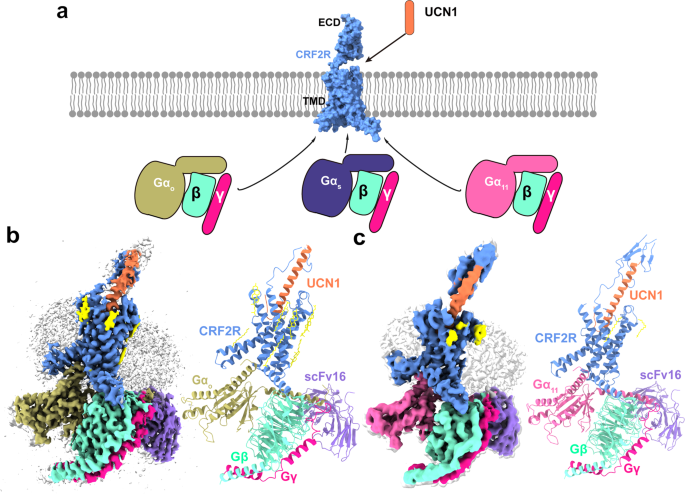
Cryo-EM construction willpower of UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go complexes
To arrange prime quality human UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go complexes, we developed the NanoBiT tethering technique to stabilize the complexes30,31,32 (Supplementary Fig. 1a, b). We used dominant adverse DNGα11 and DNGαo, that are modified types of Gα11 and Gαo which have two amino acid replacements equal to these in a printed dominant-negative bovine Gαs (DNGαs) assemble33. As well as, DNGα11 (residues 1-24) is changed with Gαi1 (residues 1-18) and DNGαo (residues 1-29) is changed with Gαi1 (1-29) to own the flexibility to bind scFv1634. Giant-scale purification was carried out to acquire the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go complexes for cryo-EM research (Supplementary Fig. 1a, b).
The pictures of UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go complexes had been collected by a Titan Krios with a Gatan K3 detector and a Titan Krios with a Gatan K2 detector, respectively (Supplementary Figs. 2a and 3a). 2D classification confirmed clear secondary construction options and random distribution of the particles, which enabled a high-resolution reconstruction of the cryo-EM density maps (Supplementary Figs. 2b and 3b). The buildings of the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go complexes had been decided from a complete of three,402,020 and 1,840,659 preliminary particles to an total decision of three.7 Å and a couple of.8 Å, respectively (Fig. 1, Supplementary Figs. 2c, d, 3c, d and 4a, b). Each buildings had been rigorously examined, and refined with actual house refinement in Phenix35. The mannequin of the CRF2R-G11 complicated had been additional refined with Rosetta refinement methods towards the cryo-EM map (Supplementary Fig. 4c–f)36. The Rosetta refinement improved the atomic particulars within the CRF2R-G11 complicated construction that was in-built a 3.7 Å cryo-EM map, with chemically optimized aspect chain rotamers and the worldwide protein geometry (Supplementary Information 1). We truncated many aspect chains within the Rosetta-refined mannequin of the CRF2R-G11 complicated to acquire the ultimate mannequin for Protein Information Financial institution deposition, to replicate the standard of the electron density map. Nonetheless, we used the aspect chain rotamers from the Rosetta-refined mannequin for the aim of debate herein, that are indicated within the related determine legends.
a Cartoon illustration of signaling selectivity of CRF2R. b Left, cut-through view of the cryo-EM density map of the UCN1-CRF2R-Go complicated and the disc-shaped micelle. The unsharpened cryo-EM density map on the 0.016 threshold proven as mild grey floor signifies a micelle diameter of 11 nm. The coloured cryo-EM density map is proven on the 0.022 threshold. Proper, cartoon illustration of the UCN1-CRF2R-Go complicated is proven with annular lipids in yellow stick illustration. Cornflower blue, CRF2R; coral, UCN1; darkish khaki, Go; aquamarine, Gβ; deep pink, Gγ; medium purple, scFv16. c Left, cut-through view of the cryo-EM density map that represents the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 complicated and the disc-shaped micelle. The unsharpened cryo-EM density map on the 0.013 threshold proven as mild grey floor signifies a micelle diameter of 11 nm. The coloured cryo-EM density map is proven on the 0.016 threshold. Proper, cartoon illustration of the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 complicated proven with annular lipids in yellow stick illustration.
