Carbohydrates are the foremost supply of power within the physique, in line with the American Diabetes Affiliation. Since they’ve carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as chemical constituents, roughly (C.H₂O)n the place n≥3, they’re often called carbohydrates. Sugars, fibers, and starches, present in fruits, greens, grains, and milk merchandise, are examples of carbohydrates.
- Monosaccharides are the constructing blocks of carbohydrates. Many of those substances are fashioned via a course of often called glyconeogenesis from easier molecules. Others are byproducts of photosynthesis. These are categorised in line with the variety of carbon atoms, comparable to triose for 3 C-atoms within the carbohydrate, tetrose for 4 C-atoms, pentose for five C-atoms, and so forth. Some examples embody glucose, fructose, galactose, and many others.
- A small variety of covalently bonded monosaccharide molecules make up an oligosaccharide. They incessantly cooperate with proteins (glycoproteins) and lipids (glycolipids), serving each regulatory and structural roles. They comprise 3-10 monosaccharide items linked collectively via glycosidic linkage. Examples are:
- Maltose (Glucose+Glucose)
- Sucrose (Glucose+ Fructose)
- Lactose (Glucose+Galactose)
- Raffinose (Glucose+Fructose+Galactose)
- Polysaccharides have molecular weights far into the hundreds of thousands of daltons and are made up of a number of covalently bonded monosaccharide items. These are also referred to as glycans that are additional categorised as homopolysaccharides or heteropolysaccharides whether or not they consist of 1 sort or multiple sort of monosaccharide residue.
- Glucans (Polymer of glucose)
- Galactans (Polymer of galactose)
- Heparin (Polymer of D-glucuronic acid, L-iduronic acid, N-sulfo-D-glucosamine)
- Hyaluronic acid (Polymer of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-glycosamine)
What are Decreasing Sugars?
Decreasing sugars are carbohydrates that may oxidize different substances by contributing electrons whereas being lowered.
An aldehydic (-CHO) or ketonic (-CO-) group shall be current in lowering sugars. The presence of free carbon on the finish of those lowering sugars is named lowering ends. All classes of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides embody lowering sugars, whereas all monosaccharides, some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and a few polysaccharides are lowering sugars.
- Two types of sugars discovered within the monosaccharides, aldose, and ketose, are lowering sugars, as ketone teams are current in ketoses whereas aldehyde teams are current in aldoses. Examples of ketoses are fructose, and aldoses are glucose and galactose.
- Tautomerization is the method by which a compound’s isomers are became tautomers. Ketoses bear tautomerization to kind aldoses after which act as lowering sugars.
- Disaccharides can both be lowering or non-reducing. For instance, Sucrose and trehalose are non-reducing sugars since glycosidic bonds between their anomeric carbons don’t allow them to remodel into an open-chain kind with an aldehyde group. As a substitute, they continue to be within the cyclic kind. Nonetheless, lactose and maltose are lowering disaccharides.
Traits of Decreasing Sugars
The sugar that has the potential to lose an electron to a different chemical or organic entity, thereby itself being lowered, whereas oxidizing the opposite is the lowering sugar. They function a lowering agent. The next factors summarize a few of lowering sugar’s most important qualities.
- A free aldehyde group and a ketone, respectively, are current within the constructions of lowering sugars comparable to glucose and fructose.
- Normally, lowering sugar just isn’t oxidized, however Some comparatively weak oxidizing substances, comparable to metallic salts, can be utilized to oxidize them.
- When carbon is joined to some oxygen molecules to generate alcohol or ether, a hemiacetal construction develops.
- Osazones are generated when mutarotation is produced in lowering sugars.
- The lowering brokers in an aqueous answer usually produce a number of compounds with an aldehyde group.
- Maillard’s response causes the browning of meals gadgets comparable to muffins, slices of bread, candies, espresso, and processed and baked meals as a result of interplay between lowering sugars and amines. This response is obvious when the meals is heated for prolonged intervals or stays at room temperature.
- Decreasing sugars cut back cupric ions of Fehling’s answer and Tollen’s reagent into cuprous ions to kind brick-red precipitates.
Examples of Decreasing Sugars
All monosaccharides are lowering sugars. These comprise free aldehyde (aldoses) and ketone (ketoses) teams. Ketone tautomerizes in answer to provide an aldehyde. Examples are glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose, glyceraldehyde, xylose, and many others. The Aldehydic group readily undergoes oxidation to kind carboxylic acid and cut back the opposite reactive agent within the course of concurrently.
