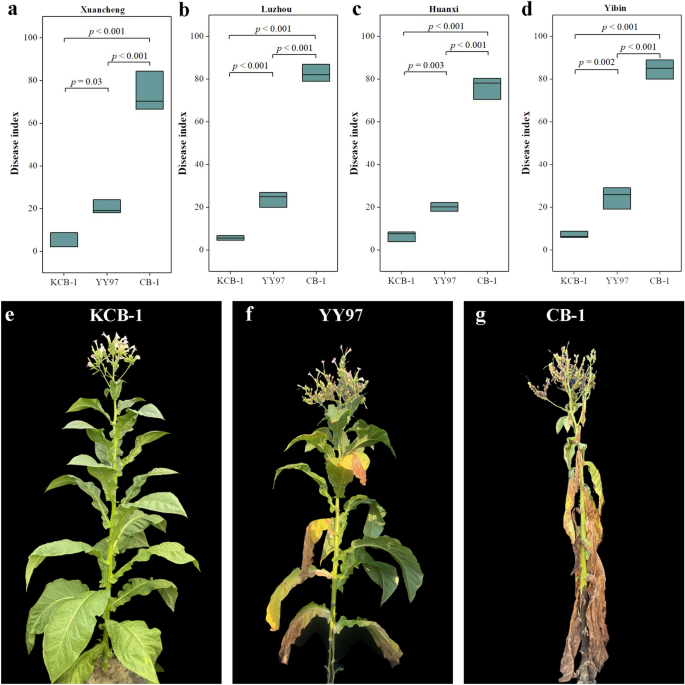
Excessive resistance of KCB-1 to bacterial wilt
We carried out DI statistical evaluation within the area for CB-1, KCB-1 and YY97, which have been planted three rows with 20 crops in every row. The outcomes confirmed that the DI of YY97 was considerably smaller than that of CB-1 (p < 0.001) (Fig. 2a–d). the DI of KCB-1 was considerably smaller than that of YY97 and CB-1 (p = 0.03, p < 0.001) (Fig. 2a–d). Consultant photographs of KCB-1, YY97 and CB-1 from the identical interval are proven in Fig. 2e–g. The statistical outcomes indicated that KCB-1 is a extremely resistant tobacco to bacterial wilt.
Illness index statistics for KCB-1, CB-1 and YY97. (a) Illness index statistics for KCB-1, CB-1 and YY97 in Xuancheng. (b) Illness index statistics for KCB-1, CB-1 and YY97 in Luzhou. (c) Illness index statistics for KCB-1, CB-1 and YY97 in Huanxi. (d) Illness index statistics for KCB-1, CB-1 and YY97 in Yibin. (e–g) Consultant photographs of the KCB-1, YY97 and CB-1 from the identical interval. Information have been analyzed utilizing one-way ANOVA.
