Characterization of nanoparticles
Though the emphasis of this work was on antiviral results of CeO2 nanomaterials, nanoparticles of Ag and SiO2 have been added to the testing as controls for a usually authorised antiviral agent and an inert nanoparticle (Desk 1). Acknowledging the significance of nanoparticles floor of their organic results, nano-CeO2 have been synthesized with two totally different states of floor, these with almost “naked” floor carrying massive constructive cost (nano-CeO2(+)) and nanoparticles stabilized by citric ions and, thereby presenting negatively charged floor (nano-CeO2(−)). Nano-CeO2(+) have been synthesized at maximal focus of 6500 mg Ce/l (ca. 45 mM) and nano-CeO2(−) at 8200 mg Ce/l (ca. 60 mM). Hereafter, in described experiments, mg/l focus for investigated compounds at all times refers to milligrams per liter of the aspect, i.e. Ce, Ag or Si.
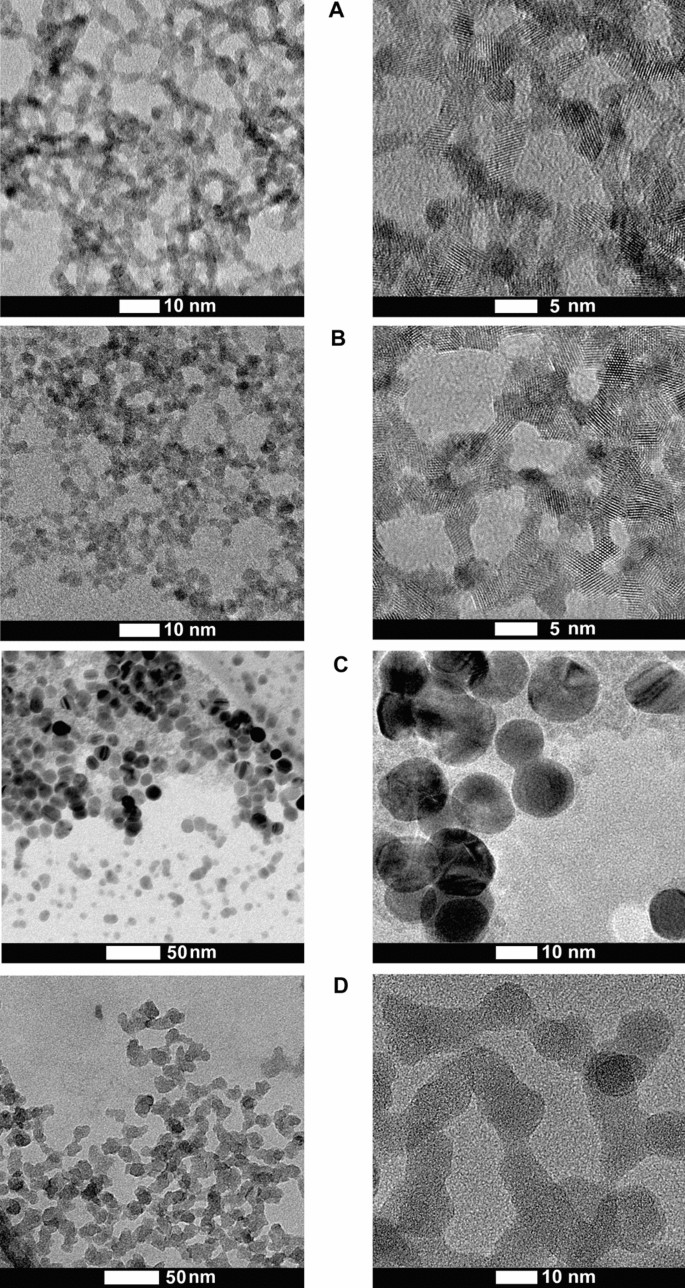
As synthesized, nano-CeO2(+) and nano-CeO2(−) shaped steady aqueous colloids on account of their massive (+ 41 mV or − 53 mV, respectively) ζ-potential (Desk 1). In keeping with excessive decision transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) (consultant TEM photographs of CeO2 nanoparticles are proven on Fig. 1), the typical particle measurement of each, nano-CeO2(+) and nano-CeO2(−) was shut to three nm (Fig. S1). Dynamic mild scattering-measured hydrodynamic measurement of nano-CeO2(−) decided at highest examined antiviral focus was comparatively near the particles major measurement (Desk 1) and solely nano-CeO2(+) confirmed some aggregation. Apparently, with lower in nano-CeO2 focus obvious improve in particle measurement and thus, the chance for aggregation was noticed with lowering particle focus for each, nano-CeO2(+) and nano-CeO2(−), whereas the latter was extra delicate to dilution-mediated instability (Fig. S2). We advise that desorption of stabilizing citric ions from the floor of nanoparticles upon dilution of colloid result in the thinning of nanoparticles double electrical layer and deteriorated colloidal stability.