Comparability of total buildings
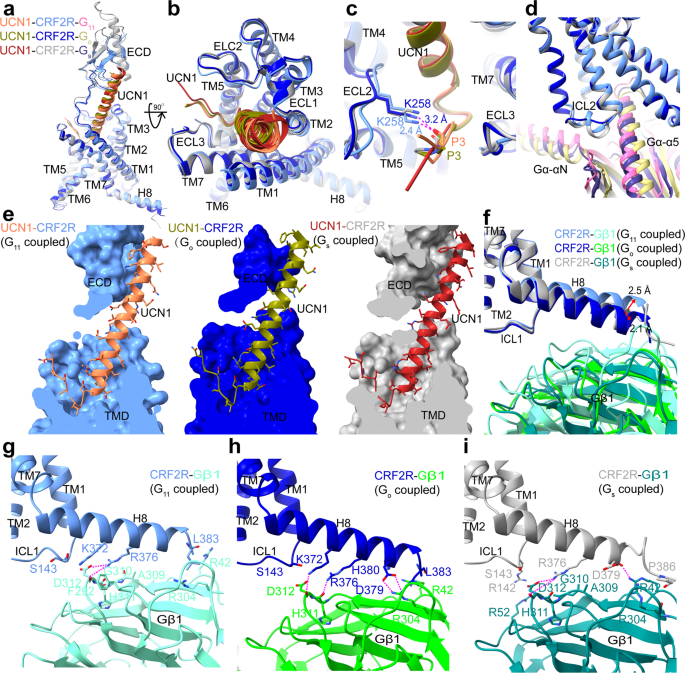
The general buildings of the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go complexes are just like the earlier construction of the UCN1-CRF2R-Gs complicated (PDB: 6PB1)21, with root imply sq. deviation (RMSD) values of 1.01 Å and 0.64 Å for the Cα atoms of the receptor. We noticed structural variations within the second extracellular loop (ECL2), the second intracellular loop (ICL2), helix 8 (H8) of the receptor and the Gβ subunit (Fig. 2), the αN and α5 helices of Gα in these complexes (Fig. 3). Though UCN1 binds at a really comparable website (Fig. 2a–c and e), the ECL2 is nearer to the N terminus of UCN1 within the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 construction. The primary chain carbonyl group of P3UCN1 kinds an H-bond with the side-chain of K258ECL2, which was modeled with Rosetta within the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 construction and P3UCN1 additionally kinds an H-bond with the side-chain of K258ECL2 in UCN1-CRF2R-Go construction (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Fig. 4c). Constantly, alanine mutation of K258ECL2 diminished the receptor coupling to G11 and Go in contrast with wild-type (WT) CRF2R, whereas this mutation doesn’t have an effect on Gs coupling of the receptor (Supplementary Fig. 5 b, e, h and Desk 2). The primary modifications within the receptor are the completely different conformations of ICL2, whose conformation is vital for mediating G protein recognition and specificity (Fig. 2nd), as mentioned later (Fig. 4).
a Comparability of UCN1 and CRF2R within the G protein-bound buildings within the aspect view. b Comparability of UCN1 and the TMD conformation within the G protein-bound buildings in an extracellular view. c Comparability of the N terminus of UCN1 and the place of the ECL2 of CRF2R within the G protein-bound buildings. d Comparability of the distinct conformational modifications of ICL2 and the variations within the orientation of Gα in these three UCN1-CRF2R-G protein buildings. e The binding pocket of UCN1(coral) in CRF2R (cornflower blue)-G11 (scorching pink), UCN1(olive) in CRF2R (medium blue)-Go (darkish khaki), and UCN1 (hearth brick) in CRF2R (darkish grey)-Gs (darkish slate Blue). Many UCN1 aspect chains within the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 construction had been truncated, whose rotamers proven right here had been primarily based on the Rosetta-refined mannequin. f Structural comparability of CRF2R H8 and Gβ1. g CRF2R H8 (cornflower blue)-Gβ1 (aquamarine) interface within the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 complicated. The aspect chains of K372, and D379 of the receptor, and R42 and D312 of Gβ1were truncated within the construction, whose rotamers proven on this panel was from the Rosetta-refined mannequin. h CRF2R H8 (medium blue)-Gβ1 (lime inexperienced) interface within the UCN1-CRF2R-Go complicated. i CRF2R H8 (darkish grey)-Gβ1 (teal) interface within the UCN1-CRF2R-Gs complicated (PDB: 6PB1). The polar contacts are proven as purple dashed strains.
