World transcriptomic evaluation
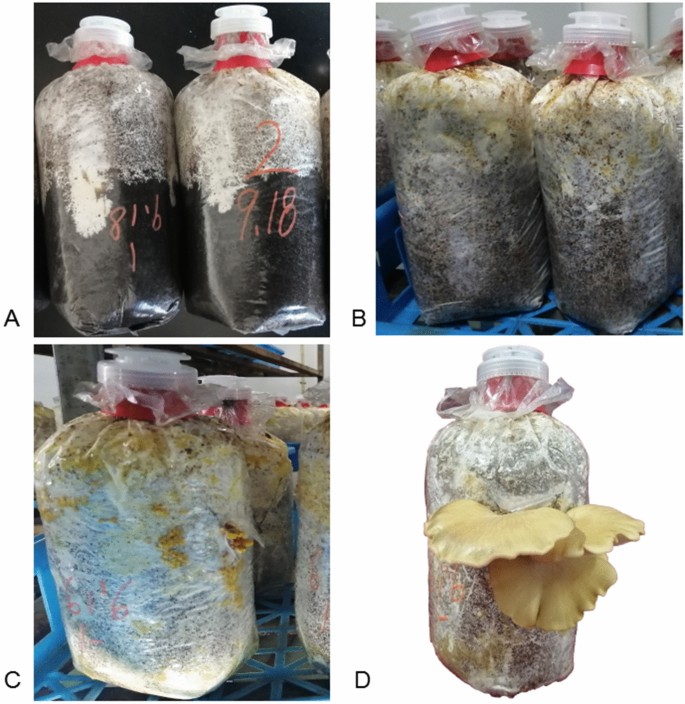
To characterize gene expression patterns throughout improvement, 18 libraries have been constructed utilizing samples from the six developmental levels of S. edulis (Fig. 1). A complete of 774.59 million uncooked reads have been generated by Illumina paired-end sequencing. Which is 150 base pair by paired finish sequenced. After cleansing and high quality checks, 742.29 million clear reads have been obtained, averaging 41.23 million reads per replicate (Suppl. Desk S1). Greater than 77.56% of the reads per replicate may very well be mapped to the S. edulis genome. The Q30 share of all sequences within the 18 libraries was over 91%.
Gene expression evaluation
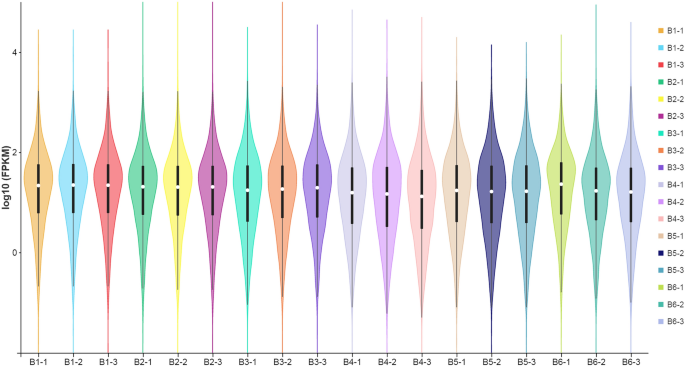
Values of FPKM larger than 1 point out that the gene is expressed, and better FPKM values point out larger expression. The gene expression evaluation outcomes revealed that the median of the 18 samples was comparable in values, and the log10 FPKM values ranged from 3.82 to 4.59. The gene expression ranges have been highest within the B2 stage (log10 FPKM, 16.13) (Fig. 2; Suppl. Desk S2).
Violin map of horizontal distribution of gene expression (FPKM) in numerous samples. The abscissa is the title of the pattern, and the ordinate is log10 (FPKM). The values from high to backside symbolize the utmost, the higher quartile, the median, the decrease quartile and the minimal in flip. The width of every violin represents the variety of genes underneath the identical expression.
