Toxicity and adhesion screening
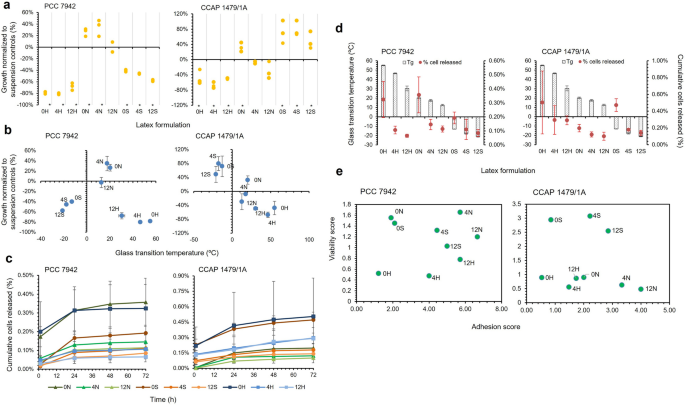
9 latexes with three polymer formulations (H—‘Onerous’, N—‘Regular’, S—‘Gentle’) and three ranges of Texanol (0, 4, 12% v/v) have been examined for toxicity and adhesion with two cyanobacteria strains. Latex sort considerably influenced cell development for S. elongatus PCC 7942 (Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Latex: DF = 2, H = 23.157, P = < 0.001) and CCAP 1479/1A (Two-way ANOVA, Latex: DF = 2, F = 103.93, P = < 0.001) (Fig. 1a). There was no vital impact of Texanol focus on S. elongatus PCC 7942 development; solely the N-latexes have been non-toxic (Fig. 1a), with 0 N and 4 N supporting elevated development of 26 and 35% respectively (Mann–Whitney U, 0 N vs. 4 N: W = 13.50, P = 0.245; 0 N vs. management: W = 25.0, P = 0.061; 4 N vs. management: W = 25.0, P = 0.061), and 12 N sustaining development that was corresponding to the biotic controls (Mann–Whitney U, 12 N vs. management: W = 17.0, P = 0.885). For S. elongatus CCAP 1479/1A, latex mix and Texanol focus have been each vital elements, with a big interplay between the 2 (Two-way ANOVA, Latex: DF = 2, F = 103.93, P = < 0.001, Texanol: DF = 2, F = 5.96, P = 0.01, Latex*Texanol: DF = 4, F = 3.41, P = 0.03). The 0 N and all ‘tender’ latexes enhanced development (Fig. 1a). There was a development of improved development because the styrene composition decreased.
Toxicity and adhesion testing of cyanobacteria (Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 and CCAP 1479/1A) with latex formulations, relationships with glass transition temperature (Tg), and determination matrices derived from toxicity and adhesion knowledge. (a) Toxicity testing utilizing particular person plots of share development of cyanobacteria normalized to suspension tradition controls. Remedies marked with * have been considerably totally different from the controls. (b) Cyanobacteria development knowledge plotted in opposition to Tg of latex (Imply ± StDev; n = 3). (c) Cumulative variety of cyanobacteria launched from adhesion testing of biocomposites. (d) Adhesion knowledge plotted in opposition to Tg of latexes (Imply ± StDev; n = 3). e Determination matrix derived from toxicity and adhesion knowledge. ‘Onerous’ (H) latex had a styrene to butyl acrylate ratio of 1:3, ‘regular’ (N) was 1:1, and ‘tender’ (S) was 3:1. The previous quantity within the latex code corresponds to the Texanol content material.
