profiling assay was carried out by the use of stream cytometry to enumerate microbial cells of every organic replicate and tradition situation, as beforehand described50. The obtained cell counts had been subsequently employed to normalize shallow shotgun sequencing information and rework relative metagenomic information into absolute abundances.
Notably, bacterial cell variety of the 24 h cultures exceeded the common of the inoculum cell quantity from 1.23- to 42.65-fold, confirming that every one examined tradition media help the expansion of the toddler intestine microbial neighborhood (Supplementary Determine 2). Nevertheless, excessive variability in dominant- in addition to accessory-ssIGCST species development performances was noticed relying on tradition medium (Supplementary Determine 2), suggesting that the success of culturing the toddler intestine microbial neighborhood is severely affected by the actual development medium formulation used. So as to consider if and the way a particular medium part impacts on the expansion of ssIGCST-specifying bacterial species, a Pearson correlation index-based co-variance evaluation was carried out (Supplementary Desk 12). Particularly, bacterial taxa typical of the 1-6 M group intestinal microbiota along with sure bacterial species characterizing the opposite two age teams positively correlated with no less than one complicated plant-derived glycan, resembling inulin, pectin, arabinogalactan, maltodextrin, guar gum or xylan (Supplementary Desk 12). Notably, members of the genus Bifidobacterium are expert degraders of a variety of plant-derived carbohydrates because of the presence, of their genetic arsenal, of a number of genes devoted to this exercise51,52,53, whereas in addition they take part in intra- and inter-genus cross-feeding behaviour25,54,55,56. Equally, members of the genera Anaerostipes, Faecalibacterium, Prevotella and Ruminococcus are recognized for his or her capacity to make the most of totally different complicated sugars as vitality supply57,58,59,60. Moreover, the presence of a host-derived complicated glycan, i.e., mucin, considerably sustained development of Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium longum and R. gnavus, three bacterial taxa possessing, of their genetic repertoire, genes concerned within the degradation of this host-related carbohydrate (Supplementary Desk 12)52,61,62,63,64,65,66. Furthermore, contemplating easy carbon sources, Blautia wexlerae, B. bifidum, B. longum and E. coli positively correlated with lactose, whereas Bacteroides fragilis and V. parvula with glucose. Conversely, xylo-oligosaccharides, cellobiose and maltose don’t considerably help development of any of the ssIGCST-identifying species (Supplementary Desk 12).
Along with chemically outlined carbon sources, development media usually used for the in vitro cultivation of intestine microbiota include quite a few chemically undefined substances performing as suppliers of a number of natural and inorganic vitamins. Particularly, tryptone, casein, peptone and yeast extract had been proven to elicit constructive correlations with numerous dominant bacterial species of the toddler microbial intestine neighborhood, suggesting that these undefined parts are needed to make sure the survival and proliferation of the toddler intestine bacterial gamers (Supplementary Desk 12). Moreover, Bacteroides fragilis and V. parvula (and normally all of the species belonging to the genus Veillonella) exhibited statistically important constructive correlations solely with the varied undefined parts of medium 9 (GAM broth) (Supplementary Desk 10 and Supplementary Desk 12), as beforehand described for V. parvula, a bacterial species that, regardless of the presence of complicated plant-derived carbohydrates within the tradition medium, appears to require solely undefined substances for its development and proliferation67.
Remarkably, screening of the accent micro organism constituting the expected ssIGCST confirmed the relevance of the vary of macronutrients required for the expansion of dominant taxa (Supplementary Desk 12). Altogether, these information allowed the identification of 16 macronutrients, which had been used to formulate an optimized development medium for the in vitro cultivation of toddler intestine microbial communities, right here known as Toddler Intestine Tremendous Medium (IGSM).
Prediction of micronutrient necessities to maintain the expansion of ssIGCST communities
Past macronutrients, bacterial development requires micronutrients, usually represented by natural and inorganic salts in addition to nutritional vitamins. Particularly, two inorganic salts broadly exploited in tradition medium formulation, i.e., sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl), confirmed a constructive correlation with most of ssIGCST-dominant species (Supplementary Desk 12), in all probability attributable to their involvement in tradition medium osmolarity upkeep68,69. Moreover, traces of different mineral salts appeared to maintain the expansion of assorted bacterial species typical of the toddler intestine microbiota, together with each dominant and non-dominant taxa (Supplementary Desk 12), suggesting that a number of bacterial intestine colonizers want the provision of various metals for his or her proliferation. Equally, a lot of the ssIGCST-dominant bacterial species positively correlated with vitamin supplementation (Supplementary Desk 12), thus highlighting the related function performed by these hint components in sustaining toddler intestine microbiota metabolism70.
