IL-27 p28 deficiency aggravates aGVHD in mice
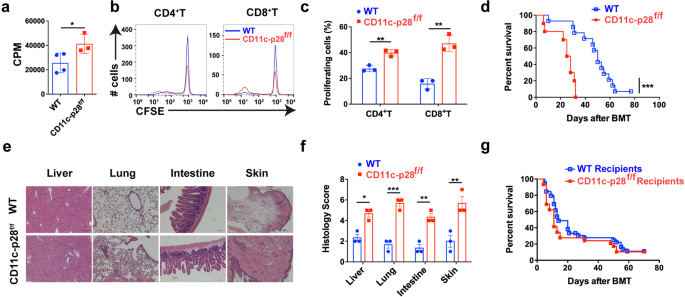
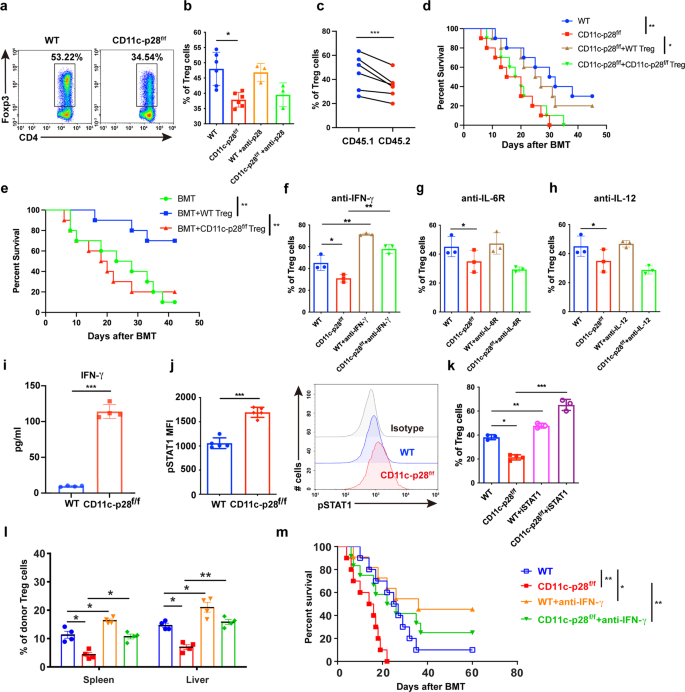
To deal with the physiological function of IL-27 p28 in aGVHD pathogenesis, we first assessed the mobile supply of IL-27 p28 throughout aGVHD. Outcomes confirmed that DCs, fairly than T cells, neutrophils, or monocytes, had been the predominant supply of IL-27 p28 in each murine aGVHD fashions and sufferers on the onset of aGVHD (Supplementary Fig. 1a, b). We due to this fact generated IL-27 p28 conditional knockout (p28 cKO) mice in DCs by crossing p28f/f mice with CD11c Cre mice.35 IL-27 p28 expression within the serum was markedly lowered in CD11c-p28f/f mice in contrast with WT mice at a steady-state or on day 7 after allogenic-bone marrow transplantation (BMT) (Supplementary Fig. 1c, d). Furthermore, the degrees of IL-27 heterodimer had been additionally lowered in CD11c-p28f/f mice in contrast with WT mice (Supplementary Fig. 1e, f). In vitro combined lymphocyte response (MLR) revealed that T cells from p28 cKO mice displayed aggravated alloreactivity than these from WT mice (Fig. 1a), as evidenced by enhanced cell proliferation (Fig. 1b, c). We then established an MHC-mismatched murine aGVHD mannequin utilizing CD11c-p28f/f or WT mice as donors. In contrast with WT recipients, mice that obtained CD11c-p28f/f splenocytes confirmed accelerated aGVHD mortality (Fig. 1d). Histological evaluation additionally revealed that recipients of CD11c-p28f/f splenocytes confirmed way more extreme tissue injury (Fig. 1e, f). Nonetheless, the mortality confirmed no vital distinction when CD11c-p28f/f mice had been used as recipients (Fig. 1g). Collectively, these outcomes display that donor-derived IL-27 p28 protects from aGVHD improvement in mice.