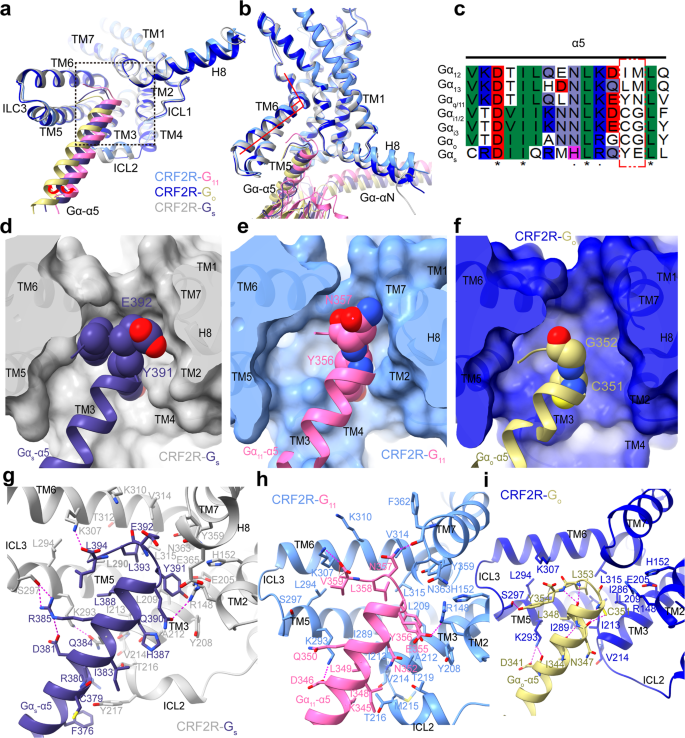
a Comparability of the TMD conformation and the place of the Gα-α5 helix C terminus within the G protein-bound buildings is proven in cartoon illustration in an intracellular view. The purple arrows point out the α5 helix of G11 and Go shift away from TM5 or ICL2, in comparison with these of Gs. Construction of every CRF2R-G complicated was superposed onto CRF2R-G11 primarily based on the receptor element. CRF2R (cornflower blue)-G11 (scorching pink), CRF2R (medium blue)-Go (darkish khaki), CRF2R (darkish grey)-Gs (darkish slate blue) (PDB: 6PB1). b Comparability of the TM6 conformation in three complexes. c Sequence alignment of α5 within the completely different Gα proteins. The purple field point out the C-tail distinction of G protein. d–f Binding pocket for the Gα-α5 C terminus. d UCN1-CRF2R-Gs (PDB: 6PB1); e UCN1-CRF2R-G11; f UCN1-CRF2R-Go.The receptors are proven in cartoon and floor representations in an intracellular view. g Interactions between CRF2R and Gα-α5 in UCN1-CRF2R-Gs (PDB: 6PB1). h Interactions between CRF2R and Gα-α5 in UCN1-CRF2R-G11. Many receptor aspect chains and people of K345, D346, and E355 on Gα-α5 had been truncated within the construction, whose rotamers proven on this panel had been from the Rosetta-refined mannequin. i Interactions between CRF2R and Gα-α5 in UCN1-CRF2R-Go. The polar contacts are proven as purple dashed strains.
a Comparability of ICL2 conformations within the UCN1-CRF2R-G11, UCN1-CRF2R-Go and UCN1-CRF2R-Gs buildings (PDB: 6PB1). The purple arrows point out the relative orientation variations of the completely different Gα. b Sequence alignment of αN and β1 within the completely different Gα proteins. c Interactions between ICL2 and Gs. d Interactions between ICL2 and G11. The aspect chains of receptor residues, and N198, I199, and K345 of G11 on this panel had been truncated within the construction. These residues proven right here had been ready primarily based on the Rosetta-refined mannequin. e Interactions between ICL2 and Go. The polar contacts are proven as purple dashed strains. f G protein activation and signaling assays of wild-type (WT) and ICL2 mutant CRF2R utilizing a Gαs-Gβγ dissociation assay g utilizing a Gα11-Gβγ dissociation assay and h utilizing Gαo-Gβγ dissociation assay. Information from three impartial experiments (n = 3) are offered as imply ± SEM.
In contrast with the UCN1-CRF2R-Gs construction, H8 of CRF2R moved 2.5 Å and a couple of.1 Å in the wrong way between the UCN1-CRF2R-G11 and UCN1-CRF2R-Go buildings (Fig. 2f–i). The interactions between the C terminus of CRF2R and the Gβ subunit had been additionally noticed in these buildings. The aspect chain of D3798.63b, R3768.60b and K3728.56b in H8 kinds a hydrogen bond with R304, H311 and D312 within the Gβ subunit from the CRF2R-Go construction, respectively. Whereas the aspect chain of R3768.60b and the primary chain carbonyl of D3798.63b in H8 kinds a hydrogen bond with D312 and R42 within the Gβ subunit from the CRF2R-Gs construction, respectively. Within the CRF2R-G11 construction, presumably because of poor map high quality, just one hydrogen bond was noticed between the aspect chain of R3768.60b in H8 and D312 within the Gβ subunit (Fig. 2f–i, Supplementary Fig. 4d).