Along with mineral salts and nutritional vitamins, different development elements could also be important to spice up proliferation of sure toddler intestine microbiota-associated micro organism. On this context, the presence of L-cysteine considerably correlated with a spread of micro organism, together with Bifidobacterium spp. and Ruminococcus gnavus. Conversely, as anticipated for his or her capacity to inhibit the expansion of a large spectrum of micro organism, solely few constructive correlation traits had been noticed between commercialized bile salt combination and toddler intestine microbiota accent species, whereas ssIGCST-dominant taxa negatively correlated with these compounds (Supplementary Desk 12)70. Nevertheless, an in-depth analysis of those compounds revealed that the substitute of commercialized bile salt combination with two outlined main human main bile acids, i.e., sodium cholate and sodium chenodeoxycholate, resulted in considerably constructive correlations additionally with dominant taxa, thus corroborating a earlier discovering in response to which this substitute was efficient in sustaining the in vitro microbiome composition21.
Screening for micronutrients pivotal for the in vitro cultivation of ssIGCST resulted within the identification of 27 compounds which had been employed, along with the above-defined macronutrients, to develop the IGS medium.
Validation of the optimized tradition medium IGSM for the in vitro cultivation of the toddler intestine microbiota
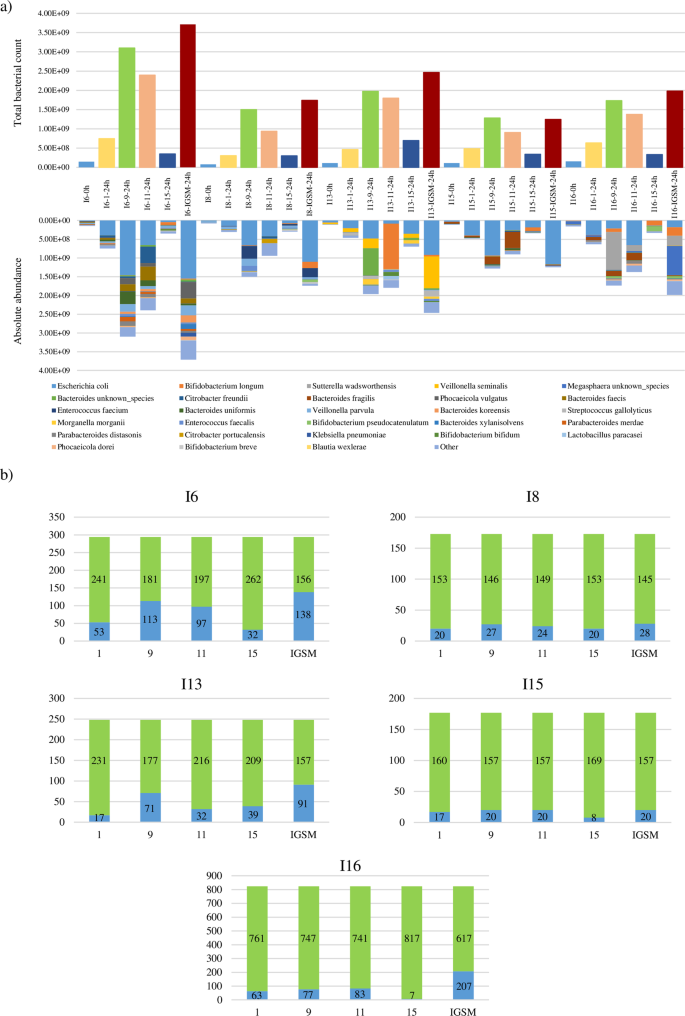
To guage the effectiveness of the IGSM, 5 fecal samples belonging to infants aged from one to 6 months and possessing the 1-6 M group ssIGCST-characterizing bacterial species had been cultured for twenty-four h in duplicate in IGSM in addition to in media 1, 9, 11 and 15 that, from the above-mentioned evaluation, had been proven to permit development of the best variety of species current within the inoculum (Supplementary Desk 10 and Supplementary Determine 2). After cultivation, development performances of every toddler fecal pattern had been assessed by stream cytometry-based bacterial cell enumeration. Curiously, though a rise in bacterial cell quantity was recorded for all fecal samples per every examined tradition medium, stream cytometry readouts associated to 24 h cultivations exceeded by no less than 10 instances (when in comparison with the cell counts of the inoculum) for less than three development media, i.e., medium 9, 11 and IGSM (Fig. 3), aside from I15 and I16 fecal samples whose development in medium 11 resulted in an 8-fold improve. Moreover, in depth perception into the latter three development media revealed that the best cell numbers had been achieved for IGSM, with a rise starting from 11.1- to 25.3-fold, in opposition to the utmost improve of 21.1- and 16.3-fold obtained in medium 9 and 11, respectively (Fig. 3). This means that the optimized development medium formulation helps development of the toddler intestine microbiota when it comes to whole bacterial rely. Nevertheless, such enhanced development capability of the toddler intestine microbial ecosystem by IGSM isn’t the one prerequisite for effectiveness of this new formulation. To attain this objective, it’s, certainly, additionally needed that IGSM isn’t solely in a position to maintain development of the predominant species of the toddler intestine microbiota, however it also needs to guarantee development of many, if not all, of the accent species. To evaluate this, every 24 h replicate and 0 h baseline samples had been subjected to shallow shotgun sequencing leading to a complete of two,224,237 reads, decreased to 1,657,573 reads with a median of 27,626 reads per pattern after high quality filtering (Supplementary Desk 13). Moreover, following taxonomic reconstruction, every obtained taxonomic profile was transformed from relative to absolute abundance exploiting stream cytometry-based bacterial counts. Subsequently, to be able to consider which of the 5 examined tradition media was in a position to help development of the best variety of species, solely bacterial taxa displaying an elevated rely within the 24 h samples that’s greater than 10 instances that of the inoculum, had been thought of. This