Typically, cell viability decreased because the Texanol focus elevated; nonetheless, there was no vital correlation for both pressure (CCAP 1479/1A: DF = 25, r = − 0.208, P = 0.299; PCC 7942: DF = 25, r = − 0.127, P = 0.527). Determine 1b presents the connection between cell development and glass transition temperature (Tg). There have been sturdy adverse correlations between the Texanol focus and Tg values (H-latex: DF = 7, r = − 0.989, P = < 0.001; N-latex: DF = 7, r = − 0.964, P = < 0.001; S-latex: DF = 7, r = -0.946, P = < 0.001). The info point out an optimum Tg for S. elongatus PCC 7942 development of roughly 17 °C (Fig. 1b), whereas S. elongatus CCAP 1479/1A favored a Tg of under 0 °C (Fig. 1b). There was a robust adverse correlation between Tg and toxicity knowledge for S. elongatus CCAP 1479/1A solely (DF = 25, r = − 0.857, P = < 0.001).
All latexes had good adhesive affinity, with none releasing greater than 1% of cells after 72 h (Fig. 1c). There have been no vital variations between latexes for both S. elongatus pressure (PCC 7942: Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Latex * Texanol, DF = 4, H = 0.903; P = 0.924; CCAP 1479/1A: Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Latex * Texanol, DF = 4, H = 3.277, P = 0.513). Extra cells have been launched because the Texanol focus elevated (Fig. 1c). There was a stronger adverse correlation between Texanol focus and cell adhesion affinity for S. elongatus CCAP 1479/1A (DF = 25, r = − 0.428, P = 0.026) than for S. elongatus PCC 7942 (DF = 25, r = − 0.660, P = < 0.001) (Fig. 1d). Moreover, there was no statistical relationship between Tg and cell adhesion for both pressure (PCC 7942: DF = 25, r = 0.301, P = 0.127; CCAP 1479/1A: DF = 25, r = 0.287, P = 0.147).
For each strains the ‘exhausting’ latex polymers carried out poorly. In distinction, 4 N and 12 N have been the perfect performing for S. elongatus PCC 7942, whereas 4S and 12S have been finest for CCAP 1479/1A (Fig. 1e); though clearly there’s scope to additional optimize the polymer matrix. These polymers have been taken ahead for semi-batch internet CO2 absorption exams.
Photosynthetic responses to latex polymers
Photophysiology was monitored over seven days utilizing cells suspended within the aqueous latex formulations. Usually, each the obvious charge of photosynthesis (PS) and the utmost PSII quantum yield (Fv/Fm) decreased over time, though the decreases weren’t uniform and several other of the PS datasets displayed a bi-phasic response indicating partial, albeit short-lived restoration of PS exercise (Figs. 2a and 3b). The biphasic response was much less pronounced for Fv/Fm (Figs. 2b and 3b).
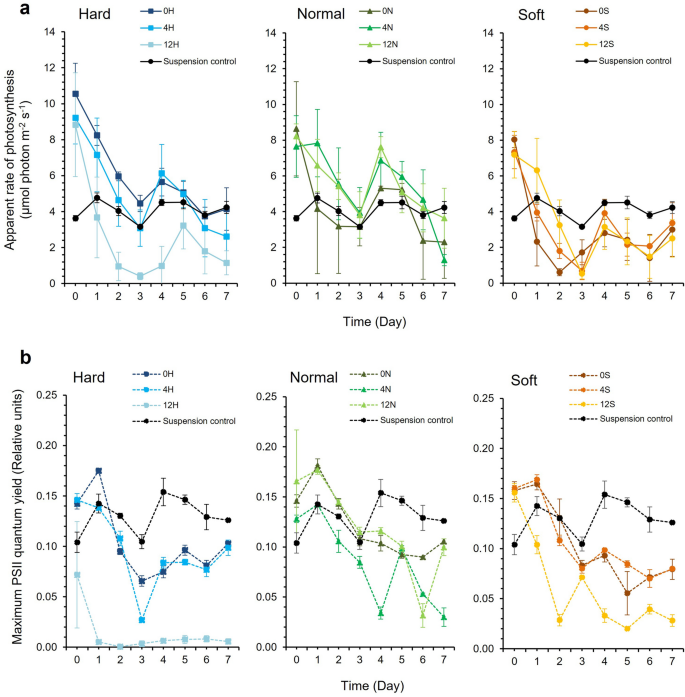
(a) Obvious charge of photosynthesis (PS) and (b) Most PSII quantum yield (Fv/Fm) of Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 in response to latex formulation in comparison with suspension tradition controls. ‘Onerous’ (H) latex had a styrene to butyl acrylate ratio of 1:3, ‘regular’ (N) was 1:1, and ‘tender’ (S) was 3:1. The previous quantity within the latex code corresponds to the Texanol content material. (Imply ± StDev; n = 3).