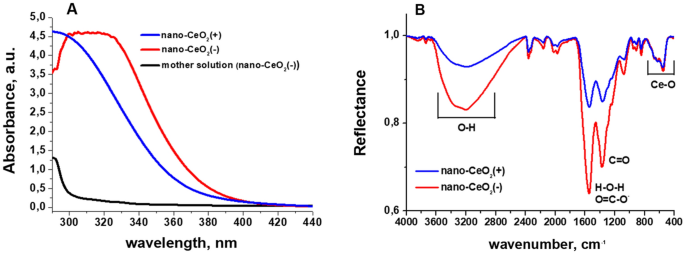
UV–Vis spectra of CeO2 nanoparticles (Fig. 2A) confirmed that in comparison with nano-CeO2(+) the elemental absorption fringe of nano-CeO2(−) was roughly 10 nm pink shifted. Additionally, visibly, the colloid of nano-CeO2(−) confirmed a deeper yellow colour in comparison with nano-CeO2(+). This distinction in shift of absorption edge could also be as a result of totally different Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratio on the floor of nanoparticles, or originate from oxidized and polymerized citrate ions on the floor of nano-CeO2(−) particles, as a remnant of the synthesis course of. The seeming “drop” of the absorption of nano-CeO2(−) colloid under 300 nm is a compensation error on account of a symmetric rise of absorption of the mom resolution (the liquid remaining after centrifugation of nanoparticles) of this colloid precipitated, almost certainly, by a excessive focus of citrate ions and merchandise of their oxidation and/or complexing with cerium ions. Infrared (IR) spectrum of the synthesized nano-CeO2 (Fig. 2B) is in settlement with the literature knowledge40 and displays peaks in round 3600 to 3200 cm−1, which correspond to –OH stretching of absorbed water and floor OH-groups. Peaks round 1600 cm−1 and 1400 cm−1 are H–O–H deformational vibrations and C–O stretching vibrations from floor water molecules and carbonate ions, respectively. The height from 700 to 500 cm−1 is because of Ce–O stretching vibrations. The variations between nano-CeO2(+) and nano-CeO2(−) spectra are primarily intensities of peaks round 1600 cm−1 and 1400 cm−1, which in case of nano-CeO2(−) correspond additionally to COO– group vibrations of absorbed citrate ions41. Additionally we noticed a small blue-shift of the band from 1539 cm−1 nano-CeO2(+) to 1546 cm−1 for nano-CeO2(−), which might be on account of summing of H–O–H deformational vibrations with anti-symmetric COO– group stretching band with most needs to be round 1585 cm−1 based on literature knowledge41. Along with DLS knowledge, UV–Vis and IR-spectroscopy clearly present, that regardless of very shut imply particle measurement, form, and measurement distribution parameters, nano-CeO2(+) and nano-CeO2(−) particles are chemically and electrostatically moderately totally different and, due to this fact, we are able to anticipate from them totally different impact on organic objects. The experimentally established (by way of ICP-MS) concentrations of Ce3+/Ce4+ ions in supernatants from 1.4 × 10–2 M (2000 mg Ce/l) CeO2 colloids have been moderately low: 8 × 10–5 M (12 mg Ce/l) for CeO2(+) and 1.7 × 10–4 M (24 mg Ce/l) for CeO2(−). These values are but considerably greater than literature knowledge42, which needs to be within the vary of 10–7–10–8 M, in water at impartial pH vary, and doubtless are the results of incomplete separation of the nanoparticles. Nonetheless, even measured focus ought to have minimal impact on the viruses.