Identification of differentially expressed genes throughout varied developmental levels
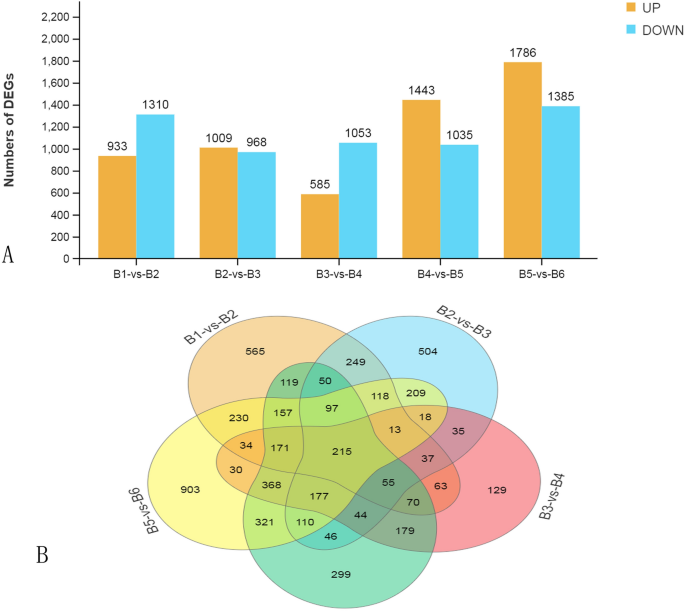
The very best variety of DEGs was noticed between the B5 and B6 levels (3,171), adopted by B4 versus B5 (2,478) and B1 versus B2 (2,243) (Fig. 3A). These outcomes indicated that the expression profiles in B4 and B6 differed significantly in comparison with B5. The best variety of distinctive DEGs have been noticed within the B5 versus B6 comparability (903). However, solely 153 DEGs have been distinctive to the B3 versus B4 comparability (Fig. 3B). There have been 215 shared DEGs amongst all 5 carried out comparisons between the six levels. These have been primarily enriched within the GO class response to catalytic exercise (GO:0003824) (Suppl. Fig. S2).
Purposeful classification of the differentially expressed genes
All DEGs have been labeled into three classes: organic course of (BP), mobile element (CC), and molecular operate (MF). The considerably enriched phrases of the DEGs within the B1 vs. B2, B2 versus B3, B3 versus B4, B4 versus B5, and B5 versus B6 comparisons have been extremely comparable (Suppl. Fig. S3A–E).
The DEGs have been mapped to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database to judge their features. The considerably enriched pathways of the DEGs within the B1 versus B2, B2 versus B3, B3 versus B4, B4 versus B5, and B5 versus B6 comparisons shared excessive similarity. All of the considerably enriched pathways have been assigned to “world and overview maps” and “carbohydrate metabolism” throughout the “Metabolism” pathways (Suppl. Desk S3).
Gene co-expression networks building
The minimal energy worth was utilized in subsequent analyses when the correlation coefficients reached their plateau values (or values larger than 0.8; as proven on the left of Suppl. Fig. S4). We decided the modifications in common gene connectivity underneath totally different energy values (as proven on the correct of Suppl. Fig. S4). The minimal energy worth of 8 was used for the next evaluation.
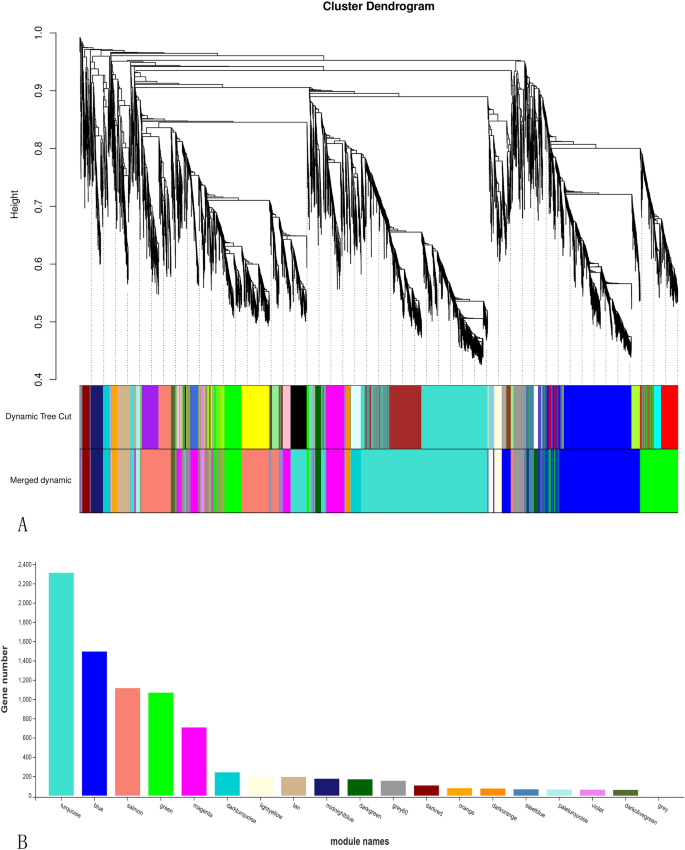
The 19 modules (marked with totally different colours, Fig. 4A), every akin to a department of the gene clustering tree, have been analyzed. The 19 modules correlated with totally different levels of improvement, indicating that the expression profiles have been developmental stage-specific. The variety of genes in every module is proven in Fig. 4B. The very best variety of genes (2,312) was noticed within the turquoise module, whereas the bottom (1 gene) was noticed within the grey module.