IL-27 p28 deficiency aggravates aGVHD in mice. a–c BALB/c DCs had been cocultured with CFSE-labeled T cells (ratio 1:10) from CD11c-p28f/f mice or management littermates, respectively. Proliferations had been assessed by a 3H-TdR or b, c circulation cytometry 5 days publish coculture. d–f BALB/c recipients had been transplanted with 1 × 107 WT BMs and 5 × 106 splenocytes from both WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice (n = 10–14 per group). General survival curve is depicted (d). Consultant H&E stained sections and histological scores of aGVHD tissues from recipients 14 days post-transplantation are proven (e, f). g C57BL/6 or CD11c-p28f/f recipients had been deadly irradiation and obtained 1 × 107 BMs and seven.5 × 107 splenocytes from BALB/c mice (n = 15 per group). The general survival curve is depicted. Knowledge are consultant of three impartial experiments and offered as imply ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
Lack of IL-27 p28 enhances T cell responses after allo-HSCT
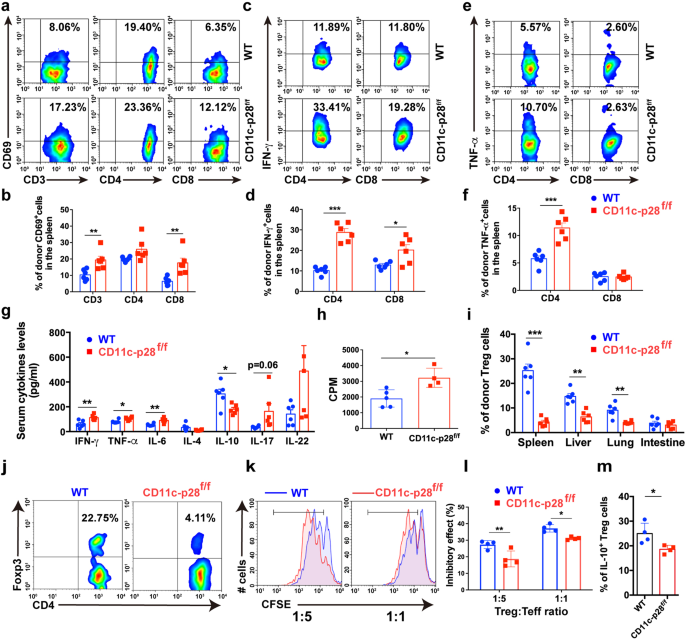
To analyze the mechanisms by which IL-27 p28 alleviates aGVHD, we profiled the immune cell responses in aGVHD goal tissues publish transplantation. Donor T cells had been considerably elevated in aGVHD goal tissues from recipients that obtained CD11c-p28f/f grafts in contrast with these obtained WT grafts (Supplementary Fig. 2a). Notably, T cells from recipients transplanted with CD11c-p28f/f splenocytes confirmed extra activated phenotypes, indicated by elevated CD69 expression in contrast with these from WT recipients (Fig. 2a, b and Supplementary Fig. 2b). Moreover, the frequencies of IFN-γ- and TNF-α-production in donor T cells had been considerably upregulated in recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts in contrast with WT controls (Fig. 2c–f and Supplementary Fig. 2c). Nonetheless, the IL-17A and IL-4 expression had no adjustments in aGVHD goal tissues (Supplementary Fig. 2nd). As well as, productions of IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α had been considerably upregulated, whereas IL-10 was downregulated in recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts in contrast with those who obtained WT grafts (Fig. 2g). Moreover, recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts exhibited enhanced donor T cell alloreactivity in vivo (Fig. 2h). These findings display that lack of IL-27 p28 results in enhanced alloreactive T cell responses which accelerates the aGVHD-related mortality.
