Demographic traits of the topics
Age ranges of 20–60 years have been chosen for individuals within the present examine. There have been 16 feminine individuals and 14 male individuals. The imply age ± SD of the included respondents from the three tribes have been: Adi tribe (39.5 ± 4.3; vary 20–60), Apatani tribe (42.5 ± 4.1; vary 21–60) and Nyshi tribe (41.9 ± 4.7; vary 20–60). The frequent eating regimen of the Adi and Nyshi tribes consisted primarily of rice with distinction in consumption of cereals, millets, leaves, fish and meat. The Apatani tribe primarily consumed boiled rice, boiled greens, boiled fish, meat and dairy merchandise in every serving. All three tribes additionally consumed fermented bamboo shoot, smoked pork and smoked fish (Supplementary Desk S1).
Statistics of sequencing knowledge
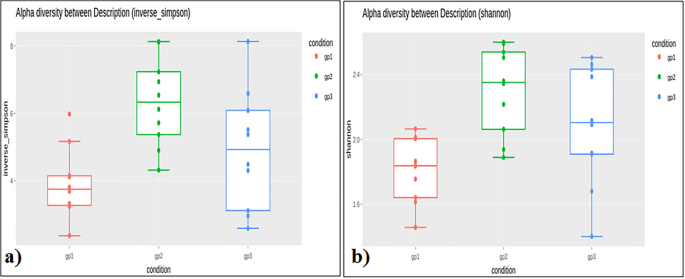
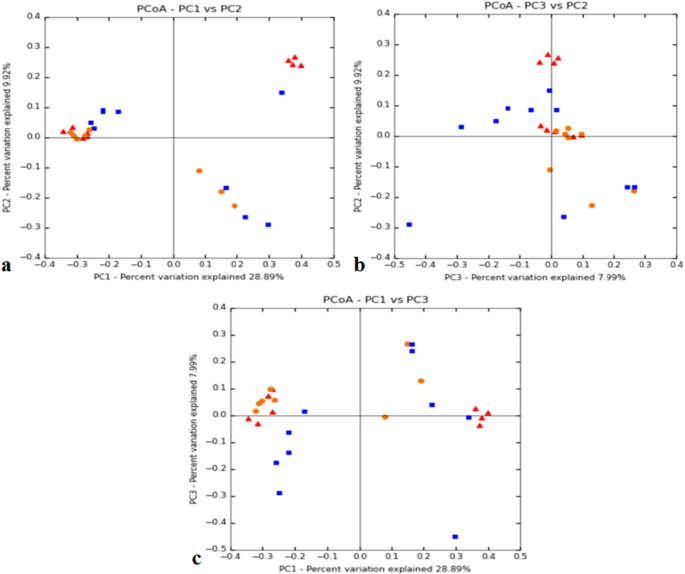
The variety of reads per particular person ranged from 44,090 to 70,718 for the Adi tribe; 43,377–112,936 for the Apatani tribe; and, 54,972–109,291 for the Nyshi tribe (Desk 1). Alpha variety evaluation of the three studied populations significance distinction amongst the tribes utilizing inverse Simpsons variety index (p < 0.004) and Shannon index (p < 0.003), respectively (Fig. 1a,b). Kruskal–Wallis rank sum check revealed increased variety and abundance in Apatani tribe (group 2) than in Adi tribe (group 1) and Nyshi tribe (group 3). Beta variety was assessed by unweighted unifrac to analyse the similarity of microbiota composition amongst tribes and considerably distinction amongst the tribes was noticed (R2 = 0.084, p = 0.01, Adonis evaluation). Principal coordinate evaluation (PCoA) indicated that the Adi and Apatani tribes have distinct intestine microbiota, whereas the Nyshi tribe has variable microbiota with their variation in Principal Element (PC1) of 28.89% adopted by 9.9% of Principal Component2(PC2) and Principal Element (PC3) of seven.9% (Fig. 2), which can be as a consequence of residing in remoted villages with completely different meals habits and way of life.