Nineteen totally different modules recognized. (A) Gene co-expression community gene clustering quantity and modular chopping. Dynamic Tree Lower is the module divided in keeping with clustering outcomes. Merged Dynamic is the module division of merged modules with comparable expression patterns in keeping with module similarity. The next evaluation is carried out in accordance with merged modules. Within the case of timber, the vertical distance represents the gap between two nodes (between genes), and the horizontal distance is meaningless. (B) Variety of genes per module. The abscissa represents every module, and the ordinate represents the variety of genes.
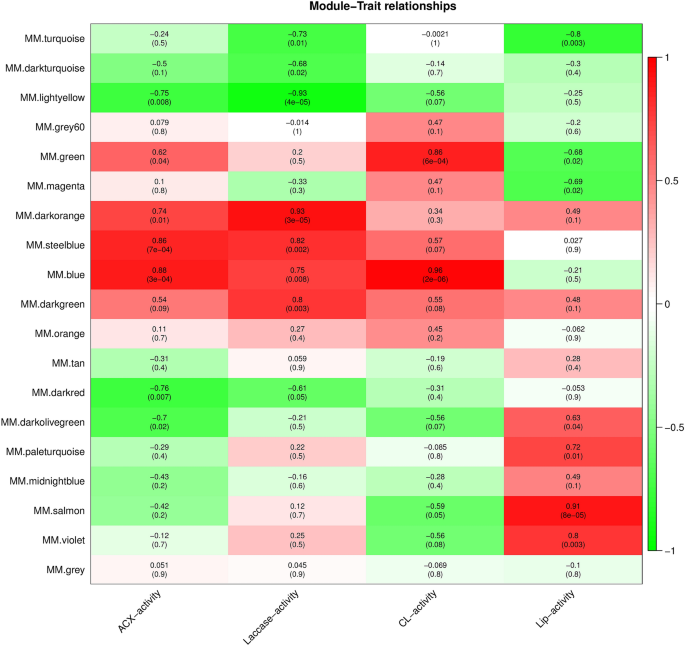
Correlation analyses between module eigenvalues and particular traits and phenotypic information have been carried out to determine the modules with the best potential associations with traits and phenotypes. Correlation analyses have been carried out between 4 physiological and biochemical traits (laccase, acidic xylanase (ACX), cellulase (CL), and lignin peroxidase (Lip) actions) of the samples with the above modules underneath totally different developmental levels (Suppl. Desk S4). Sure modules have been extremely correlated with physiological and biochemical traits (Fig. 5). For instance, the blue module was considerably positively correlated with CL and ACX (r = 0.96, r = 0.88, respectively). Moreover, a major constructive correlation was noticed between the darkish orange module and laccase (r = 0.93), laccase and ACX (r = 0.82, r = 0.86), the salmon module and Lip (r 128 = 0.91), and the salmon module and Lip (r = 0.91).The genes in these 4 modules have been additional evaluated.
Affiliation evaluation of gene co-expression community modules with physiological and biochemical traits. The horizontal axis represents totally different traits, and the vertical axis represents every module. The pink lattice represents a constructive correlation between the physiological traits with the module, whereas the inexperienced lattice represents a adverse correlation.
GO annotation of goal modules
We mapped the genes in every module to the GO database (http://www.geneontology.org/), to additional discover their operate. We calculated the variety of genes for every time period to acquire the checklist of genes and statistics related to the GO features. The genes in these 4 modules have been considerably enriched in a number of GO pathways in BP, MF, and CC (Suppl. Fig. S5). They have been enriched in “catalytic exercise” and “binding”, indicating that WGCNA successfully labeled genes into biologically important co-expression modules. These modules have been the main target of our subsequent research.
Screening and purposeful evaluation of key genes in goal modules
The standard attribute of a scale-free community is that the majority nodes within the community are solely related with a small variety of nodes, and just a few are related with most. Due to this fact, these nodes are the important thing nodes to determine, containing the so-called hub genes. These hub genes have a excessive diploma of connectivity of their modules, making them biologically extra significant than different nodes. The genes with MM worth > 0.8 and P < 0.01 have been screened from the above 4 modules as hub genes. Blue, darkgreen, lightcyan1 and cyan modules contained 675, 146, 175, and 131 hub genes, respectively. Then these hub genes have been in comparison with the CAZY database (http://www.cazy.org, particular for carbohydrate enzyme genes)20, which additional decreased the variety of key genes to 64. Lastly, mixed with the annotation of NR, GO, and KEGG databases, a complete of 12 key genes doubtlessly associated to lignocellulose degradation exhibiting the best correlations with the goal traits, have been chosen from the 4 modules (Desk 1). 11 key genes have been recognized from the blue module, and 1 key gene have been recognized from the steelblue module.