cut-off was set to incorporate solely these bacterial species within the evaluation which have undergone considerable development in the course of the 24 h of cultivation and, on the identical time, eliminating all these bacterial taxa whose presence within the 24 h samples could also be attributable to the DNA of the inoculum. Curiously, for every thought of toddler fecal pattern, the best variety of species displaying a 10-fold rely improve with respect to the inoculum was achieved in IGSM (Fig. 3). This discovering helps the notion that the optimized IGSM in vitro higher maintains toddler intestine microbiota biodiversity when in comparison with different examined development media. Altogether, these information point out the effectiveness and robustness of this newly formulated development medium in supporting development and upkeep of most related bacterial gamers of the toddler intestine microbiota.
Panel a depicts the stream cytometry-based bacterial counts and absolute abundance-based taxonomic profiles obtained by cultivating 5 toddler fecal samples in 4 totally different tradition media in addition to in IGSM. Panel b stories the variety of bacterial species displaying a 10-fold improve in bacterial enumeration greater (gentle blue) or decrease (inexperienced) than the inoculum bacterial rely. All information are expressed as common of the 2 obtained replicates per every situation.
Analysis of the results of medicine on the toddler intestine microbiota underneath in vitro settings
To guage the affect of sure medication on the toddler intestine bacterial neighborhood, a 24 h in vitro cultivation of feces collected from the 5 infants whose stool had been used for the IGSM validation, was carried out in IGSM within the presence of two pharmacological compounds usually exploited in pediatrics, i.e., acetaminophen and simethicone. Feces had been freshly recollected three weeks after the primary assortment and checked for the presence of the ssIGCST-characterizing species by shallow shotgun sequencing. Particularly, whereas acetaminophen is an analgesic/antipyretic drug broadly used to deal with fever in infants, simethicone, a combination of dimethicone and SiO2, is an inert antifoaming generally used as a remedy to scale back bloating and belly discomfort related to childish colic71,72,73,74. Moreover, the microbiota of every toddler fecal pattern was cultivated in IGSM with out the addition of any drug to acquire the management pattern. Samples had been subjected to stream cytometry bacterial enumeration in addition to to shallow shotgun sequencing producing a complete of 772,908 reads (with a median of 51,527 reads per pattern) which following chimera and high quality filtering was decreased to a complete of 637,447 reads and a median of 42,496 reads per pattern (Supplementary Desk 14). Particularly, stream cytometry readouts revealed no considerable variations in whole bacterial cell hundreds between the management and drug-treated samples (Supplementary Determine 3). On the identical time, in depth perception into absolute abundance-based taxonomic profiles demonstrated that remedy with the abovementioned medication didn’t induce any important modification within the abundance of bacterial species above-identified as toddler intestine microbiota predominant taxa, aside from E. coli whose abundance was proven to extend practically ten instances in I16 pattern handled with simethicone (Supplementary Determine 3). Moreover, though the abundance of sure accent bacterial species underwent alterations when toddler fecal samples are handled with medication, no widespread traits had been noticed throughout the analyzed 5 fecal samples. These findings recommend that neither acetaminophen nor simethicone inhibit development of the general toddler intestine microbiota, and that neither drug appears, normally, to have an effect on the taxonomic composition and abundance of toddler intestine microbial gamers. Nevertheless, these analyses don’t reveal if drug remedy did affect on toddler intestine microbiota metabolic capabilities. Due to this fact, a metabolomic evaluation might make the evaluation extra complete to be able to absolutely perceive the doable results of medicine on the intestinal microbial neighborhood.