Lack of IL-27 p28 enhances T cell responses after allo-HSCT. a, b BALB/c recipients had been transplanted with 1 × 107 WT BMs along with 5 × 106 splenocytes from both C57BL/6 or CD11c-p28f/f mice. Immune cell subsets had been examined 14 days post-transplantation. Consultant circulation cytometric plots and quantification of activated T cells in spleens (amongst H2-Kb+H2-Kd– cells) from recipients (n = 6 per group) are depicted. c–f Consultant circulation cytometric plots and quantification of IFN-γ-producing T cells (c, d) and TNF-α-producing T cells (e, f) in spleens (amongst H2-Kb+H2-Kd– cells) from recipients (n = 6 per group) are depicted. g Serum from BALB/c recipients was collected 14 days post-transplantation and cytokines manufacturing was examined utilizing LEGENDplex (n = 5–6 per group). h Splenocytes from aGVHD recipients had been cocultured with irradiated BALB/c splenocytes. Proliferation charge was detected by 3H-TdR incorporation assay 3 days after coculture. i, j Treg cells had been detected 14 days post-transplantation through FACS. Quantitative information (i) and consultant plots (j) of donor Tregs are proven (n = 6 per group). ok, l CFSE-labeled effector T cells (CD4+CD25− T cells) had been cocultured with Treg cells sorted from the spleens of C57BL/6 or CD11c-p28f/f mice on the indicated ratios for five days. Consultant figures (ok) and frequency of cell proliferation are depicted (l) (n = 4 per group). m The frequency of IL-10+ Treg cells is proven (n = 4 per group). Knowledge are consultant of three impartial experiments and offered as imply ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
Tregs suppress typical T cell activation and management GVHD.36 In our fashions, we noticed that Tregs had been considerably decreased in aGVHD goal tissues of recipients that obtained CD11c-p28f/f grafts in contrast with these obtained WT grafts (Fig. 2i, j). Nonetheless, CD11c-p28f/f Treg cells exhibited an identical apoptosis charge to that of WT recipients (Supplementary Fig. 2e), indicating that IL-27 p28 deficiency didn’t have an effect on Treg cell survival in vivo. In distinction, Treg cells remoted from recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts displayed impaired suppressive results towards CD4+ Teff cells in comparison with these from WT recipients (Fig. 2k, l). IL-27 has been recognized as a differentiation issue that contributes to Tr1 cell era.16,19,37 We discovered that IL-10 ranges had been considerably downregulated within the serum of recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts (Fig. 2g). Nonetheless, no vital adjustments of Tr1 populations had been noticed in aGVHD goal tissues between these two teams (Supplementary Fig. 2f), suggesting that the lowered IL-10 ranges could also be as a result of decreased Treg cells. Certainly, IL-10 producing-Treg cells had been considerably lowered in recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts (Fig. 2m). Collectively, these outcomes display that the exacerbation of aGVHD mediated by IL-27 p28 deficiency associates with faulty Treg cell operate, which fails to suppress the alloreactive T cell responses.
Donor DC-derived IL-27 p28 deficiency and intrinsic practical defects of T cells are each chargeable for exacerbated aGVHD
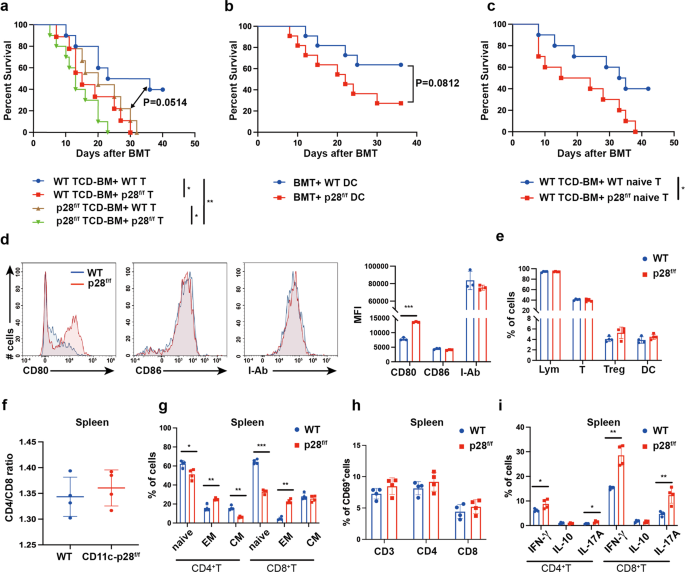
Primarily based on our outcomes, three hypotheses could clarify the improved aGVHD by IL-27 p28 deficiency in CD11c constructive cells. First, donor CD11c+ DC-derived IL-27 p28 instantly impacts allogenic-T cell exercise throughout aGVHD. Second, splenic T cells from p28 cKO mice could have unleashed effector features earlier than transferring to aGVHD receipt. Third, a current research reported {that a} sure subset of T cells additionally specific CD11c.23 This minor inhabitants of T cells acquired IL-27 p28 deficiency could have an effect on aGVHD improvement. To make clear whether or not donor T cells or DCs contribute to the impact of IL-27 p28, we transplanted recipients with T cell-depleted (TCD)-BMs and purified T cells from both WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice. As proven in Fig. 3a, recipients obtained TCD-BM from WT mice along with T cells from CD11c-p28f/f mice (hereinafter known as WK) had considerably shortened survival in contrast with these obtained TCD-BM and T cells each from WT mice (hereinafter known as WW). These outcomes had been in keeping with our mannequin