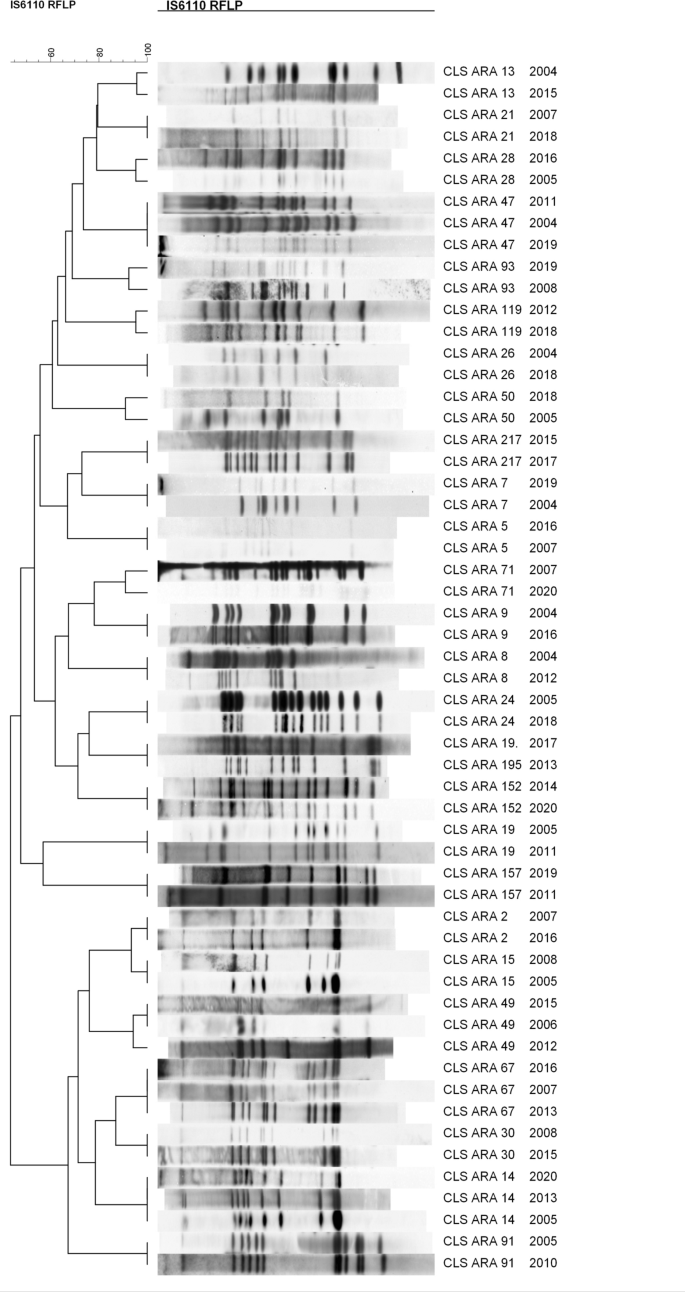
With the goal of characterising on the molecular stage the accountable strains of the most important outbreaks in our neighborhood, comprising 665 out of the 2553 circumstances registered, we sequenced the genomes of the consultant IS6110-clustered strains. The dendrogram primarily based on their IS6110-RFLP patterns is proven in Fig. 1, and the MIRU-VNTR patterns and spoligotypes are detailed in Desk S1.
Common views
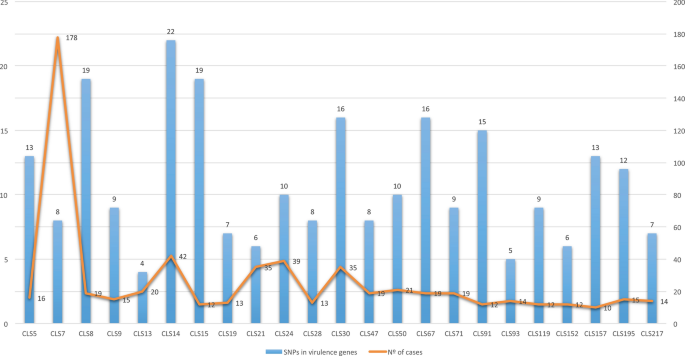
The 26 IS6110-outbreaks studied ranged from 10 to 178 circumstances since 2004. Seven outbreaks have been brought on by L4.8 strains producing 291 circumstances. These embrace CLS_77, the most important outbreak we ever had, with 242 circumstances from 1993 to 2020 (no knowledge for 1996–2000). Eight outbreaks have been brought on by L4.1.2/Haarlem strains producing 170 circumstances. Six outbreaks have been produced by L4.3/LAM strains (two by a L4.3.2 pressure, three by a L4.3.3 pressure and one by a L4.3.4 pressure), producing 121 circumstances. These included CLS_217, which was independently studied8. The remainder of the outbreaks have been brought on by strains from totally different lineages: one by a L4.1.1.3/X pressure, with 21 circumstances9; one by a L4.7 pressure, with 19 circumstances; one by a L4.4.1.1 pressure, with 16 circumstances; one by a L4.9 pressure, producing 13 circumstances; and one by a L4.6.1.1 pressure, with 14 circumstances.