Bacterial composition at completely different taxa of tribal teams
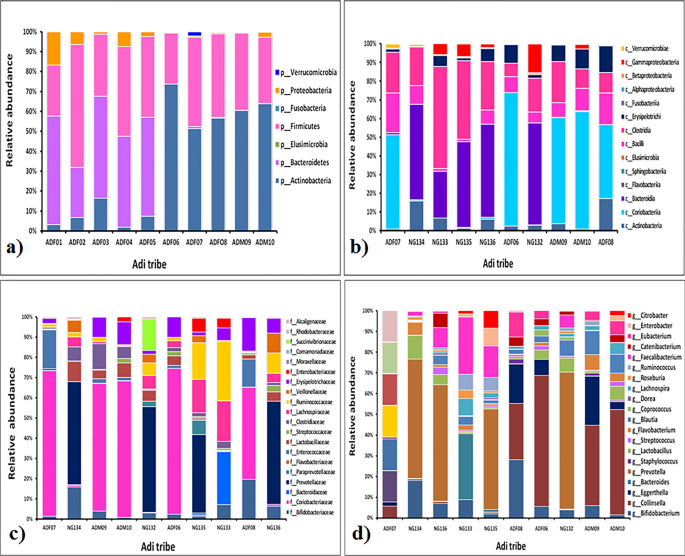
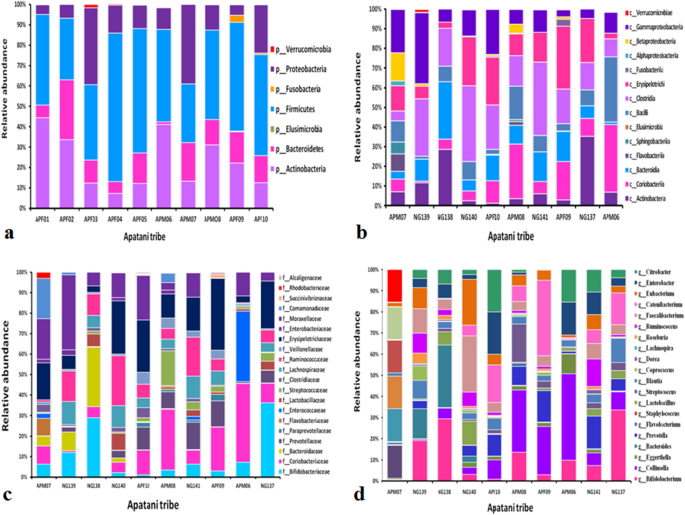
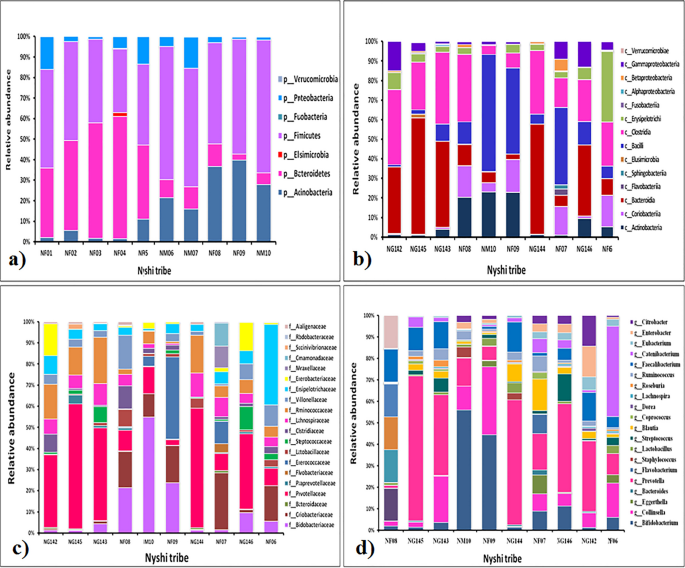
Relative abundance of fecal microbiota composition amongst the tribes have been categorized at class, phylum, household and genus stage. Metagenomics evaluation was carried out to be able to decide the bacterial composition of the GI microbiota of Adi, Apatani and Nyshi tribes of Arunachal Pradesh. It was discovered that on the phylum stage, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Protebacteria, Bacteroidates confirmed important distinction in abundance in all of the tribes (p < 0.05 Kruskal–wallis H check) (Figs. 3a, 4a, 5a). On the class ranges, most micro organism amongst tribes belonged to Actinobacteria, Coriobacteriia, Bacteroidia, Bacilli, Clostridia, Erysipelotrichi, Gammaproteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria, and Elusimicrobia (Figs. 3b, 4b, 5b).
Essentially the most plentiful households discovered within the Adi, Apatani and Nyshi tribes of Arunachal Pradesh have been Prevotellaceae, Bifidobacteriaceae, Coriobacteriaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Streptococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae, Veillonellaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae, Succinivibrionaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, and Rhodobacteraceae (p < 0.05 Kruskal–wallis H check)(Figs. 3c, 4c, 5c). On the genus stage, important abundance of Bifidobacterium, Collinsella, Bacteroides, Prevotella, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Clostridium, Coprococcus, Dorea, Lachnospira, Roseburia, Ruminococcus, Faecalibacterium, Catenibacterium, Eubacterium, Citrobacter and Enterobacter have been noticed amongst the three tribes (p < 0.034 Kruskal–wallis H check) (Figs. 3d, 4d, 5d). PERMANOVA evaluation additionally revealed that the completely different tribal populations have considerably completely different microbial composition variance at phylum stage (F = 3.113, p = 0.03), class stage (F = 2.801, p = 0.024), household stage (F = 2.790,p = 0.001) and genus ranges (F = 2.523, p = 0.001).