by which BM and splenocytes had been used as grafts, suggesting that T cells from p28 cKO mice are extra pathogenic than these from WT mice, which contribute to the exacerbated aGVHD. Recipients of TCD-BM from CD11c-p28f/f mice and T cells from WT mice (hereinafter known as KW) confirmed a pattern of shortened survival in contrast with the WW group (P = 0.0514), suggesting that donor DC-derived IL-27 p28 deficiency additionally contributes to the exacerbated aGVHD, albeit to a lesser extent (Fig. 3a). To mechanistically interrogate the function of DC-derived IL-27 p28 in aGVHD, we co-transferred bone marrow-derived DCs (BMDCs) from both WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice into WW recipients. We noticed that co-transfer of BMDCs from CD11c-p28f/f mice exacerbated aGVHD, in contrast with these from WT mice, though the distinction was not statistically vital (P = 0.082, Fig. 3b). These outcomes point out that donor DC-derived IL-27 p28 certainly contributes to the aGVHD improvement. To additional make clear whether or not the aggravated aGVHD are on account of pre-activation and distribution of T cell cargo earlier than switch or an altered differentiation upon transplantation, we in contrast the results of donor-derived naive T cells in aGVHD induction. Curiously, naive T cells from CD11c-p28f/f mice considerably enhanced aGVHD improvement than these from WT mice (Fig. 3c), indicating that the intrinsic practical defects happen earlier than T cells are activated. We additionally noticed an upregulation of co-stimulatory molecule CD80 expression on DCs (Fig. 3d). As well as, recipients transplanted with TCD-BM and T cells each from CD11c-p28f/f mice had the shortest survival in contrast with WW (P = 0.004) and KW teams (P = 0.04), and confirmed a pattern of shorter survival than WK group (P = 0.1698). These outcomes point out that DC-derived IL-27 p28 and T cells of p28 cKO donors are each chargeable for aGVHD pathogenesis.
Donor DC-derived IL-27 p28 deficiency and intrinsic practical defects of T cells are each chargeable for exacerbated aGVHD. a BALB/c recipients obtained both WT or CD11c-p28f/f allografts of 5 × 106 TCD-BMs and 1 × 106 T cells as indicated (n = 10 per group). b WW recipients had been injected with both 1 × 106 WT DCs or CD11c-p28f/f DCs at day 0, day1, and day2 post-BMT (n = 10 per group). The general survival curve is depicted. c BALB/c recipients obtained 5 × 106 TCD-BMs from WT mice along with 1 × 106 naive T cells from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice, respectively (n = 10 per group). d–i Splenocytes from regular donors had been detected by circulation cytometry. d CD80, CD86, and MHC-II expression on DCs. e Percentages of lymphocytes, CD3+ T, Tregs, and DCs. f The ratio of T cells within the spleen. g Percentages of T cell suesets. h CD69 expression on T cells. i IFN-γ, IL-17A, and IL-10 expression in T cells (n = 4 per group). Knowledge are consultant of three impartial experiments and offered as imply ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
We discovered that T cells at a steady-state didn’t specific CD11c (<0.5%) however had very low ranges in vitro (about 2% amongst whole T cells) with allo-stimulation or in vivo (about 1% amongst whole T cells) at 7 days after allo-BMT in each WT and CD11c-p28f/f mice (Supplementary Fig. 3a-c). Each CD11c+ and CD11c− T cells didn’t secrete any detectable IL-27 p28 (information not proven). As well as, the IFN-γ manufacturing by CD11c+ and CD11c− T cells had been comparable between WT and CD11c-p28f/f mice underneath allo-stimulation (Supplementary Fig. 3d, e). Thus, CD11c+ T cell-deficient of IL-27 p28 unlikely contributes to aGVHD improvement. Of notice, though WT and p28 cKO mice exhibited the equal ranges of T cells, Treg cells, DCs, and CD4/CD8 ratio within the spleen at a steady-state (Fig. 3e, f), T cells from p28 cKO donors confirmed the next activation phenotype, as evidenced by elevated effector reminiscence T cell populations (Fig. 3g). Nonetheless, CD69 expression confirmed no distinction amongst these T cells (Fig. 3h). Moreover, elevated proportions of IL-17A and IFN-γ producing T cells had been noticed in p28 cKO mice (Fig. 3i), indicating that T cells from p28 cKO mice are intrinsically completely different from these T cells from WT mice. DC-derived IL-27 p28 could mediate aGVHD improvement by affecting T cell pathogenicity throughout allo-HSCT.