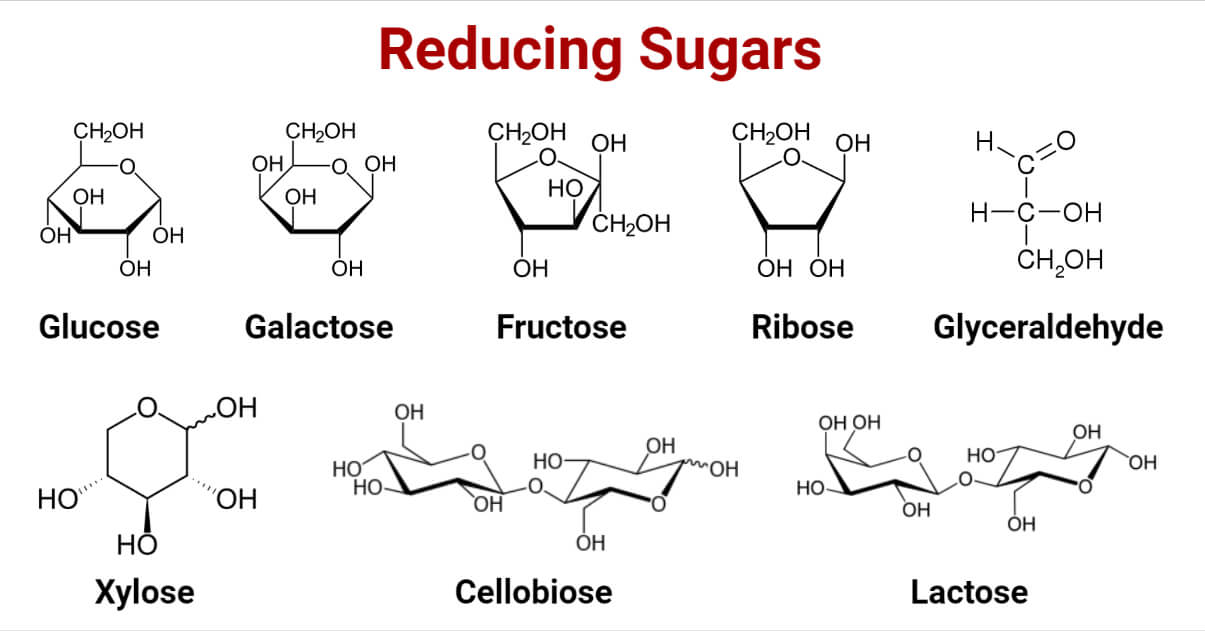
- Decreasing disaccharides have a free hemiacetal unit as an aldehydic group in one in every of its monosaccharides. For instance, Lactose, cellobiose, and maltose are lowering disaccharides whose one hemiacetal unit is free. On the identical time, the opposite is occupied by the glycosidic bond, and the free hemiacetal unit facilitates it to behave as a lowering agent.
- The nonreducing disaccharides and polysaccharides are acetals. Normally, complicated polysaccharides have a single hemiacetal unit which isn’t sufficient for such an enormous molecule to provide a constructive check for lowering sugars. That molecule which doesn’t have any hemiacetal teams is lowering in nature.
Figuring out Exams for Decreasing Sugar
Generally carried out exams to determine whether or not there may be the presence of lowered sugar or not within the pattern are Benedict’s check and Fehling’s check.
Benedict’s Check
The check process begins with dissolving the meals samples in water to find out whether or not lowered sugar is current. A really restricted quantity of Benedict’s reagent is added, and at this level, the answer begins to chill, adopted by the onset of cooling of the answer. The answer begins to vary its shade after about 10 minutes. The presence of lowering sugar is indicated if the hue turns blue. Nonetheless, if the hue shifts progress to inexperienced, yellow, orange, crimson, and eventually to darkish crimson or brown, that signifies that the meals comprises lowering sugar.
[ Benedict’s solution is the aqueous solution of anhydrous sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate.]
Fehling Check
The pattern through which the presence of lowering sugar is to be detected is uniformly blended in water, after which the nice and cozy Fehling’s answer is added. The presence of lowering sugar is confirmed by the change of the colour of the answer right into a red-brown rusty shade.
[Fehling’s solution is prepared from an aqueous solution of potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate and copper II sulfate pentahydrate combined in equal parts.]
Functions of Decreasing Sugars
A number of the utilization of lowering sugars are listed under:
- Decreasing sugar consumption particularly lowers the prospect of being obese and overweight, decreasing the danger of getting diabetes.
- Moreover, it considerably lowers dental cavities.
- The standard of drinks is indicated by the extent of lowering sugars.
References
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Ancillary_Materials/Reference/Organic_Chemistry_Glossary/Reducing_Sugar
- https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/reducing-sugar
- https://examine.com/academy/lesson/reducing-vs-non-reducing-sugars-definition-comparison.html
- https://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/programs/351/Carey5th/Ch25/ch25-2-5.html
- https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-8146-8_6
- https://sciencing.com/sucrose-nonreducing-sugar-5882980.html
- https://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/2017/09/12/reducing-sugars/
- https://www.livestrong.com/article/386795-the-definition-of-reducing-sugars/
- https://researchtweet.com/reducing-sugar-definition-characteristic-examples/
- https://www.biologyexams4u.com/2012/10/differences-between-reducing-and-non.html?m=1
- Zoecklein, B.W., Fugelsang, Ok.C., Gump, B.H., Nury, F.S. (1990). Carbohydrates: Decreasing Sugars. In: Manufacturing Wine Evaluation. Springer, Boston, MA.