The synthesis of nano-Ag was carried out by means of seed-mediated citrate route and the utmost focus reached was 480 mg/l (corresponds to 4.4 mM). Nano-SiO2 was synthesized utilizing Stöber approach and the utmost focus reached for amorphous silica nanoparticles was 3100 mg/l (corresponds to 110 mM). Each, nano-Ag and nano-SiO2 particles have been spherical with common major measurement round 15 nm (Desk 1). In keeping with hydrodynamic measurement and DLS evaluation, nano-Ag remained in non-aggregated state whereas nano-SiO2 exhibited a sure degree of aggregation and formation of two–10 nanoparticle aggregates. The floor ζ-potential of nano-Ag and nano-SiO2 particles was adverse (− 52 ± 5 and − 34 ± 3 mV, respectively) being similar to nano-CeO2(−), thus permitting the comparability of their organic results. Sadly, we have been unable to synthesize neither silica nor silver nanoparticles with major measurement similar to CeO2 nanoparticles with out the addition of sturdy surfactants that may have their very own pronounced antimicrobial properties.
Antiviral exercise of CeO2 nanoparticles
For the demonstration of antiviral efficiency of nano-CeO2, nano-SiO2 and nano-Ag, we analyzed the lower of infective counts (expressed as plaque forming models, PFU) of 4 mammalian viruses and two bacteriophages after 1-h contact with nanoparticles. Nano-CeO2 with each constructive and adverse floor ζ potentials have been used to know the impact of CeO2 floor of their antiviral exercise. To rule out the chance that the antiviral exercise is just as a result of nanometer scale particle measurement, parallel antiviral exercise testing was carried out with supposedly biologically inert, low toxicity SiO2 nanoparticles. Conversely, nano-Ag particles which are extensively thought-about to exhibit antiviral impact, have been examined as constructive controls in antiviral assessments (see Desk 2). Regardless of the very low potential CeO2 solubility, we additionally examined the antiviral impact of soluble Ce(III) compound Ce(NO3)3 as a supply of Ce3+ ions. Though each, Ce3+ and Ce4+ ions might kind at low focus throughout the dissolution of CeO2, Ce3+ ions have been used on account of their greater chance of presence42.
Our choice of viruses included mammalian and bacterial, each enveloped and non-enveloped viruses (Desk 2). Usually, enveloped viruses surrounded by a lipid membrane have been thought-about extra delicate to inactivation by numerous environmental circumstances than non-enveloped viruses possessing solely a proteinaceous capsid43. Pathogenic viruses can belong to both of those teams, due to this fact, a lot of the antiviral testing requirements foresee the inclusion of each sorts of viruses44,45. The enveloped mammalian viruses used on this research included influenza virus46, SARS-CoV-2 and TGEV47, and picornavirus EMCV was used as a mannequin of the non-enveloped mammalian viruses48. Enveloped Ф649 and non-enveloped MS250 have been used as respective bacterial virus (bacteriophage) examples. Each of these phages have been advised as fashions for antiviral testing51,52,53,54. In case of all of the viruses, publicity to nanoparticles was carried out in sterile water or extremely diluted progress medium over 1 h. The numbers of infectious viral particles with and with out therapies have been expressed as plaque forming models (PFU/ml).
Previous to antiviral exercise testing, the impact of all of the examined compounds was studied on viral host cells. Many of the examined compounds and concentrations have been non-cytotoxic to the host cells of mammalian viruses (Fig. S3). Solely the best examined concentrations of nano-Ag, Ce(NO3)3 or SiO2 decreased the viability of a number of the host cell strains, which nonetheless didn’t intrude with antiviral assays, the place the concentrations of these compounds didn’t attain the poisonous ranges. Aside from nano-Ag not one of the compounds affected the expansion of host micro organism of bacteriophages. As nanosilver is well-known for its antibacterial results, its bacterial toxicity that was noticed from 14 μM (1.5 mg/l) was not a shock. To have the ability to research the results of nano-Ag in the direction of bacteriophages, its bacterial toxicity was neutralized by the addition of threefold molar extra of l-cysteine to the an infection response instantly previous to the plaque assay step.