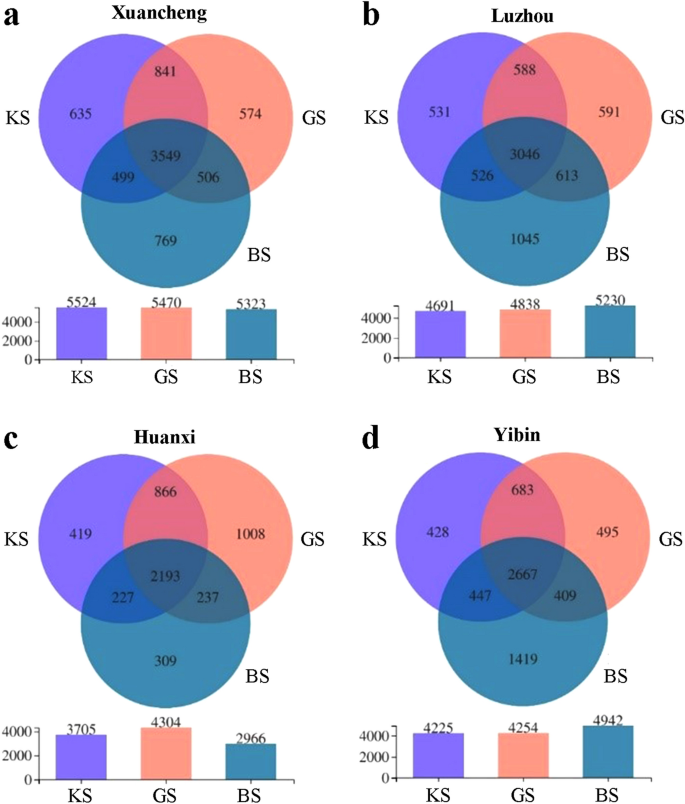
Bacterial variety evaluation of KS, GS and BS in 4 areas
The low high quality reads have been filtered to acquire a complete of 1,632,420 prime quality sequence reads. We refined the dataset by randomly deciding on the variety of reads within the pattern. At 97% similarity, the whole variety of OTUs for all samples was 12,132. The scalability curves meet the experiment necessities (Fig. S1).
Xuancheng had a core OTU rely of 3549, with a mean of 635, 574 and 769 distinctive OTUs for KS, GS and BS, respectively (Fig. 3a). Luzhou had a core OTU rely of 3046, and KS, GS and BS had a mean of 531, 591 and 1045 distinctive OTUs, respectively (Fig. 3b). Huanxi had a core OTU rely of 2193, with KS, GS and BS having a mean of 419, 1008 and 309 distinctive OTUs, respectively (Fig. 3c). Yibin had a core OTU rely of 2667, and KS, GS and BS had a mean of 428, 495 and 1419 distinctive OTUs, respectively (Fig. 3d). The full OTUs have been divided into 50 phylum and 1309 genera.
Venn evaluation of OTUs amongst KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng, Luzhou, Huanxi and Yibin. (a) Venn evaluation of OTUs amongst KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng. (b) Venn evaluation of OTUs amongst KS, GS and BS in Luzhou (c) Venn evaluation of OTUs amongst KS, GS and BS in Huanxi. (d) Venn evaluation of OTUs amongst KS, GS and BS in Yibin.
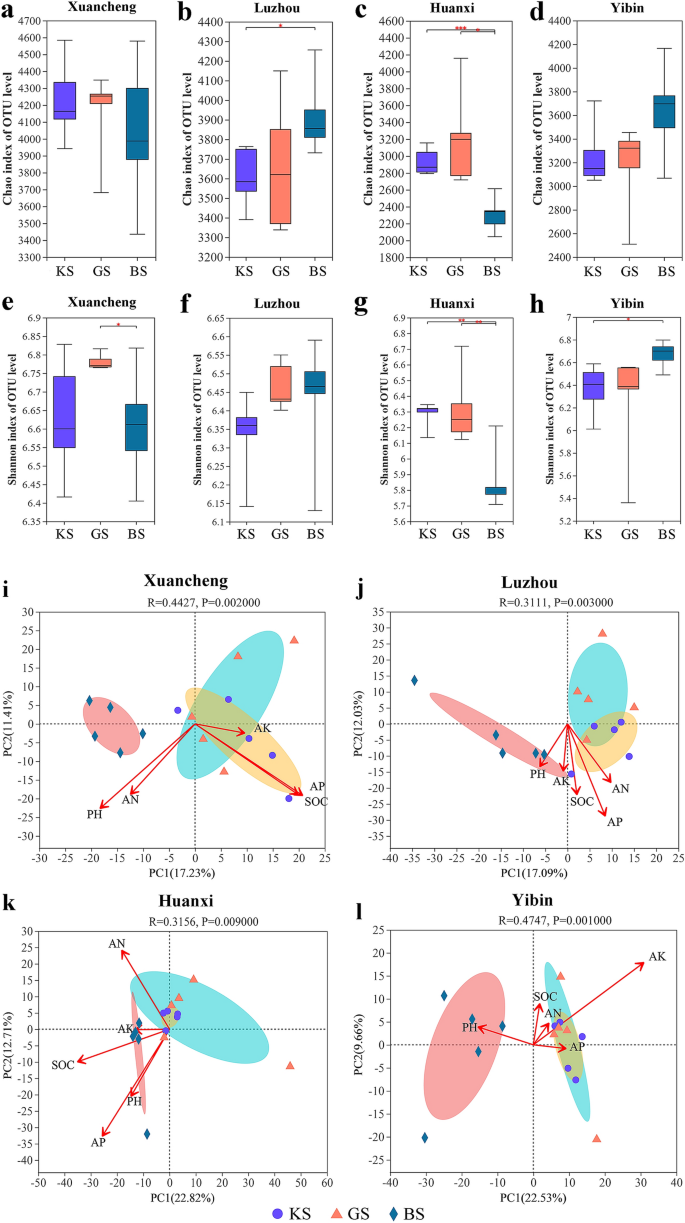
Alpha and PCA evaluation of KS, GS and BS in 4 areas
Alpha variety refers back to the variety of species in a area. We used Chao1 and Shannon to evaluate the abundance and variety of rhizosphere bacterial communities in three soils from 4 areas, respectively. Chao1 was not considerably completely different for KS and GS in Xuancheng, Luzhou, Huanxi and Yibin (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.65, p = 0.72, p = 0.32 and p = 0.65) (Fig. 4a–d). Nevertheless, Chao1 of KS and BS have been considerably completely different in Luzhou and Huanxi, respectively (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.03, p < 0.001) (Fig. 4b,c). As well as, Chao1 was additionally considerably completely different between GS and BS in huanxi (p = 0.01) (Fig. 4c).