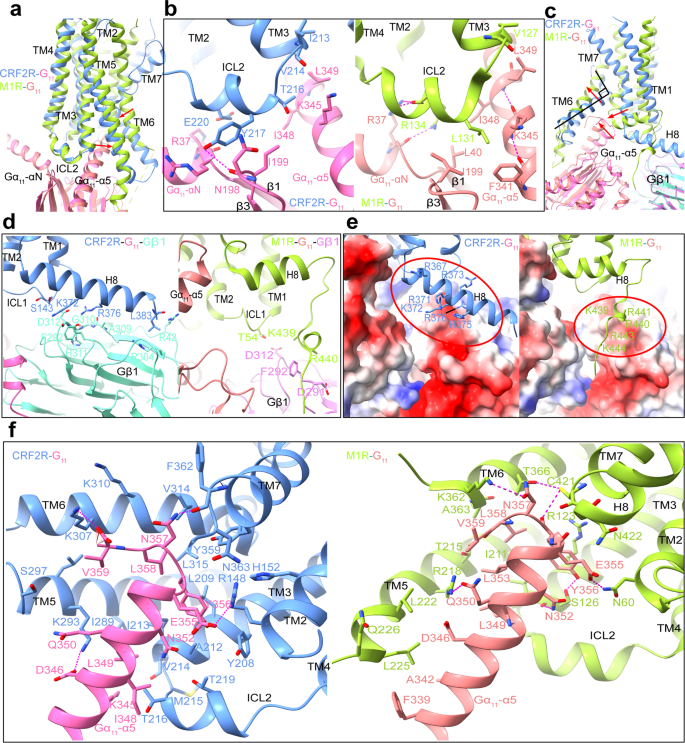
Apart from our CRF2R-G11 complicated construction, G11-coupled muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 1 (M1R) and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) encodes GPCR US28 are the one two obtainable G11-bound GPCR buildings (PDB: 6OIJ and 7RKF)37,38. Solely US28-G11 is in GDP-bound kind, whereas each CRF2R-G11 and M1R-G11 complexes are nucleotide-free. The nucleotide-free G11 in M1R-G11 and CRF2R-G11 complexes share a number of widespread structural options, however present clear variations in conformational particulars between one another. To research how G11 {couples} to largely completely different class A M1R and sophistication B CRF2R, we in contrast our CRF2R-G11 construction with the M1R-G11 complicated construction. We noticed that TM6 and TM7 of the 2 receptors undertake largely completely different conformations of their G11 complexes. In distinction, ICL2 of each receptors kind an analogous helix when binding to G11 (Fig. 5a–c), which extensively work together with the Gα-αN helix and Gα-α5 helix of the G protein. Within the CRF2R-G11 construction, E220 ICL2 in ICL2 interacts weakly with R37 on the C-terminal finish of the αN helix of G11, whereas R134ICL2 in ICL2 of M1R kinds robust hydrogen bond with R37 of G11. As well as, each Y217ICL2 of the CRF2R and the associated L131ICL2 of M1R work together with the β2-β3 loop and Gα-α5 helix of G11 (Fig. 5b, Supplementary Fig. 4f). We additionally discovered variations within the C termini of the receptors and the Gβ subunit within the CRF2R-G11 and M1R-G11 complexes. Within the M1R-G11 complicated, the C terminus after H8 is prolonged right into a groove fashioned by the Ras area of G11 and the Gβ (Fig. 5d, e)37. CRF2R had a polybasic cluster in H8 that exhibits completely different mode of interplay with Gβ (Fig. 5d, e). Plainly M1R has a polybasic C-terminal cluster to have interaction Gq/11 subtype of G proteins extra effectively than class B GPCRs37. As well as, there are some conformational modifications of the Gα-αN and Gα-α5 helices relative to the receptor (Figs. 2d, 3 and 4), which can be essential for receptor activation and transducer coupling in several Gα-bound complexes.
a Superposition of CRF2R-G11 and M1R-G11 (PDB: 6OIJ) complexes. The UCN1-CRF2R-G11 construction is coloured cornflower blue (CRF2R), scorching pink (G11) and aquamarine (Gα-β1); the M1R-G11 construction is coloured inexperienced yellow (M1R), mild coral (G11) and violet (Gα-β1). b Interplay comparability between ICL2 and G11 in CRF2R-G11 and M1R-G11 buildings. Most ICL2 aspect chains of the receptor, the aspect chains of N198, I199, and K345 of Gα11 had been truncated within the construction. The rotamers of these residues proven on this determine had been primarily based on the Rosetta-refined mannequin. c Comparability of TM6, TM7 and H8-Gβ1 conformation in CRF2R-G11 and M1R-G11 complicated. d Interactions comparability between CRF2R H8-Gβ1 and M1R H8-Gβ1. The aspect chains of K372, and D379 of the receptor, and R42 and D312 of Gβ1were truncated within the construction, whose rotamers proven on this panel was from the Rosetta-refined mannequin. e Comparability of positively charged residues in H8 of CRF2R, on the C-terminus of M1R and electrostatic floor potential of G protein. f Comparability of the Gα11-α5-TMD interactions within the CRF2R-G11 and M1R-G11 buildings. Hydrogen bonds are proven as purple dashed strains. Most aspect chains of the receptor, and people of K345, D346 and E355 of Gα11 had been truncated within the construction. The rotamers of these residues proven on this determine had been primarily based on the Rosetta-refined mannequin.