SNP distances
It has been proposed {that a} distance of ≤ 5 SNPs between two isolates is taken into account current contact and that 12 SNPs ought to be the utmost distance to think about each isolates to be the identical pressure and subsequently the identical outbreak10. Eighteen out of the 26 IS6110-clusters studied match this threshold, indicating that the sequenced isolates belong to the identical WGS-outbreak. We discovered a distance of 1–10 SNPs among the many two or three isolates sequenced for 18 of the IS6110-clusters studied (Desk 1). In Desk S2, an outline of the SNPs present in these clusters (level, gene, sort of mutation, impact of the mutation) could be discovered. For CLS_15, lineage identification revealed that one chosen isolate belonged to L4.1.2.1 and the opposite to L4.8. A brand new revision of the genotype patterns confirmed that the right one was L4.1.2.1, so the L4.8 isolate was a variety error. The SNP distance couldn’t be studied for this IS6110-cluster. For 3 clusters, the SNP distance was massive sufficient to ensure that the chosen isolates weren’t the identical pressure. CLS_2 had an SNP distance of 145, CLS_49 of 143 among the many three sequenced isolates, and CLS_26 of 93. However, 4 clusters had a distance greater than 12 SNPs however shut. CLS 157 had a distance of 34 SNPs between the 2 sequenced isolates. CLS_47 had an SNP distance of 35 among the many three sequenced isolates; nonetheless, nearly all of SNPs have been as a consequence of one of many isolates, with the opposite two being extra associated (lower than 12 SNPs). Lastly, CLS_119 had an SNP distance of 18 and CLS_9 of 14 (Tables 1, Desk S2).
Areas of Distinction (RDs) research
We regarded for giant deletions (Areas of Distinction or RDs)11 to seek out variations between the clustered strains and non-clustered strains beforehand analysed in our laboratory of the identical lineage. In line with Coll et al.12, RD182 is restricted to L4.1.2.1, RD219 is restricted to L4.8, RD115 is restricted to L4.3.3 and RD724 is restricted to L4.6.1.1. All clustered and non-clustered strains have been concordant with these particular traits. No totally different RD was discovered among the many clustered and non-clustered strains, with nearly all of them being lineage conserved. As well as, the RDs of the isolates belonging to the identical IS6110-outbreak have been the identical even in these with a excessive SNP distance. We solely discovered one totally different massive deletion, not beforehand described as an RD, between the isolates of CLS_119: one of many isolates had Rv3054c-Rv3055-dinP-Rv3057 genes deleted, whereas the opposite conserved this area because the reference pressure. The RDs of the totally different strains are proven in Desk 2.
IS6110 areas
WGS allowed us to find all of the IS6110 copies within the genomes of the clustered strains. The very best variety of copies was discovered among the many strains belonging to L4.3 (common variety of IS6110 copies = 16.3), adopted by the L4.8 strains (12.6) and the L4.1.2.1 strains (11.4). The outline with the precise areas in all of the isolates studied is in Desk S3. For the L4.3 strains, three copies have been current in all of the strains studied—lpqQ:Rv0836c, Rv1754c (RD152 space), and Rv3113. Furthermore, copies positioned at cut1, ppe38 and MT3426:MT3427 have been frequent. For L4.1.2.1, 5 copies positioned at Rv0403c, Rv2336, Rv1754c, Rv0963c and MT3429 have been current in all of the strains studied. We noticed the identical areas for different sequenced non-clustered strains of the identical lineages (L4.3 and L4.1.2.1). For the L4.8 strains, copies inside MT3429, Rv1668:Rv1669c and Rv1762c:Rv1763c (RD152 space) have been current in all of the strains studied, whereas copies positioned at ppe71 and Rv0795-Rv0796 have been frequent. A abstract with the widespread and frequent IS6110 copies within the totally different lineages is proven in Desk 3.