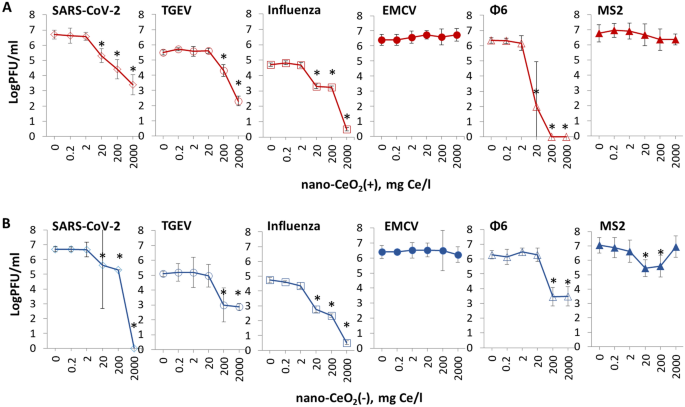
The outcomes of antiviral assay confirmed that regardless of being non-toxic to mammalian cells and micro organism, nano-CeO2 affected the infectivity of a lot of the mammalian viruses and bacteriophages (Fig. 3). Vital lower (p ≤ 0.05) of viral infectivity on account of 1-h nano-CeO2(+) publicity was noticed ranging from 20 mg/l in case of SARS-CoV-2, influenza virus and ф6, and ranging from 200 mg/l in case of TGEV (Desk 3). Not one of the non-enveloped viruses confirmed vital lower in infectivity for nano-CeO2(+) as much as 2000 mg/l. Nano-CeO2(−) affected the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus ranging from 20 mg/l and the infectivity of TGEV and ф6 ranging from 200 mg/l (Desk 3). Following the pattern of nano-CeO2(+), non-enveloped viruses confirmed the bottom sensitivity in the direction of nano-CeO2(−). EMCV infectivity was not affected by nano-CeO2(−) as much as 2000 mg/l, and the response of non-enveloped bacteriophage MS2 to nano-CeO2(−) was non-monotonic in order that 20 and 200 mg/l of the compound decreased the infectivity, however no impact was noticed at 2000 mg/l. Such a non-monotonic impact on antiviral exercise couldn’t be defined by rising aggregation degree of CeO2 at greater focus as based on hydrodynamic measurement measurement, as nano-CeO2 have been non-aggregated at greater concentrations and particle aggregation and instability elevated with dilution degree of the particles (Fig. S2). Non-monotonic response has been proven additionally for different sorts of nanomaterials. For instance, TiO2 displays non-monotonic UV light-induced toxicity to freshwater organisms55. In case of CeO2 nanoparticles, earlier experiences might be discovered on non-monotonic toxicity in the direction of soybean crops56, nonetheless, its precise causes are nonetheless to be clarified.
The impact of nano-CeO2(+) (A) and nano-CeO2(−) (B) on viral plaque forming exercise (log PFU/ml). Enveloped mammalian viruses and bacteriophages are proven with open symbols; closed symbols signify non-enveloped mammalian viruses and bacteriophages. The variations in preliminary viral titers are brought on by totally different viral yields in laboratory circumstances. *p < 0.05.
Though we proposed that as a result of chemical and electrostatic variations between the floor of nano-CeO2(+) and nano-CeO2(−) these nanoparticles might exhibit totally different organic results, our outcomes confirmed no notable variations between the antiviral properties of these two sorts of particles (Desk 3).
Comparability of our outcomes on antiviral properties of nano-CeO2 with earlier experiences is moderately tough as a result of variable nature of the nanoparticles, in addition to strategies used for antiviral exercise evaluation. Nonetheless, sure comparisons could also be made. For instance, in a 2010 research, 2 log discount of enveloped Enterobacter aerogenes infecting bacteriophage UZ1 PFUs was noticed after its 2-h publicity to 50 mg/l CeO2 whereas 500 mg/l of CeO2 was adequate to lower infectivity by 4 logs57. Mohamed et al.31 confirmed that 14 nm sized nano-CeO2 at concentrations lower than 50 mg/l eliminated all of the infectious viral particles (PFU) of kind 1 Sabin-like poliovirus and the authors even advised CeO2 nanoparticles as an alternative choice to therapy of polio an infection. But there are additionally experiences displaying no impact by CeO2 nanoparticles on viruses. In keeping with Neal et al.58 200 mg/l of CeO2 nanoparticles didn’t have any vital impact on infectivity of human coronavirus OC43 or rhinovirus RV14 after 6 h incubation. Nonetheless, after doping of CeO2 with Ag, antiviral exercise of CeO2 nanoparticles was achieved, based on authors, as a result of presence of elevated proportion of Ce(III) ions on the nanoparticles floor, in addition to the presence of silver nanoparticles, their measurement, morphology and the density of their inhabitants on CeO2 floor. General, these few articles printed up to now on antiviral efficacy of CeO2 have demonstrated comparatively variable outcomes, which can be attributed to variations in physico-chemical properties of nanoparticles, to totally different viruses used or antiviral assays utilized. Nonetheless, based mostly on the few earlier research demonstrating antiviral results of nano-CeO231,57 and the outcomes of our research, we might recommend that nanoceria has a big potential in antiviral therapies and that this potential needs to be studied and developed additional.