IL-27 p28 deficiency impairs Treg cell era and promotes pathogenic IL-1R2+TIGIT+ CD4+T cells within the thymus
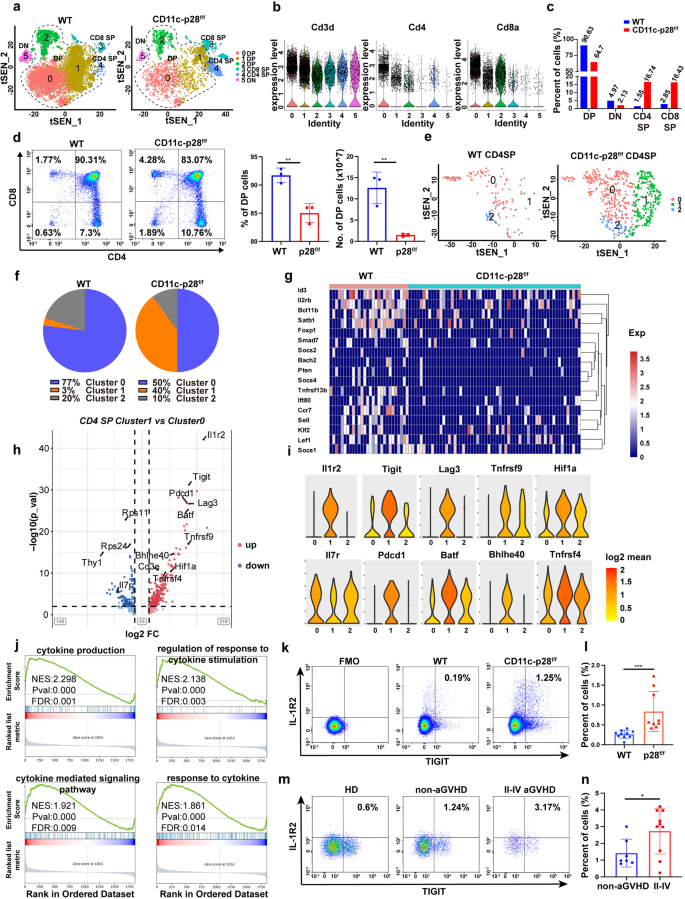
Abnormalities in thymic improvement at the very least partially limites T cell maturation and features.38 Our outcomes are in settlement with prior research by which DC-derived IL-27 p28 regulated T cell improvement within the thymus.35,39 Nonetheless, the mechanism by which IL-27 p28 regulates thymic T cell differentiation stays undetermined. To deal with this, we utilized single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to thymocytes collected from WT and CD11c-p28f/f mice, which allowed extremely detailed profiling of immune cell subsets throughout improvement on the single-cell degree. After high quality management and filtering out poor-quality cells, a whole-transcriptome database of 17922 cells from the 2 teams was analyzed. We recognized 9 clusters by t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE), together with T cells, B cells, DCs, macrophages, and fibroblasts (Supplementary Fig. 4a-c). T cells with particular expression of CD3d, CD4, or CD8a had been distinguished from different clusters and had been reclustered for additional evaluation (Fig. 4a). Violin plots revealed that cluster 5 represented double-negative (DN) T cells; clusters 0, 1, and a couple of represented double-positive (DP) T cells; and clusters 3 and 4 represented CD8 and CD4 single-positive (SP) T cells, respectively (Fig. 4b). We noticed a discount in DP cells and elevation in CD4 and CD8 SP cells in IL-27 p28-deficient mice in comparison with WT mice (Fig. 4c). Stream cytometry confirmed that CD11c-p28f/f mice had lowered DP and elevated CD4 and CD8 SP T cells in contrast with WT mice (Fig. 4d). We additional divided CD4 SP T cells into three subclusters (Fig. 4e). Principal part evaluation (PCA) confirmed a distinction amongst these three clusters (Supplementary Fig. 5a). Additional evaluation confirmed that cluster 0 and cluster 1 represented typical T cells, which was indicated by low expressions of Foxp3. Cluster 2 represented Treg cells, which was designated by excessive ranges of Foxp3 and IL2ra expression (Supplementary Fig. 5b). CD4_cluster 0 and a couple of had been decreased dramatically in IL-27 p28-deficient mice (Fig. 4f), indicating that IL-27 p28 deficiency impairs Treg cell era throughout thymic improvement. The expression ranges of genes concerned in Treg cell improvement, together with Promote, Ccr7, Tnfrsf13b, Bcl11b, Stab1, Id3, Lef1, and Bach2 had been pronouncedly lowered in Tregs from CD11c-p28f/f mice in comparison with these from WT mice (Fig. 4g).40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47 Subsequently, we discovered that the share of CD4_cluster 1 was 3% in WT mice whereas markedly elevated to 40% in CD11c-p28f/f mice. Surprisingly, this T cell cluster was hyperactivated, with extremely expressed activation marker genes, equivalent to Tnfrsf9, Tight, Lag3, Pdcd1, Batf, Maf, Bhlhe40, Tnfrsf18, and Tnfrsf4, and downregulation of the naive gene Il7r.48 As well as, Il1r2 and Tigit had been extremely and particularly expressed in Cluster 1 (Fig. 4h, i). We due to this fact named cluster 1 cells as IL-1R2+TIGIT+ activated CD4+T cells. Stream cytometry information confirmed that IL-1R2+TIGIT+CD4+T subset was markedly elevated in each thymus and spleen in CD11c-p28f/f donors than WT mice (Supplementary Fig. 6a, b). Enhanced Bhlhe40 expression in CD4+ T cells has been demonstrated to advertise aGVHD pathogenesis.49 Different T cell effector genes, together with Nr4a1 and Btla had been elevated, whereas Ccr7, Ccr9, and Klf2 had been decreased (Supplementary Fig. 7a), suggesting that IL-27 p28 deficiency promotes pro-inflammatory and pathogenic fates of CD4+ T cells within the thymus. Pathway evaluation carried out by gene-set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) evaluating CD4 SP Cluster 1 with Cluster 0 revealed that the expression patterns of genes identified to contain in cytokine manufacturing and cytokine-related responses had been elevated with IL-27 p28 