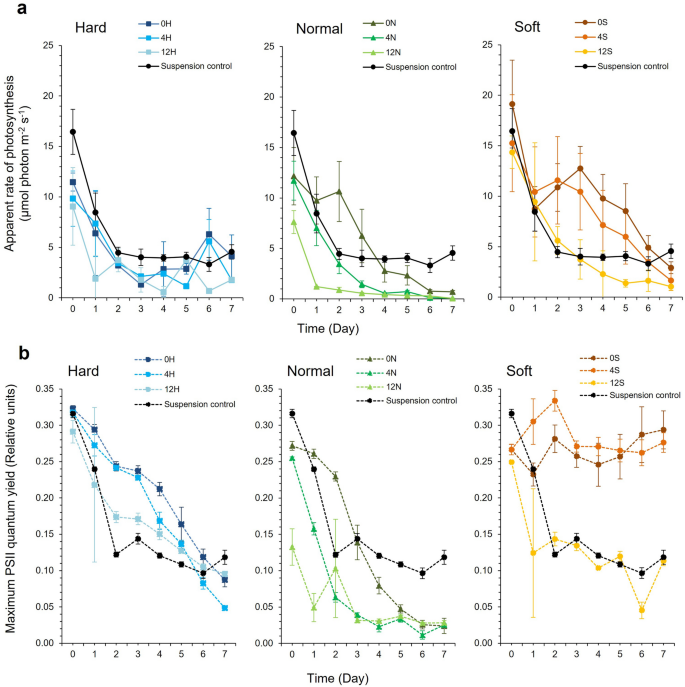
(a) Obvious charge of photosynthesis (PS) and (b) Most PSII quantum yield (Fv/Fm) of Synechococcus elongatus CCAP 1479/1A in response to latex formulation in comparison with suspension tradition controls. ‘Onerous’ (H) latex had a styrene to butyl acrylate ratio of 1:3, ‘regular’ (N) was 1:1, and ‘tender’ (S) was 3:1. The previous quantity within the latex code corresponds to the Texanol content material. (Imply ± StDev; n = 3).
For S. elongatus PCC 7942, latex formulation and Texanol focus didn’t work together to have an effect on PS over time (GLM, Latex * Texanol * Time, DF = 28, F = 1.49, P = 0.07), though the formulation was a big issue (GLM, Latex * Time, DF = 14, F = 3.14, P = < 0.001) (Fig. 2a). Texanol focus didn’t have a big impact over time (GLM, Texanol * Time, DF = 14, F = 1.63, P = 0.078). There have been vital interactions affecting Fv/Fm (GLM, Latex * Texanol * Time, DF = 28, F = 4.54, P = < 0.001). An interplay between latex formulation and Texanol focus had a big impact on Fv/Fm (GLM, Latex * Texanol, DF = 4, F = 180.42, P = < 0.001). Every parameter additionally influenced Fv/Fm over time (GLM, Latex * Time, DF = 14, F = 9.91, P = < 0.001 and Texanol * Time, DF = 14, F = 10.71, P = < 0.001). The 12H latex supported the bottom imply PS and Fv/Fm values (Fig. 2b), indicating that the polymer was extra poisonous.