Comparability of the G protein-binding pockets
Within the UCN1-CRF2R–G protein buildings, an outward shift of TM6 on the intracellular aspect of the receptor kinds a pointy kink, producing a standard binding pocket for G protein coupling, the place the C terminus of the Gα-α5 helix binds to the receptor (Fig. 3a, b). Though CRF2R shares a standard binding pocket for coupling to completely different Gα subunits, the flexibility of coupling is completely different. The C-terminus of the α5 helix is broadly thought-about to be a very powerful structural determinants of G protein coupling selectivity39,40. Comparability of those three buildings exhibits a transparent distinction within the orientation of the α5 helix of G11, Go and Gs relative to CRF2R. The α5 helix of Go is rotated ~8.2° away from receptor ICL2 and the α5 helix of G11 is rotated ~2.8° in the direction of receptor ICL2 in comparison with this of Gs (Fig. 4a). The sequences of the C-termini of the Gα-α5 are completely different amongst these G protein subtypes (Fig. 3c). The third and fourth to final residues are Y391 and E392 in Gs, C351 and G352 in Gi/o, and Y356 and N357 in Gq/11. These residues are much less conserved amongst G protein subtypes and are positioned on the interface with TM5-6, the C-terminus of TM7 and the N-terminus of H8 of the receptor. The measured interplay interface fashioned between CRF2R and the α5 C terminus (residues G.H5.16 to G.H5.26) is bigger for Gs (792.7 Å2) than for G11 (524.7 Å2) and Go (447.7 Å2) (Fig. 3d–f). The bulkier aspect chains of Y391 and E392 in Gs can kind the most important interplay interface between CRF2R and the Gs-α5 C terminus (Fig. 3g–i). Due to this fact, class B GPCRs carry out their physiological actions primarily by coupling to Gs. It may be defined by the truth that the G protein–binding pocket of sophistication B GPCRs prefers to accommodate primarily the bulkier C-terminus of the α5 in Gs, however can nonetheless couple to the much less bulkier C-terminus of the Gq/11-α5 and Gi/o-α541, according to the significance of the Gα C-terminus for G protein selectivity determinants39.
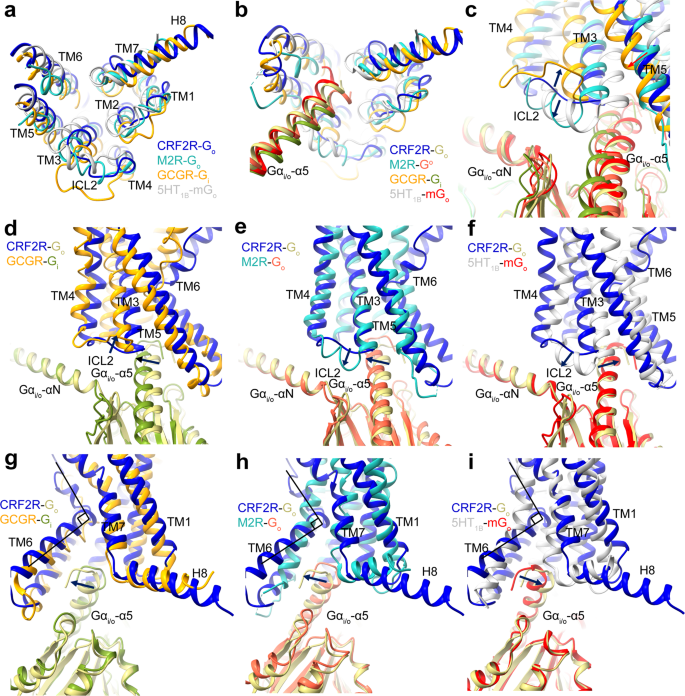
To accommodate the Gα-α5 helix, the cytoplasmic finish of TM6 has a pointy kink as noticed in all class B GPCR–G complicated buildings21,30,31,32,33,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48, together with the CRF2R-G11 and CRF2R-Go complexes (Fig. 3b), and the GCGR-Gi buildings (PDB: 6LML)41 (Fig. 6g). The interface residues from the receptor cytoplasmic cavity that contact the C terminus of the α5 helix are extremely conserved amongst class B GPCRs, suggesting a standard mechanism of G protein coupling by class B GPCRs. Comparability of the CRF2R-G11 and CRF2R-Go buildings with class A GPCR buildings, together with the M1R-G11 construction (PDB: 6OIJ)37, the M2R-Go construction (PDB: 6OIK)37 and the 5HT1B-mGo construction (PDB: 6G79)49, reveal completely different positioning of TM6 amongst these complexes (Figs. 5c and 6h–i). The completely different conformations of TM6 in these receptors permit completely different anchoring of the α5 helix of Gα into their distinct cytoplasmic pockets41 (Figs. 5a and 6a, b).