Alpha and PCA evaluation of KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng, Luzhou, Huanxi and Yibin. (a) Chao1 index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng. (b) Chao1 index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Luzhou. (c) Chao1 index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Huanxi. (d) Chao1 index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Yibin. (e) Shannon index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng. (f) Shannon index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Luzhou. (g) Shannon index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Huanxi. (h) Shannon index of OTU stage for KS, GS and BS in Yibin. (i) PCA of bacterial communities of KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng. (j) PCA of bacterial communities of KS, GS and BS in Luzhou. (ok) PCA of bacterial communities of KS, GS and BS in Huanxi. (l) PCA of bacterial communities of KS, GS and BS in Yibin. The info inside every group for (a–h) and (i–l) have been statistically analyzed by Pupil’ t take a look at and PERMANOVA, respectively (*: 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05, **: 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01, ***: p ≤ 0.001).
As well as, the shannon of KS and BS, KS and GS of Xuancheng weren’t considerably completely different (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.86, p = 0.07) (Fig. 4e), respectively. Nevertheless, there was a big distinction in shannon between GS and BS (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.04) (Fig. 4e). The shannon of KS and BS, KS and GS, GS and BS in luzhou weren’t considerably completely different (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.35, p = 0.06, p = 0.66) (Fig. 4f). The shannon of KS and BS, GS and BS of Huanxi have been considerably completely different (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.002, p = 0.01) (Fig. 4g), respectively. Nevertheless, the shannon of GS and KS weren’t considerably completely different (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.73) (Fig. 4g). The shannon of KS and BS of Yibin have been considerably completely different (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.03) (Fig. 4h), respectively. Nevertheless, the shannon of GS and BS, GS and KS weren’t considerably completely different (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.10, p = 0.66) (Fig. 4h), respectively.