deficiency (Fig. 4j). Alerts embody response to cytokine, cytokine binding, and cytokine receptor exercise had been enriched in IL-27 p28-deficient CD4 SP cells in comparison with WT CD4 SP cells (Supplementary Fig. 8). We additional assessed the proportions of IL-1R2+TIGIT+CD4+ T cells in murine aGVHD fashions and medical sufferers with or with out aGVHD. Per scRNA-seq, donor-derived IL-1R2+TIGIT+CD4+T had been considerably elevated in recipients of CD11c-p28f/f grafts in contrast with these of WT controls (Fig. 4k, l). Furthermore, this pathogenic CD4+T subset was additionally elevated in grade II-IV extreme aGVHD sufferers in contrast with non-aGVHD sufferers after allo-HSCT (Fig. 4m, n). Our outcomes due to this fact counsel that T cells are certainly faulty of their steady-state in CD11c-p28f/f mice, as demonstrated by impaired Treg cell era and elevated IL-1R2+TIGIT+ pathogenic CD4+ T cells within the thymus, that are the primary driving pressure of aGVHD improvement.
IL-27 p28 deficiency impairs Treg cell era and promotes pathogenic IL-1R2+TIGIT+ CD4+T cells within the thymus. a Reclustering of T cell subpopulations in WT and CD11c-p28f/f mice. b Violin plots of the relative expressions of CD3D, CD4, and CD8. c P.c of various thymic T cell subsets decided by scRNA-seq evaluation. d Populations and numbers of DP T cells within the thymus from WT and CD11c-p28f/f mice by circulation cytometry. e t-SNE visualization of CD4 SP T cells. f Parts of subclusters in CD4 SP cells. g Expression profile of genes concerned in Treg improvement. h Volcano plot exhibiting differential gene expression between Cluster 1 and Cluster 0 cells from CD11c-p28f/f and WT mice. i Violin plots exhibiting the expression profile of T cell effector genes. Expression is measured because the log2-fold change. j GSEA of the upregulated gene set in Cluster 1 versus Cluster 0 in CD4 SP cells from CD11c-p28f/f relative to WT mice. ok, l Populations of donor-derived IL-1R2+TIGIT+CD4+T cells had been detected by FACS 7 days post-transplantation (n = 9–10 per group). m, n Percentages of IL-1R2+TIGIT+CD4+T cells in PBMCs had been detected by FACS 30 days post-allo-HSCT. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
IL-27 p28 deficiency restrains Treg cell differentiation through the IFN-γ/STAT1 signaling pathway
To additional examine the mechanism by which IL-27 p28 deficiency regulates Treg differentiation, we carried out an in vitro Treg cell differentiation assay. We discovered that Treg cell differentiation was considerably impaired in CD11c-p28f/f mice (Fig. 5a). Nonetheless, blocking p28 signaling utilizing a p28 neutralizing antibody didn’t present comparable impact (Fig. 5b). To additional examine whether or not IL-27 p28 regulates Treg cell differentiation in a cell-intrinsic method, recipients had been injected with TCD-BM cells from CD45.1 mice, together with an equal variety of T cells from CD11c-p28f/f or CD45.1 congenic mice. Treg cell reconstitution was evaluated in vivo 14 days publish switch. The outcomes confirmed that Treg cell reconstitution from IL-27 p28-deficient mice was considerably lowered in comparison with their CD45.1 counterparts (Fig. 5c), indicating a cell-intrinsic impairment of Treg cell improvement on account of IL-27 p28 deficiency. To additional consider the features of Treg cells from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice in controlling of aGVHD, we carried out a Treg cell rescue experiment by co-transferring an equal variety of Treg cells from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice, respectively. The survival curve confirmed that co-transfer of Treg cells from WT mice considerably mitigated aGVHD, whereas co-transfer of Treg cells from CD11c-p28f/f mice had no protecting impact towards aGVHD (Fig. 5d). Furthermore, Treg cells from CD11c-p28f/f mice additionally failed to manage aGVHD induced by WT T cells, while WT Treg cells considerably extended the survival of the recipients (Fig. 5e). Subsequently, these outcomes counsel that IL-27 p28 deficiency dampened Treg cell features throughout aGVHD improvement.