a–c Comparability of the TMD conformation, the place of the Gα-α5 helix C terminus and the ICL2 conformation within the Go and Gi-bound GPCR buildings. The CRF2R-Go construction is coloured medium blue (CRF2R) and darkish khaki (Go); the M2R-Go construction is coloured mild sea inexperienced (M2R) and tomato (Go) (PDB: 6OIK); the GCGR-Gi construction is coloured orange (GCGR) and olive drab (Gi) (PDB: 6LML); the 5HT1B-mGo construction is coloured silver (5HT1B) and purple (mGo) (PDB: 6G79). d Comparability of the ICL2 conformational change within the CRF2R-Go and GCGR-Gi buildings. e Comparability of the ICL2 and Gα-α1 conformational change within the CRF2R-Go and M2R-Go buildings. f Comparability of the ICL2 and Gα-α1 conformational change within the CRF2R-Go and 5HT1B-mGo buildings. g Comparability of the Gα-α5-TM6 interactions and the H8 conformational change within the CRF2R-Go and GCGR-Gi buildings. h Comparability of Gα-α5-TM6 interactions and the H8 conformation change within the CRF2R-Go and M2R-Go buildings. i Comparability of Gα-α5-TM6 interactions and the H8 conformation change within the CRF2R-Go and 5HT1B-mGo buildings.
Conformational variations in ICL2 decide G protein recognition and specificity
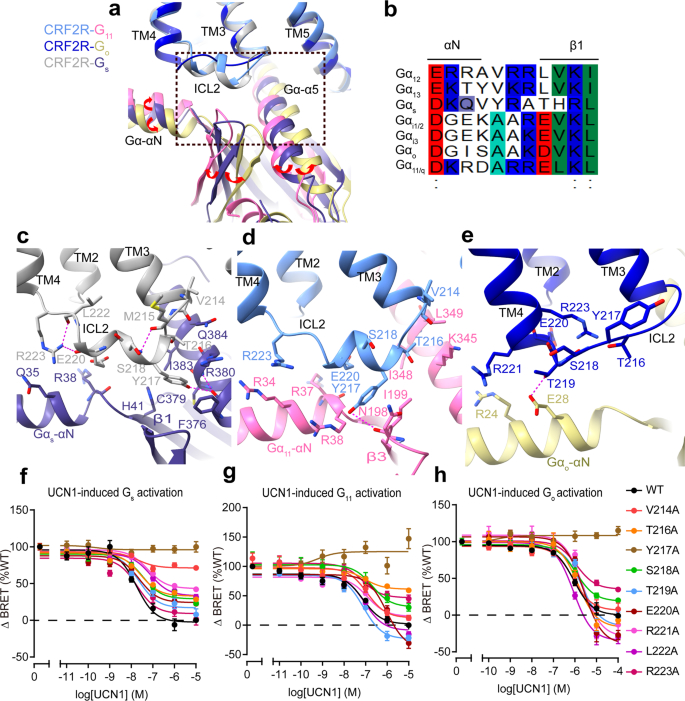
For many receptors, coupling selectivity is principally decided by the Gα-α5 helix and the Gα subunit core39,40. Along with the α5 helix, we additionally observe variations within the place of the Gα-αN and β1 strand of Gα, each components work together with ICL2 of the receptor. In contrast with the Gs-bound construction, the αN helix and β1 strand of Gα shifted away from the receptor ICL2 within the Go-bound construction and shifted in the direction of the receptor ICL2 within the G11-bound construction (Fig. 4a). This motion are related to the completely different conformations of the Gα-ICL2 interfaces of the receptor within the complexes with completely different G protein subtypes. The receptor ICL2 kinds probably the most in depth interactions with Gs and the least interplay with Go, in receptor-G protein complexes (Fig. 4c–e). The distinct conformational modifications of ICL2 in these three UCN1-CRF2R-G protein buildings might play key roles in G protein recognition and specificity.
Comparability of the three UCN1-CRF2R-G protein buildings exhibits clearly completely different conformations of ICL2 which might be doubtless induced by the completely different Gα-ICL2 interfaces. ICL2 within the CRF2R-G11 and CRF2R-Gs buildings adopts a brief helix that kinds in depth interactions with G11 and Gs (Fig. 4a, c, d). The ICL2 of the receptor within the Go complicated, nevertheless, adopts a loop and kinds a smaller interface with Go. Whereas ICL2 of the receptor in Go complicated is 4 residues shorter, the receptor TM4 is one helical flip longer than that within the complexes of Gs and G11. The prolonged TM4 within the CRF2R-Go construction offers extra interface that appears a compensation for the smaller G protein binding interface with the shorter loop of ICL2 (Fig. 4a, e).