We noticed some IS6110 actions among the many clustered isolates studied. In 5 of them, further copies have been detected within the later isolate. In CLS_21, the isolate from 2018 had an additional IS within the DR area that was not current within the isolate from 2007. In CLS_13, the isolate from 2015 had two further IS copies positioned in ppe28:ppe29 and Rv0756c that have been absent within the 2004 isolate. In CLS_93, the isolate from 2019 had an additional IS copy positioned in Rv3177, absent within the isolate from 2008. In CLS_71, the isolate from 2020 had two further IS copies positioned in Rv1371 and phoT that weren’t current within the isolate from 2007. Lastly, in CLS_152, the isolate from 2020 had an additional IS6110 in Rv1730c:gabD2 that was absent within the 2014 isolate. However, in 4 circumstances, an additional IS6110 was detected within the earlier isolate. The CLS_2 isolate of 2007 had an additional IS6110 positioned in Rv3183:Rv3184 that was not within the later isolate of 2016. In CLS_24, the isolate from 2005 had an additional IS6110 positioned at MT3426 that was absent within the 2018 isolate. In CLS 50, the isolate from 2005 had an additional IS copy positioned in MT3427. Lastly, in CLS_91, the isolate from 2005 had an IS6110 positioned on the plcA gene that was absent within the isolate from 2010. CLS_49 was a particular case: the isolate from 2012 had an additional IS inserted inside the Rv1765c gene (or its homologous Rv2015c) that was not current within the different two isolates studied, and the isolate from 2015 had an additional IS positioned at ppe49 that was absent within the different two isolates of this cluster. That is in accordance with the big variety of SNPs noticed amongst these isolates (143 SNPs). The identical could possibly be utilized to CLS_2, with an SNP distance of 145. However, we discovered similar variety of IS6110 copies and areas for the isolates that apparently have been of the identical RFLP cluster however, in accordance with the SNP distance, wouldn’t be. This occurred for CLS_9, CLS_26, CLS_47, CLS_119 and CLS_157, though the SNP distance for CLS_9 and CLS_119 was very near 12 (14 and 18 SNPs, respectively). The IS6110 actions are proven in Desk S3.
Among the deletions noticed could possibly be defined by a homologous recombination between two shut IS6110 ensuing within the lack of the intermediate genes as one IS6110 was discovered interrupting the genes concerned. This was noticed for CLS_30 isolates, exhibiting the lack of Rv2817c:Rv2819c genes; CLS_157 and the deletion of plcC-plcB-plcA genes; CLS_13 and the deletion between plcC and ppe40; CLS_5, CLS_7, CLS_28, CLS_47 and CLS_119, and the deletion between cut1 and Rv1765c; CLS_93 and the deletion between ppe38 and ppe71; CLS_8 and CLS_217, and the deletion of plcD gene; CLS_26 and the deletion between plcD and Rv1765c; CLS_9 and the Rv2810c:Rv2813 deletion; and CLS_152 and the deletion of Rv2018 and Rv2019.
SNPs in virulence components
All of the L4.1.2.1 strains, together with the non-clustered strains reviewed, had 14 widespread SNPs in genes thought of as virulence components (mce2D, ctpV, Rv1290c, Rv1505c, pks5, mgtC, secA2, Rv1915, Rv1915, Rv1982c, pks12, Rv2494, cyp125 and esxB)13. The L4.3 strains had 4 widespread SNPs (mce1D, Rv0990c, mce3F and fadE28). As well as, there have been 4 extra widespread SNPs for the L4.3.2 strains (Rv0204c, Rv1939, Rv3085 and Rv3871) and three for the L4.3.3 strains (mmaA4, pks12 and Rv3088). The L4.8 strains shared just one widespread SNP in a gene thought of as a virulence issue (ptpA). Trying into the isolates studied in the remainder of the sub-lineages, the typical SNP quantity was eight, all being distinctive SNPs. Nonetheless, there was no relation between the variety of SNPs within the genes thought of as virulence components and the variety of circumstances of the IS6110-cluster (p-value = 0.8) (Fig. 2).