There have been vital variations in PS for S. elongatus CCAP 1479/1A (GLM, Latex * Texanol * Time, DF = 28, F = 2.75, P = < 0.001), with latex formulation however not Texanol focus as vital elements (GLM, Latex * Time, DF = 14; F = 6.38; P = < 0.001; GLM, Texanol * Time, DF = 14, F = 1.26, P = 0.239). The 0S and 4S ‘tender’ polymers supported barely greater PS efficiency ranges than the suspension controls (Mann–Whitney U, 0S vs. management, W = 686.0, P = 0.044, 4S vs. management, W = 713, P = 0.01) and supported improved Fv/Fm efficiency (Mann–Whitney U, 0S vs. management, W = 794.0, P = < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U, 4S vs. management, W = 815.0, P = < 0.001) (Fig. 3a) indicating extra environment friendly photon transport into photosystem II. For the Fv/Fm values of CCAP 1479/1A cells, there have been vital variations between latexes over time (GLM, Latex * Texanol * Time, DF = 28, F = 6.00, P = < 0.001) (Fig. 3b).
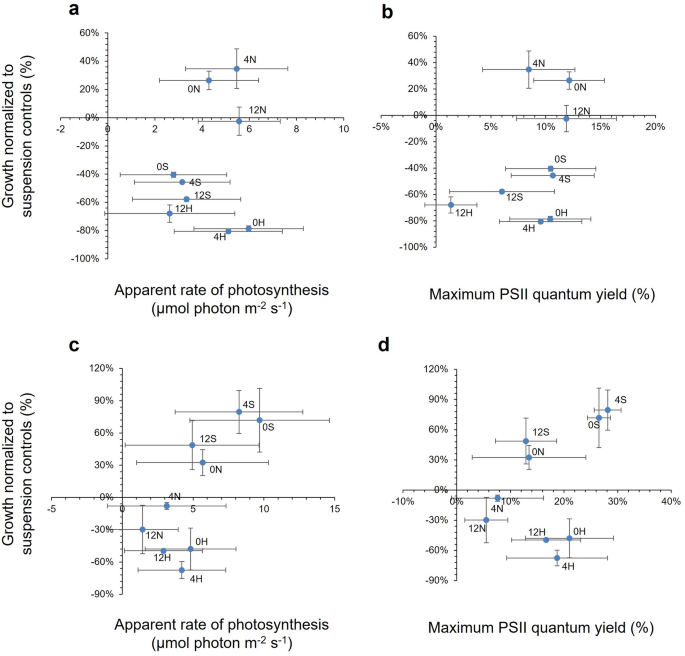
Determine 4 plots the imply PS and Fv/Fm values over the seven days interval in opposition to cell development for every pressure. There have been no clear patterns for S. elongatus PCC 7942 (Fig. 4a and b); nonetheless, CCAP 1479/1A indicated a parabolic relationship for PS (Fig. 4c) and Fv/Fm values (Fig. 4d) with development broadly following the change within the styrene and butyl acrylate ratio.
The connection between development and photophysiology for Synechococcus elongatus in response to latex formulation. (a) Toxicity knowledge plotted in opposition to the obvious charge of photosynthesis (PS) and (b) the utmost PSII quantum yield (Fv/Fm) of PCC 7942. c Toxicity knowledge plotted in opposition to PS and d Fv/Fm of CCAP 1479/1A. ‘Onerous’ (H) latex had a styrene to butyl acrylate ratio of 1:3, ‘regular’ (N) was 1:1, and ‘tender’ (S) was 3:1. The previous quantity within the latex code corresponds to the Texanol content material. (Imply ± StDev; n = 3).