Within the Gs-bound construction, ICL2 kinds in depth interactions with αN, the β1 strand and the α5 helix. The receptor residues T216ICL2, Y217ICL2, E220ICL2 and R2234.41b kind a polar interplay community with the αN helix, the β1 strand and the α5 helix. Y217ICL2 on the center of this helix, which is conserved within the CRF receptor household, inserts right into a cavity fashioned by the N-terminal helix and the α5 helix of Gs (Fig. 4c). Mutagenesis of Y217ICL2 to alanine in CRF2R virtually abolished coupling of Gs (Fig. 4f, Supplementary Fig. 6a, d and Desk 2). Moreover, mutations in ICL2 residues V214A3.59b, T216AICL2, S218AICL2, E220AICL2, R221AICL2, and L222AICL2 diminished Emax in Gs activation (Fig. 4f, Supplementary Fig. 6a, d and Desk 2). Within the G11–certain construction, T216ICL2, Y217ICL2, E220ICL2, R2234.41b fashioned an interface with the αN helix, the β2-β3 loop and the α5 helix of G11. Y217ICL2 fashioned hydrogen bonds with N198 (Fig. 4d, Supplementary Fig. 4e), mutation Y217ICL2A additionally abolished coupling of G11 (Fig. 4g, Supplementary Fig. 6b and Desk 2). Apart from Y217ICL2, mutations in ICL2 residues T216ICL2A, R2234.41bA, additionally diminished Emax in G11 activation. Alanine substitution of E220ICL2 confirmed clearly a fantastic discount within the efficiency of UCN1-mediated G11 activation, a much less diploma however vital discount within the efficiency of UCN1-mediated Go activation and virtually no impact on the efficiency of Gs activation (Fig.4f–h, Supplementary Fig. 6a–c and Desk 2), suggesting their vital roles in G11 protein engagement and specificity. Comparable interface of ICL2 with G11 are additionally noticed within the M1R-G11 construction (Fig. 5b)37. In all these instances, the receptor ICL2 mediates G protein recognition, which can function a serious determinant of G protein specificity.
In distinction, in CRFR-Go construction, ICL2 of CRF2R adopts an prolonged loop conformation, which is in a larger distance to the G protein and makes solely restricted contact with R24 and E28 within the αN helix of Go (Fig. 4e). Mutations of T216ICL2, Y217ICL2, S218ICL2 and R223A4.41b diminished Emax in Go activation (Fig. 4h, Supplementary Fig. 6c and Desk 2). R2234.41b of the receptor has distinct function for the interplay with completely different G proteins. Within the receptor that {couples} Gs or G11, R2234.41b is the second residue of a two-residue linker between ICL2 helix and TM4, and is on the interface with the G protein. Within the Go-coupled receptor, nevertheless, R2234.41b is positioned on the second flip of TM4, with its aspect chain forming polar interactions with ICL2 residues T216ICL2 and S218ICL2 and stabilize the ICL2 loop conformation (Fig. 4c–e). As well as, though Y217ICL2 doesn’t straight work together with the hinge area of the Go protein and is in a larger distance to the Go protein than these in G11 and Gs complexes, Y217ICL2 kinds many interactions with surrounding residues that stabilize the ICL2 conformation within the Go complicated. The Y217 ICL2A mutation doubtless destabilizes the ICL2 conformation, thus not directly have an effect on its coupling capability to Go (Fig. 4e, h, Supplementary Fig. 6c and Desk 2).
The restricted contacts between ICL2 and Go within the Go-bound CRF2R construction most definitely clarify the decrease potencies of UCN1 in stimulating Go activation and signaling when in comparison with these in Gs– and G11-coupled buildings. The same ICL2 loop conformation was noticed in GCGR-Gi construction41, one other class B GPCR that {couples} to Gi. The ICL2 loop of GCGR was positioned away from the Gi protein and its interface with Gi was weak (Fig. 6c, d). Against this, Go-coupled buildings of sophistication A GPCRs, together with M2R and 5HT1B, confirmed helical ICL2s carefully interacted with the αN helix, β2-β3 loop and the α5 helix of Go (Fig. 6c, e, f)37,50. The above observations point out that ICL2 is essential for the G protein specificity of GPCRs.
Molecular Recognition of the α5 helices of Gs, G11 and Go
Though all three energetic CRF2R-G complicated buildings are stabilized by in depth hydrophobic and polar interactions with Gα and Gβ of the G proteins, they present completely different molecular particulars within the recognition of the interactions from receptor to α5 helices of Gs, G11 and Go (Fig. 3g–i). Evaluating the popularity patterns for the α5 helix, we discovered that the cumbersome C-terminal α5 helix of Gs from Q390 to L394 kinds extra in depth polar and hydrophobic interactions with the receptor than G11 and Go. Particularly, Y391 within the C-terminus of the Gs α subunit, a key interface residue binds to a sub-pocket fashioned by R1482.46b, H1522.50b and E2053.50b, Y2083.53b, L2093.54b of CRF2R. Different interface residues are i) Gs E392, which kinds polar contacts with K3106.40b and N3638.47b of the receptor; ii) Q390 of Gs, which kinds a hydrogen bond with the side-chain of R1482.46b and iii) the C-terminal L394 of Gs, which kinds a cost interplay with K3076.37b of the receptor TM6. As well as, Q384 and R385, on the center of Gs-α5, kinds hydrogen bond interactions with K2935.64b on the C-terminus of the receptor TM5 and S297 ICL3, respectively (Fig. 3g). Total, the Gαs-α5 helix extensively interacts with TM2, TM3, TM5, TM6, ICL2 and ICL3, and the TM7-H8 junction of the receptor.