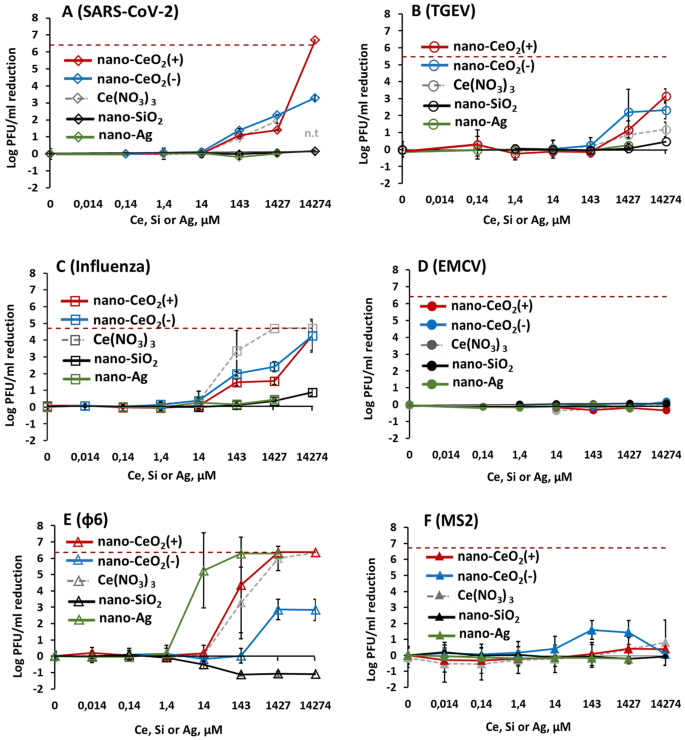
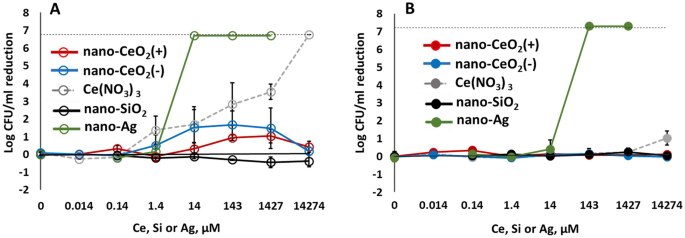
Comparability of the antiviral efficacy of nano-CeO2 compared with nano-SiO2 that was used as a adverse management, and nano-Ag used as a constructive management on account of its probably antiviral properties are proven in Fig. 4. Expectedly, the non-enveloped viruses that didn’t present any sensitivity in the direction of nano-CeO2 have been additionally not influenced by nano-SiO2 or nano-Ag (Fig. 4D,F). The inexistent antiviral impact of SiO2 nanoparticles was anticipated as silica is taken into account biologically suitable or usually considered secure59,60 and of low toxicity. We discovered no printed knowledge that may have indicated an antiviral exercise of SiO2 nanoparticles. But silica nanoparticles have been proven to impede antiviral response to norovirus an infection, decreasing the viability of macrophages61.
Antiviral exercise of all examined nanoparticles and chemical compounds expressed in µM concentrations to allow comparability. Please be aware that antiviral exercise is expressed as discount of infectious viral titer, logPFU per ml in comparison with unexposed management after 1 h. The info of nano-CeO2 are transferred from Fig. 3. (A) coronavirus SARS-CoV-2; (B) transmissible gastroenteritis virus TGEV; (C) influenza virus A/WSN/1933; (D) picornavirus EMCV; (E) bacteriophage ф6; (F) bacteriophage MS2. Closed symbols in (D,F) signify non-enveloped viruses. The outcomes of three unbiased experiments with normal deviation are proven. Observe the logarithmic scale of y-axis. Horizontal darkish pink dashed line reveals the restrict of quantification of PFU discount.