IL-27 p28 deficiency restrains Treg cell differentiation through the IFN-γ/STAT1 signaling pathway. a, b Splenocytes from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice had been induced for Treg polarization within the presence or absence of IL-27 p28 antibody (10 μg/ml). Consultant figures and abstract information of the frequency of Tregs are depicted. c BALB/c recipients had been injected with 1 × 107 TCD-BM cells from CD45.1 mice, together with an equal variety of T cells (2 × 106) from CD11c-p28f/f mice and CD45.1 congenic mice. Treg cell reconstitution was evaluated in vivo 14 days publish switch. d BALB/c recipients had been transplanted with 5 × 106 TCD-BM cells plus 1 × 106 typical T cells (Tconv) both from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice and transferred with 7.5 × 105 Treg cells from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice respectively. The general survival curve is depicted (n = 10 per group). e BALB/c recipients had been transplanted with 5 × 106 TCD-BM cells plus 1 × 106 Tconv cells from WT donors and transferred with or with out 7.5 × 105 Tregs from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice (n = 10 per group). f–h Anti-IFN-γ, anti-IL-6R, or anti-IL-12 had been added throughout Treg polarization at a focus of 10 μg/ml. Share of Treg cells was detected by FACS (n = 3 per group). i IFN-γ manufacturing within the supernatant of polarized Tregs was detected by ELISA (n = 4 per group). j The expression of phosphorylated STAT1 amongst Treg populations is proven (n = 5 per group). ok STAT1 inhibitor (10 μM) was added throughout Treg polarization. Percentages of Treg cells had been detected by FACS (n = 3 per group). l, m BALB/c recipients had been transplanted with 1 × 107 WT BMs along with 5 × 106 splenocytes from both WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice. Recipients had been injected with αIFN-γ (250 μg per mouse) after BMT. Percentages of Tregs had been detected 2 weeks after BMT (n = 4 per group). The general survival curve is depicted (n = 10 per group). Knowledge are consultant of three impartial experiments and offered as imply ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-12 are cytokines that may inhibit Treg cell differentiation. We demonstrated that blocking IFN-γ, however not IL-6 or IL-12 might restore the inhibition of Treg cell differentiation brought on by IL-27 p28 deficiency (Fig. 5f–h). We additionally noticed a considerably elevated IFN-γ manufacturing throughout Treg cell differentiation after IL-27 p28 deficiency (Fig. 5i). Nonetheless, IL-27 p28 expression was undetectable within the supernatants throughout Treg cell differentiation in each WT and CD11c-p28f/f mice (Knowledge not proven). These outcomes counsel that T cell-intrinsic IFN-γ sign is chargeable for the impaired Treg cell differentiation. STAT1 is a key mediator of IFN-γ signaling that regulates the differentiation of Treg cells.50 We noticed that phosphorylation of STAT1 was largely elevated in Treg cells differentiated from CD11c-p28f/f mice in contrast with these from WT mice (Fig. 5j). As well as, STAT1 inhibitor added within the tradition medium considerably reversed the IL-27 p28-mediated inhibition of Treg cell differentiation (Fig. 5k). Moreover, blocking IFN-γ signaling in vivo elevated Treg cell numbers within the spleen and liver and ameliorated aGVHD in mice receiving CD11c-p28f/f donor cells (Fig. 5l, m), suggesting that IL-27 p28 deficiency inhibits Treg differentiation and performance in an IFN-γ-dependent method.