On evaluating amongst tribes, it was noticed that Prevotella and Collinsella have been extremely prevalent within the Adi (p < 0.032) (Group 1) and Nyshi (p < 0.04) (Group 3) tribes than within the Apatani tribe. Alternatively, Bifidobacterium and Catenibacterium (p < 0.034, p < 0.021) have been considerably extra plentiful within the Apatani than the Adi and Nyshi tribes.
For understanding the interactions of various intestine micro organism within the completely different teams, we carried out a co-occurrence community evaluation through the use of MEGAN software. We noticed that the genera Lactococcus, Actinomyces, Enterococcus, Enterococcus and Coprococcus (p < 0.01) within the Adi tribe, Ruminococcus, Enterococcus, Streptococcus, Coprococcus and Staphylococcus (p < 0.004) in Apatani tribe, and Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Enterococcus, Coprococcus and Actinomyces (p < 0.01) within the Nyshi tribe have been positively related to one another (Supplementary Fig. S1). Hierarchical clustering evaluation revealed that the Adi, Apatani and Nyshi tribes exhibited distinctly separate clusters on the genus stage (Supplementary Fig. S2).
Differentially altered bacterial abundance in three tribes
Whereas evaluating the intestine microbiota of the Adi, Apatani and Nyshi tribes utilizing G-test evaluation on the species stage, it was noticed that Coprococcus eutactus (p = 0.01), Eubacterium biforme (p = 0.001), Bacteroides uniformis (p = 0.01), Ruminococcus flavefaciens (p = 0.023), Bifidobacterium adolescentis (p = 0.001), Bacteroides ovatus (p = 0.023), and Streptococcus anginosus (p = 0.02) have been much less plentiful within the Adi Tribe. The prevalence of Prevotella copri (p = 0.001), Prevotella stercorea (p = 0.001), Bacteroides fragilis (p = 0.004), Veillonella dispar (p = 0.01), Lactobacillus ruminis (p = 0.013), and Prevotella nanceiensis (p = 0.02) have been considerably diminished within the Apatani tribe, whereas Bifidobacterium longum, (p = 0.001) and Dorea formicigenerans (p = 0.017) have been considerably elevated in abundance within the Apatani tribe. Equally, Prevotella copri (p = 0.001), Collinsella aerofaciens (p = 0.05) andAcinetobacter johnsonii (p = 0.05) was discovered to be considerably diminished within the Nyshi tribe (Desk 2).
Purposeful potential of differentially enriched pathways by PICRUSt evaluation
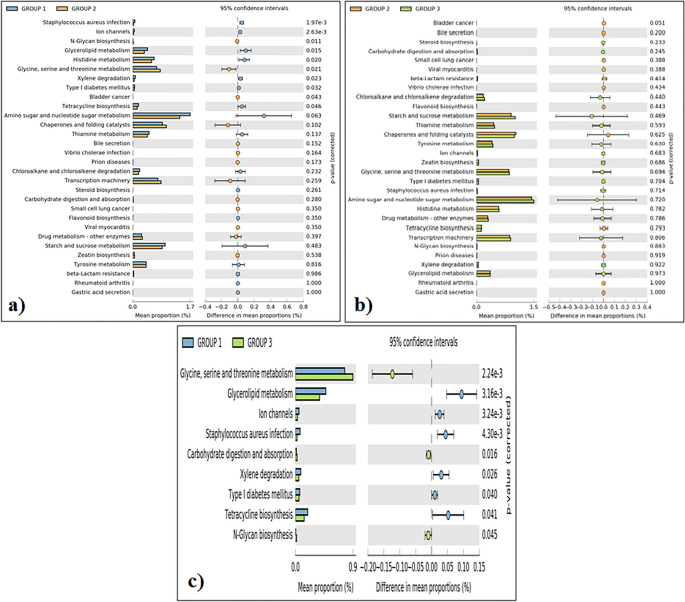
Purposeful prediction evaluation revealed that the intestine microbiota of the Adi tribe (group 1) has an abundance of genes related to Staphylococcus aureus an infection, ion channels, glycerolipid metabolism, histidine metabolism, xylene degradation, kind I diabetes mellitus and tetracycline biosynthesis (Fig. 6a). The intestine microbiota of the Apatani tribe (group 2) has an abundances of genes associated to N-glycan biosysthesis, glycine, serine and theronine metabolism, and bladder most cancers (Fig. 6b). Equally, the intestine microbiota of the Nyshi tribe (group 3) has excessive abundances of genes realted to glycine, serine and theronine metabolism, carbohydrate digestion and absorption adopted by to N-glycan biosysthesis (Fig. 6c).
Relative abundances of genes associated to completely different chosen perform amongst the tribal folks (a), Adi tribe and Apatani tribe; (b) Apatani tribe and Nyshi tribe; (c) Adi tribe and Nyshi tribe (Group 1: Adi tribe, Group 2: Apatani tribe, Group3: Nyshi tribe). The numerous variations noticed between the three teams at 95% confidence stage and p < 0.05 are reported.