The 12 key genes are proven in Desk 1. They have been all annotated to the CAZy database, indicating that all of them encode carbohydrate enzymes. This additional confirmed the robustness of our evaluation. Six genes belonged to the AA (auxiliary exercise) household, six to the GH (glycoside hydrolase) household. one to the CBMs (Carbohydrate-Binding Modules) household, and one to the PLs (Polysaccharide Lyases) household. Amongst these, 5 endoglucanases and two exoglucanases have been recognized, that are cellulose-degrading enzymes21. There was one manganese peroxidase and two laccases, that are lignin-degrading enzymes22. One pyranose dehydrogenase was recognized, which features as an auxiliary enzyme of a lignin-degrading enzyme23. There was additionally one arabinofuranase that’s concerned in hemicellulose degradation24.
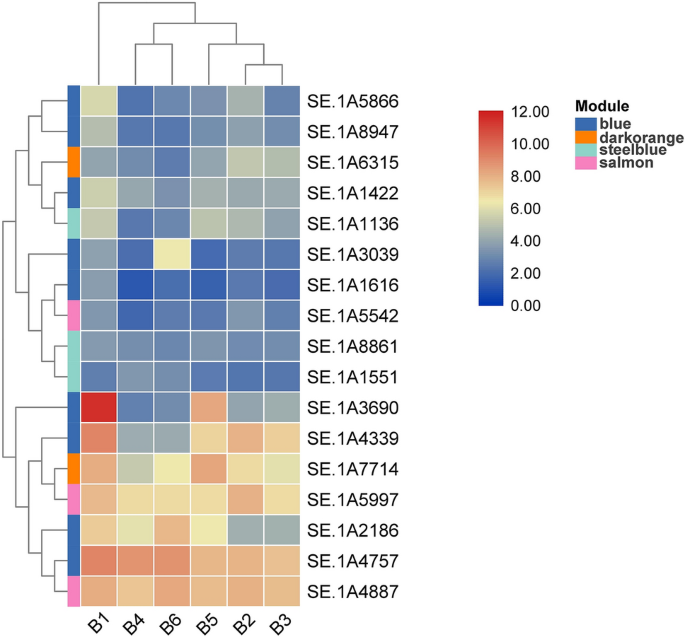
Differential expression of lignocellulose degradation-related genes
The differential expression of 12 genes described above was analyzed by TBtools (Model: 0.674) (https://github.com/CJ-Chen/TBtools/releases)25 (Fig. 6). SE.1A3347 and SE.1A4339 have been clustered collectively and exhibited excessive expression ranges in all six levels. SE.A1616, SE.1A1237, SE.1A8861, and SE.1A9306 have been clustered collectively and exhibited low expression. When evaluating the six developmental levels, most genes have been comparatively extremely expressed in A1, indicating that they have been considerably correlated with lignocellulose degradation. SE.1A8947 and SE.1A9306 are each laccase enzymes clustered collectively, indicating that they train their organic features collectively.
Screening and purposeful evaluation of transcription components (TFs) in goal modules
Utilizing the filtering technique described in “Screening and purposeful evaluation of key genes in goal modules” part, mixed with the plant transcription issue database (http://planttfdb.gao-lab.org/), a complete of 37 TFs doubtlessly associated to lignocellulose degradation have been recognized from the 4 modules exhibiting the best correlations with the goal traits (Desk 2). They belong to eight forms of TF households, specifically bHLH (primary helix loop helix dimerization area), bZIP (primary leucine zipper), C2H2 (zinc finger sequence incorporates two cysteines and two histidines), C3H (Cys3His zinc finger area), GATA (proteins that work together with conserved WGATAR motifs), HB (homeo field), MYB (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog) and NF-YB (nuclear factor-YB). The bZIP household was essentially the most populous, with 10 transcription components, and the HB household the least, with 2 transcription issue.
Validation of DEGs by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
To confirm the reliability of the transcriptome information, eight DEGs associated to lignocellulose degradation have been chosen for qRT-PCR evaluation (Suppl. Fig. S6). The expression patterns of the chosen eight genes evaluated with qRT-PCR have been in line with the expression patterns through the six developmental levels. Nevertheless, a couple of genes differed at sure levels. These disparities perhaps attributable to the methodological variations between transcriptome sequencing and qRT-PCR, which have been proven to have a sure diploma of inconsistency (roughly 30–40%)26. Due to this fact, general the outcomes thus didn’t exceed the anticipated vary of deviation, because the qRT-PCR outcomes have been in line with the transcriptome information for many genes.