IL-27 p28 is a beneficial marker for predicting aGVHD after allo-HSCT in people
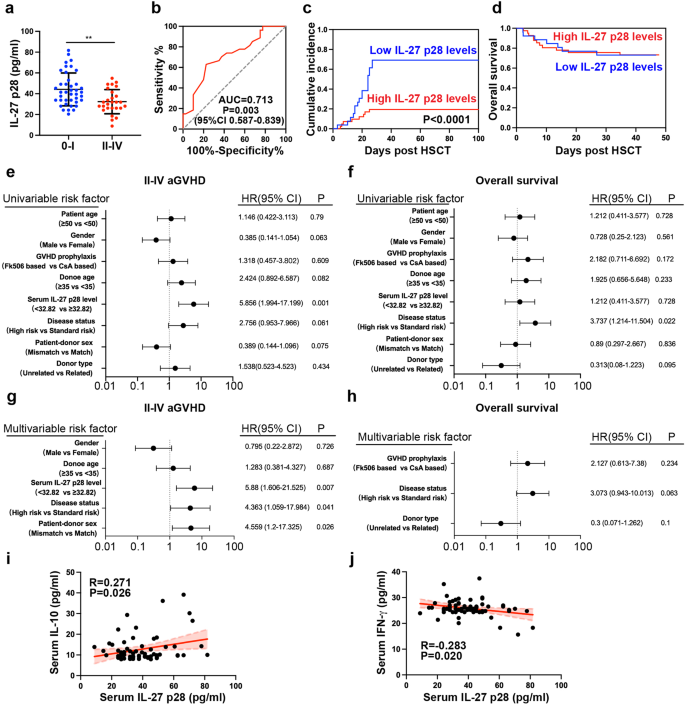
Though the impact of IL-27 p28 in murine aGVHD has been reported, the medical significance of IL-27 p28 in aGVHD sufferers stays undetermined. Therefore, we detected IL-27 p28 expression within the serum of 67 sufferers who underwent allo-HSCT and located that sufferers with extreme aGVHD (Grade II-IV, n = 27) displayed considerably decreased IL-27 p28 ranges in contrast with sufferers with no/low-grade aGVHD (Grade 0-I, n = 40, P = 0.0015, Fig. 6a). When utilizing 32.82 ng/ml because the cutoff worth, IL-27 p28 ranges might predict the prevalence of extreme aGVHD primarily based on ROC evaluation (Fig. 6b). The sensitivity and specificity had been 77.5% and 63%, respectively. Sufferers with excessive ranges of IL-27 p28 had a considerably decrease incidence of extreme aGVHD however confirmed an identical OS charge in contrast with sufferers with low ranges of IL-27 p28 (Fig. 6c, d). Persistently, univariate analyses confirmed that prime ranges of IL-27 p28 had been considerably related to a low incidence of extreme aGVHD however not OS (Fig. 6e, f). Excessive IL-27 p28 and illness standing had been impartial elements for predicting extreme aGVHD (HR = 5.88, 95% CI 1.606-21.525, P = 0.007, and HR = 4.363, 95% CI 1.059-17.984, P = 0.041, Fig. 6g) however not OS (Fig. 6h). IL-27 p28 confirmed comparable ranges amongst completely different major ailments or cGVHD improvement (Supplementary Fig. 9a, b). Comparable outcomes had been noticed by evaluating IL-27 heterodimer in predicting aGVHD (Supplementary Fig. 10). Thus, IL-27 p28 or IL-27 could function helpful predictors of extreme aGVHD. As well as, we discovered that IL-27 p28 was positively correlated with IL-10 (r = 0.271, P = 0.026), whereas negatively correlated with IFN-γ (r = −0.283, P = 0.02; Fig. 6i, j), indicating that serum ranges of IL-27 p28 are related to Treg/Teff cell stability in people.
IL-27 p28 is a beneficial marker for predicting aGVHD after allo-HSCT in people. a IL-27 p28 manufacturing in sufferers after allo-HSCT had been examined by ELISA. b ROC curve was constructed to foretell extreme aGVHD prevalence. c, d The cumulative incidence of extreme aGVHD (c) and total survival (d) between sufferers with excessive and low IL-27 p28 ranges are proven. e, f Univariate analyses of things related to extreme aGVHD prevalence (e) or total survival (f) after allo-HSCT. g, h Multivariate analyses of things related to extreme aGVHD prevalence (g) or total survival (h) after allo-HSCT. i, j The associations between the expression of IL-27 p28 and IL-10 (i), and IFN-γ (j) had been analyzed. Knowledge are offered as imply ± SD. **P < 0.01