We carried out PCA evaluation of the bacterial communities of KS, GS and BS in Xuancheng, Luzhou, Huanxi and Yibin. As well as, we used physiological indicators resembling pH, AN, AP, AK and SOC of the three rhizosphere soils within the 4 areas as covariates for PCA. The physiological indicators of the three rhizosphere soils within the 4 areas are proven in Fig. S2. The outcomes confirmed that the bacterial group of BS was considerably completely different from that of KS and GS in Xuancheng, Luzhou, Huanxi and Yibin, respectively (PERMANOVA, p = 0.002, p = 0.003, p = 0.009 and p = 0.001). In distinction, there have been no vital variations in bacterial group composition between KS and GS within the three areas, aside from Luzhou. (Pupil’ t take a look at, p = 0.55, p = 0.44 and p = 0.13). As well as, to additional analyze the connection between environmental elements, rhizosphere soil samples and rhizosphere bacterial communities within the 4 areas, we carried out an evaluation utilizing RDA/CCA. The outcomes confirmed that pH, AN, AP and SOC had a larger impact on the bacterial group in Xuancheng, whereas AK had a smaller impact on the bacterial group in Xuancheng (Fig. 4i). As well as, the bacterial group of GS in Xuancheng was negatively correlated with pH, AN and SOC, whereas the bacterial group of KS was positively correlated with pH, AN, AP and SOC (Fig. 4i). In Luzhou, pH, AN, AP, AK and SOC have been all positively correlated with bacterial communities in KS, whereas they have been negatively correlated with GS (Fig. 4j). In Huanxi, pH, AN, AP, AK and SOC had related results on KS and GS (Fig. 4ok). In Yibin, pH, AN, AK, AP and SOC have been positively correlated with the bacterial group of KS, whereas pH, AN, SOC have been negatively correlated with the bacterial group of KS (Fig. 4l). To additional examine the diploma of rationalization of variations in KS, GS and BS bacterial communities within the 4 areas by soil physicochemical indicators. We additionally carried out PERMANOVA evaluation for every of the three soils within the 4 areas. The outcomes confirmed that AN, AK, SOC, pH and AP defined 0.15 (p = 0.002), 0.12 (p = 0.002), 0.13 (p = 0.002), 0.12 (p = 0.002) and 0.09 (p = 0.003) of the variations within the rhizosphere bacterial communities of the three soils within the 4 areas, respectively.
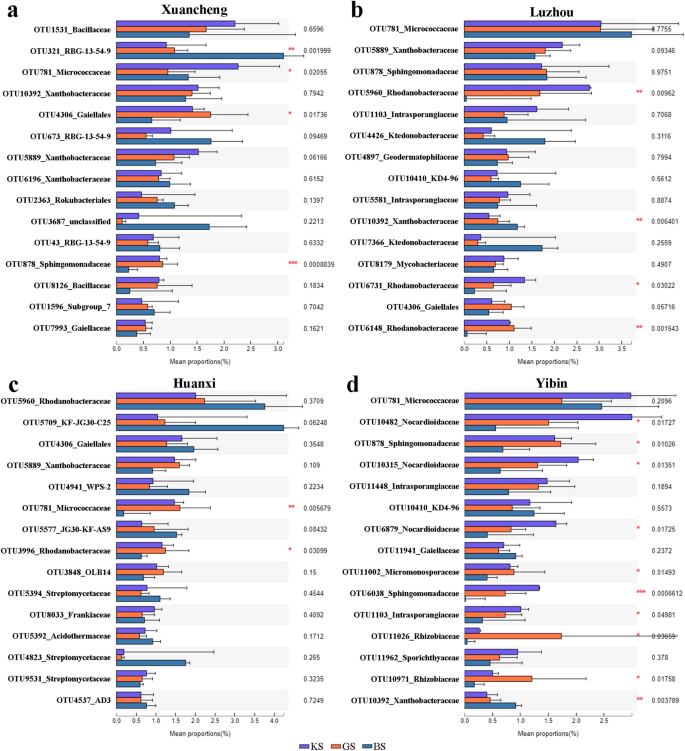
The key bacterial group composition of KS, GS and BS within the 4 areas
We in contrast the variations between teams for the highest 15 most ample species in every of the 4 areas. The outcomes confirmed that among the many high 15 species in Xuancheng, OTU321_RBG-13-54-9, OTU781_Micrococcaceae, OTU4306_Gaiellales and OTU878_Sphingomonadaceae had vital variations (One-way ANOVA, p = 0.002, p = 0.02, p = 0.017 and p < 0.001), respectively, whereas the opposite species didn’t have vital variations (Fig. 5a). Among the many high 15 species in Luzhou, OTU5960_Rhodanobacteraceae, OTU10392_Xanthobacteraceae, OTU6731_Rhodanobacteraceae and OTU6148_Rhodanobacteraceae have been considerably