In comparison with that within the construction of Gs-coupled CRF2R, the C-terminal α5 helix of G11 kinds comparatively few polar and hydrophobic contacts with the interface of CRF2R. Residues D346, L349, E355, Y356 and N357 on the α5 helix of G11 are essential for the interplay with each CRF2R and M1R (Fig. 5f, Supplementary Fig. 4e). They kind giant polar and hydrophobic interplay networks with the receptor. A hydrogen bond interplay is noticed between CRF2R TM5 residue K2935.64b and D346 on α5 of G11, which is conserved within the interactions with Gs (corresponding residue D381) and Go (corresponding residue D341). The carboxyl group of the C-terminal V359 of G11-α5 can also be noticed to kind a hydrogen bond with receptor residues K3076.37b and weak K3106.40b. As well as, E355 and N357 of G11-α5, kinds an electrostatic interplay with R1482.46b and a hydrogen bond contact with F3627.60b, respectively (Fig. 3h, Supplementary Fig. 4e), all are essential for stabilizing the interface of α5 of G11 with TM2, TM3, TM5, TM6 and TM7 of the receptor.
In distinction, the C-terminal helix of Go kinds the fewest interactions with the receptor. D341 of Go-α5, comparable to D346 of G11, kinds hydrogen bonds interactions with K2935.64b. The C-terminal residue Y354 of Go exhibits interactions with residues K2935.64b and kinds a hydrogen bond interplay with the aspect chain of S297ICL3 of the receptor (Fig. 3i). Mutation of S297ICL3A very abolished UCN1 efficiency on Go signaling (Supplementary Figs. 5h, 6c and Desk 2). C351 of Go-α5, comparable to Y391 of Gs, has no cumbersome hydrophobic aspect chain. C351, due to this fact, kinds solely weak contacts with L2093.54b and I2133.58b on TM3 of the receptor. That is notably completely different to Y391 in Gs that wants a bigger sub-pocket within the receptor TM bundle. L353 of Go-α5 interacts with the hydrophobic residues I2133.58b, I2865.57b, I2895.60b, L3156.45b from TM3, TM5 and TM6, respectively (Fig. 3i). These hydrophobic interactions are essential for Go activation, and their key roles in Go activation had been confirmed by our mutagenesis research. All of alanine mutations of those hydrophobic residues drastically diminished Go activation. Specifically, L3156.45bA very abolished UCN1 efficiency on Go signaling (Supplementary Fig. 5h, i, 6c and Desk 2).
To review these essential G protein subtype-specific interactions with the receptor (Supplementary Fig. 6e), we assessed UCN1-induced G protein subtype activation by serially mutated CRF2R utilizing G protein dissociation assay and UCN1-induced cAMP accumulation assay (Supplementary Figs. 5, 6 and Desk 2). Though the popularity patterns of the C-terminal α5 helix of Gα by the receptor is completely different, mutations of R1482.46bA, H1522.50bA, E2053.50bA, L2093.54bA, K2935.64bA, L2945.65bA, K3076.37bA and L3156.45bA, diminished UCN1 efficiency or Emax in any G protein activation (Supplementary Figs. 5, 6 and Desk 2). These alanine mutations break the interplay networks required in any G protein activation. I2895.60bA abolished the coupling of G11 and diminished Emax in Go activation, which solely barely alters Gs activation. V3146.44bA and Y3596.45bA abolished the coupling of G11, however diminished Emax in Gs activation, which solely barely alters Go activation. Quite the opposite, L2905.60bA diminished effectivity and efficiency in Go activation, however confirmed considerably weaker results on Gs and G11 activation. Receptor residue S297ICL3 is on the interface with each Gα-α5 and β3 of any coupled G protein. Its mutation to alanine decreased UCN1 efficiency in any G protein activation and Go proteins seemed to be probably the most delicate to amino acid substitution at S297ICL3A as a result of the C-terminal residue Y354 of Go kinds a hydrogen bond with S297ICL3, which is according to S301ICL3 in CRF1R reported beforehand (Supplementary Fig. 5b, c, e, f, h, i, 6 and Desk 2)8. Because of its interplay with particular G protein residues, this Ser performs a major function in figuring out the G protein activation effectivity of the CRF receptors. Much like the M1R-G11 complicated (PDB: 6OIJ), many of the interactions occurring between TM5 and TM6 of CRF2R and above recognized G11 residues could also be vital for stabilizing the conformations of those TM segments for optimum interactions with the C terminus of the G protein (Fig. 5f).