CO2 fixation charges
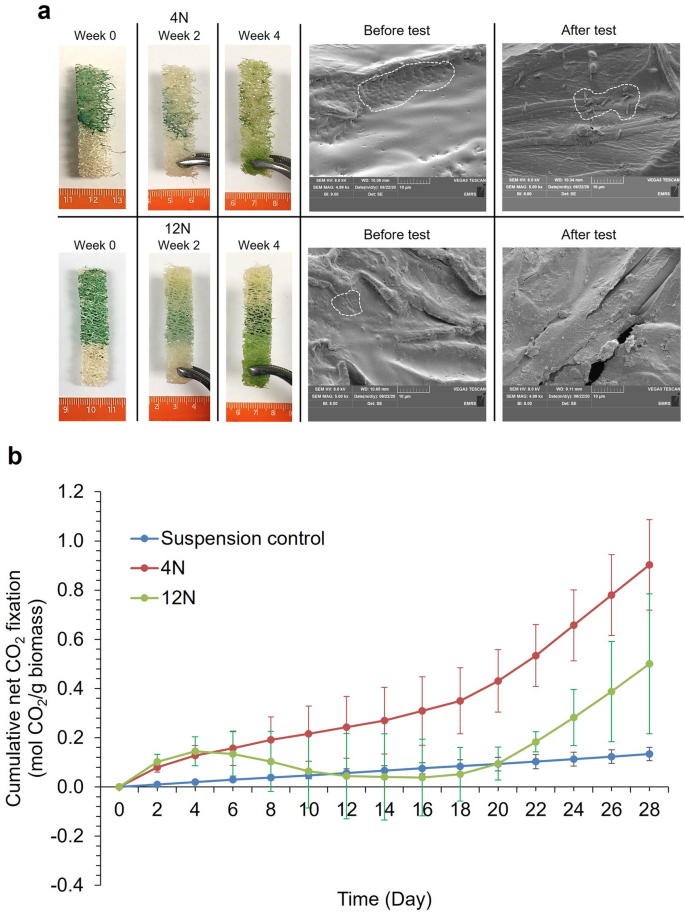
The PCC 7942 biocomposites had restricted effectiveness in retaining cells, with appreciable cell leaching throughout the first 4 weeks (Fig. 5). After an preliminary CO2 absorption section, cells immobilized with the 12 N latex started to launch CO2, sustaining this sample between days 4 to 14 (Fig. 5b). These knowledge correspond to observations of pigment bleaching. Web CO2 absorption commenced once more from day 18. Regardless of the discharge of cells (Fig. 5a), the PCC 7942 12 N biocomposites nonetheless gathered extra CO2 than the suspension controls throughout the 28 days, though not considerably so (Mann–Whitney U check, W = 2275.5; P = 0.066). The CO2 absorption charges with the 12 N and 4 N latexes have been 0.51 ± 0.34 and 1.18 ± 0.29 g CO2 g−1biomass d−1. There have been statistically vital variations between remedy and time ranges (Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Therapy: DF = 2, H = 70.62, P = < 0.001 Time: DF = 13, H = 23.63, P = 0.034) however there was no vital interplay between remedy and time (Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Time * Therapy: DF = 26, H = 8.70, P = 0.999).
Semi-batch CO2 absorption exams with Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 biocomposites with the 4 N and 12 N latexes. (a) Pictures display cell launch and pigment bleaching in addition to SEM photographs of biocomposites earlier than and after exams. White sprint traces point out the place cells have been deposited on the biocomposites. (b) cumulative internet CO2 absorption over the 4 weeks interval. ‘Regular’ (N) latex had a styrene to butyl acrylate ratio of 1:1. The previous quantity within the latex code corresponds to the Texanol content material. (Imply ± StDev; n = 3).