completely different (One-way ANOVA, p = 0.01, p = 0.006, p = 0.03 and p = 0.002), respectively, whereas the opposite species weren’t considerably completely different (Fig. 5b). Among the many high 15 species in Huanxi abundance, OTU781_Micrococcaceae and OTU3996_Rhodanobacteraceae have been considerably completely different (One-way ANOVA, p = 0.006 and p = 0.03), respectively, whereas the opposite species weren’t considerably completely different (Fig. 5c). Among the many high 15 species of Yibin abundance, OTU10482_Nocardioidaceae, OTU878_Sphingomonadaceae, OTU10315_Nocardioidaceae, OTU6879_Nocardioidaceae, OTU11002_Micromonosporaceae, OTU6038_Sphingomonadaceae, OTU1103_Intrasporangiaceae, OTU11026_Rhizobiaceae, OTU10971_Rhizobiaceae, OTU10392_Xanthobacteraceae have been considerably completely different (One-way ANOVA, p = 0.017, p = 0.01, p = 0.014, p = 0.017, p = 0.015, p < 0.001, p = 0.049, p = 0.037, p = 0.018 and p = 0.004) and the opposite species weren’t considerably completely different (Fig. 5d).
One-way ANOVA and FDR comparability evaluation of microbial communities on the OTU stage. (a) One-way ANOVA and FDR comparability evaluation of microbial communities in Xuancheng. (b) One-way ANOVA and FDR comparability evaluation of microbial communities in Luzhou. (c) One-way ANOVA and FDR comparability evaluation of microbial communities in Huanxi. (d) One-way ANOVA and FDR comparability evaluation of microbial communities in Yibin. Information have been analyzed by One-way ANOVA (*: 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05, **: 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01, ***: p ≤ 0.001).
Community evaluation of KS,GS and BS in 4 areas
We carried out a one-way correlation community evaluation of the highest 50 species by way of whole abundance of KS, GS and BS within the 4 areas. Apart from Yibin, the interplay networks of KS in Xuancheng, Luzhou and Huanxi have been all bigger than that of GS (Fig. S2, Desk S2). Total, the community complexity of KS bacterial communities was increased than that of GS and BS in each Luzhou and Huanxi. In Xuancheng, the community complexity of BS bacterial communities was increased than that of KS and GS. In Yibin, the community complexity of GS bacterial communities was increased than that of KS and BS. Along with Xuancheng, the helpful genera current within the KS of Yibin, Luzhou and Huanxi had extra interactions. For instance, Micromonospora and Sphingomonas within the KS of Yibin, Rhodanobacter, Sphingomonas and Streptomyces within the KS of Luzhou and Sphingomonas within the KS of Huanxi (Desk S3).
PICRUSt practical predictive evaluation
PICRUSt perform was predicted for 60 samples from 4 areas. The outcomes confirmed that the COG capabilities have been comparatively related in all samples. All of the colonies have been concerned in RNA processing and modification, chromatin construction and dynamics, power manufacturing and conversion, cell cycle management, cell division, chromosome partitioning, amino acid transport and metabolism, and so on. (Fig. S4).