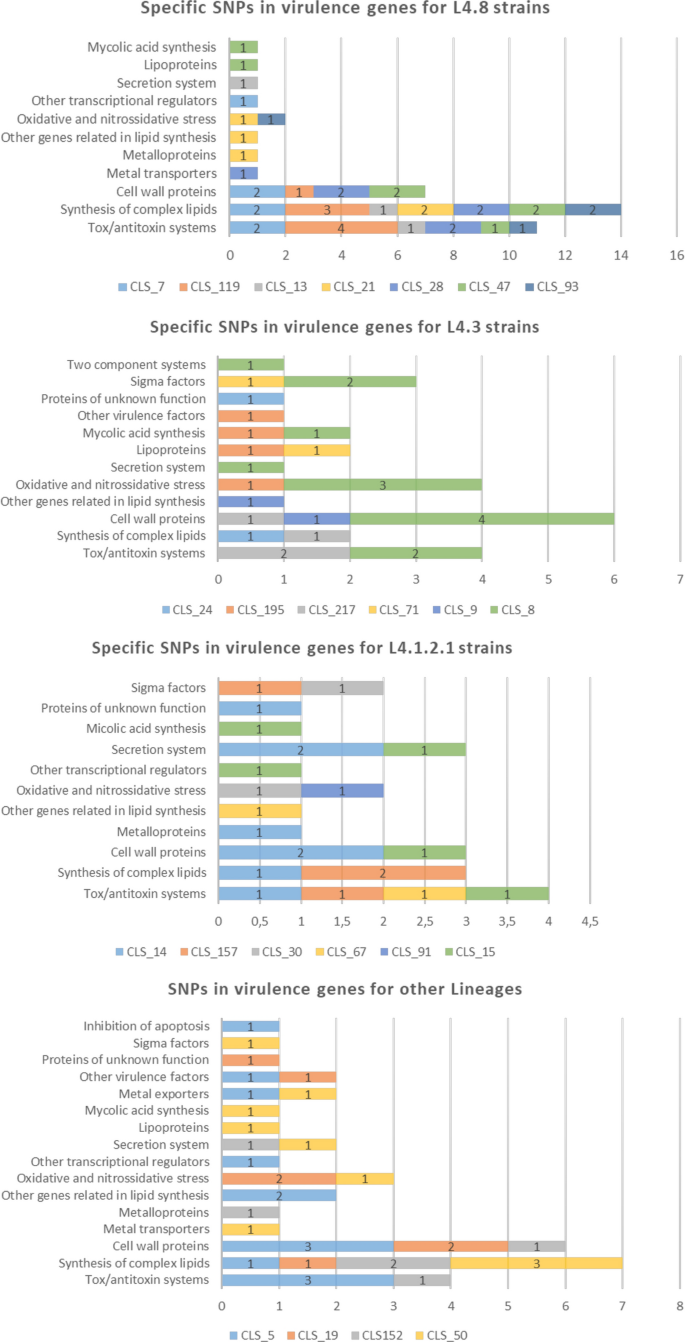
As these widespread sub-lineage SNPs have been current within the clustered strains in addition to non-clustered strains, we additionally determined to deal with the particular SNPs of every WGS-cluster pressure. The L4.1.2.1 strains turned out to have much less particular SNPs (a mean of three.6), adopted by the L4.3 (4.7) and L4.8 (5.9) strains. Graphics with the SNPs labeled in accordance with the gene classes that Forrellad et al. and Ramage et al.13,14 described are proven in Fig. 3. The L4.8 strains had extra SNPs within the cell wall proteins (often mce genes), synthesis of the complicated lipids and toxin/antitoxin programs classes. For the L4.3 strains, the cell wall proteins class stands out above the remainder. For the L4.1.2.1 strains, the secretion programs, cell wall proteins and toxin/antitoxin programs classes have extra SNPs. An in depth checklist of the particular SNPs and descriptions of the genes could be present in Desk S4. Relating to the WGS-clusters from different lineages, the synthesis of complicated lipids, cell wall proteins and toxin/antitoxin programs classes had extra SNPs.
Particular SNPs in virulence genes for every WGS-cluster labeled by lineage in accordance with the classes of Forrellad et al. and Ramage et al.13,14. The variety of classes stays fixed among the many three major lineages studied (L4.8, L4.3 and L4.1.2.1). The oxidative and nitrossidative stress, different genes associated to lipid synthesis, cell wall proteins, synthesis of complicated lipids and toxin/antitoxin programs classes are current within the three lineages. For clusters belonging to the L4.4.1.1, L4.9, L4.6.1.1 and L4.1.1.3/X households, there have been no widespread and particular SNPs as just one cluster of every lineage had been sequenced, so comparability was not attainable. The classes with extra SNPs for these lineages have been cell wall proteins, the synthesis of complicated lipids and toxin/antitoxin programs. Clusters with greater than 90 SNPs weren’t thought of.