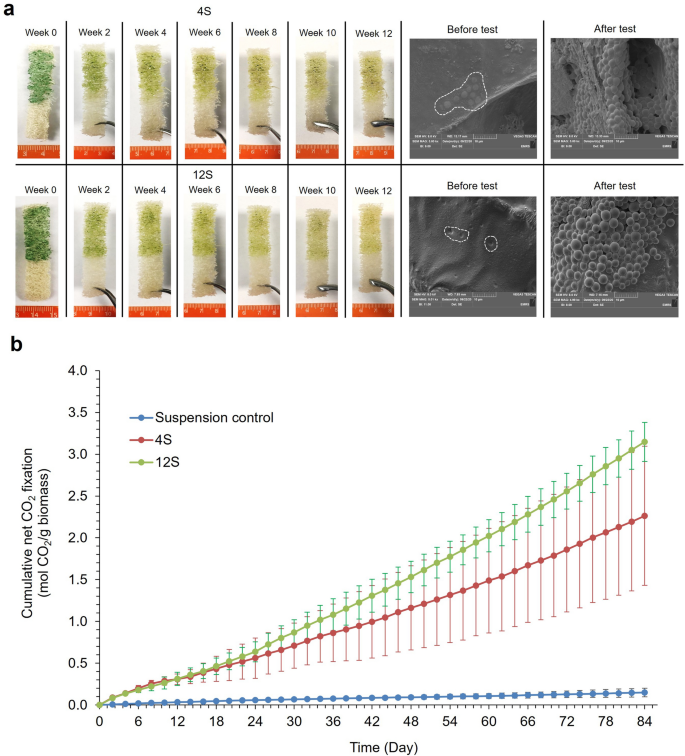
Cell retention was a lot improved for the CCAP 1479/1A pressure with 4S and 12S, regardless of the pigments slowly discoloring with time (Fig. 6a). CCAP 1479/1A biocomposites absorbed CO2 for the total 84 days (12 weeks) with out extra nutrient supplementation. SEM evaluation (Fig. 6a) supported the visible statement of little cell detachment. Initially, the cells have been embedded throughout the latex coatings and, regardless of cell development, the integrity held. The CO2 absorption charges have been considerably greater than the suspension controls (Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Therapy: DF = 2; H = 240.59; P = < 0.001, Time: DF = 42; H = 112; P = < 0.001) (Fig. 6b). The 12S biocomposites achieved the best CO2 absorption charge (1.57 ± 0.08 g CO2 g−1biomass d−1), with the 4S latex being 1.13 ± 0.41 g CO2 g−1biomass d−1, however they weren’t considerably totally different (Mann–Whitney U check, W = 1507.50; P = 0.07) and there was no vital interplay between remedy and time (Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Time * Therapy: DF = 82; H = 10.37; P = 1.000).
Semi-batch CO2 absorption exams with Synechococcus elongatus CCAP 1479/1A biocomposites with the 4 N and 12 N latexes. (a) Pictures display cell launch and pigment bleaching in addition to SEM photographs of biocomposites earlier than and after exams. White sprint traces point out the place cells have been deposited on the biocomposites. (b) cumulative internet CO2 absorption over the twelve weeks interval. ‘Gentle’ (S) latex had a styrene to butyl acrylate ratio of 1:1. The previous quantity within the latex code corresponds to the Texanol content material. (Imply ± StDev; n = 3).
There have been no vital variations in carbohydrate content material for both S. elongatus PCC 7942 (Scheirer-Ray-Hare check, Time * Therapy: DF = 4, H = 3.243, P = 0.518) or S. elongatus CCAP 1479/1A biocomposites (two-way ANOVA, Time * Therapy: DF = 8, F = 1.79, P = 0.119) (Fig. S4). Carbohydrate content material was highest by week 2 within the PCC 7942 biocomposites (4 N = 59.4 ± 22.5% w/w, 12 N = 67.9 ± 3.3% w/w), whereas the carbohydrate content material of the suspension management was highest by week 4 (Management = 59.6 ± 2.84% w/w). Aside from at first of the trial, the full carbohydrate content material of the CCAP 1479/1A biocomposites was equal to the suspension controls, with some variation within the 12S latex on week 4. The best biocomposite values have been 51.9 ± 9.6% w/w for 4S and 77.1 ± 17.0% w/w for 12S.