Whereas the low antiviral exercise of SiO2 was anticipated, our outcomes indicating no vital antiviral exercise of nano-Ag as much as 150 mg/l (1.4 mM), apart from bacteriophage ф6 (Desk 2) have been shocking. Earlier research have advised that nanosilver might have an effect on viruses in a wide range of methods; by means of interactions with viral floor and subsequently interfering the viral attachment to its targets, inhibition of viral penetration into host cells and even by interacting with viral genome26, and that silver nanoparticles are affecting viruses already ranging from tens of mg/l. Nonetheless, curiously, a better look to Ag nanoparticles antiviral outcomes revealed that in a lot of the research solely a comparatively small, lower than 1 log (< 90%) lower in infectivity has been noticed. Yadavalli et al.8 have proven inhibition of fifty% HIV by Ag nanoparticles between 25 and 5000 mg/l, Rogers et al.24 have demonstrated 60–80% lower in monkeypox virus plaque formation exercise within the presence of 20–2000 mg/l of Ag nanoparticles. As much as 90% inhibition of human parainfluenza virus within the presence of 0.1–9 mg/l Ag nanoparticles has been demonstrated by Gaikwad et al.62. Barely greater, as much as 2 log lower of influenza virus titer was noticed in response to 50–70 mg/l Ag nanoparticles therapy63 and Castro-Mayorga et al.20 demonstrated 4 log lower of median tissue tradition infectious dose of feline calicivirus after publicity to 10 mg of nano-Ag/l. Contemplating that the lower of viral titers ≥ 2 log might be considered the bottom biologically significant exercise in antimicrobial functions and at the very least 4 log discount inside as much as 1 h is required for biocidal merchandise in suspension assessments within the framework of European laws64, there’s solely little goal proof that Ag nanoparticles can be efficient antivirals from the standpoint of those necessities. Due to this fact, our conclusion on low antiviral exercise of nano-Ag when it comes to log PFU lower throughout 1-h publicity (Desk 2) is at broad degree in keeping with the earlier experiences. Nonetheless, usually view this conclusion is moderately shocking because it doesn’t show the antiviral efficacy of nanosilver opposite to the widespread perception.
The mechanism of antiviral exercise of nano-CeO2
There is no such thing as a clear mechanism of motion proposed as the premise of antiviral exercise of CeO2 nanoparticles. The basic evaluation of the mom resolution in contrast with literature knowledge allowed us to exclude the potential of the motion of CeO2 nanoparticles by way of launched Ce ions65. The equilibrium focus of launched ions was discovered to be extraordinarily low (10–7–10–8 M)42,66 and our experiments with Ce(NO3)3 confirmed that the antiviral exercise Ce3+ ions might be solely evidenced at concentrations a number of orders greater than achievable on account of dissolution of CeO2 nanoparticles (Fig. 4).
As a special mechanism of inactivating viruses, binding of CeO2 nanoparticles on viral genetic materials has been reported. Hyperlink et al.67 confirmed excessive binding capability of nanoparticles of CeO2 for nucleic acids in adeno-associated virus, adenovirus, human immunodeficiency virus, and murine leukemia virus67. Binding of nanoparticles onto the genetic materials of viruses might nonetheless happen solely when the latter is non-protected by the capsid, e.g., throughout replication. One other mode of binding has been proposed by Neal et al.58, who advised that Ag-doped CeO2 nanoparticles might bodily work together with the membrane of enveloped viruses, thus resulting in the disruption of their lipid bilayer. In case of non-enveloped viruses, an interplay with virion proteins was advised.
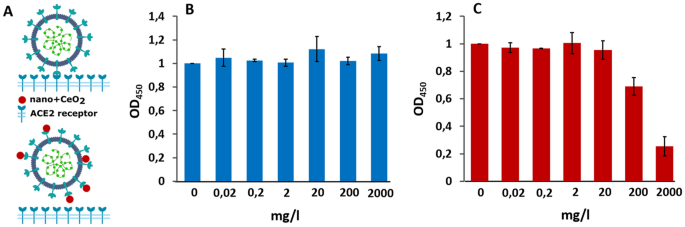
As our antiviral assay concerned publicity of complete virions to nanoparticles previous to cell an infection, we analyzed whether or not nano-CeO2 might have an effect on the binding of a virus to its pure ligand. ELISA assay was carried out to measure the in vitro binding exercise of nano-CeO2 uncovered SARS-CoV-2 to its mobile goal, the human recombinant ACE2 receptor (Fig. 5). Apparently, publicity of SARS-CoV-2 to nano-CeO2(−) and nano-CeO2(+) affected the virus considerably in a different way. Whereas publicity of SARS-CoV-2 to ≥ 200 mg/l of nano-CeO2(−) inhibited the binding of the virus to ACE2, publicity of SARS-CoV-2 to nano-CeO2(+) had no observable impact. Nonetheless, because the antiviral profiles of each CeO2 nanoparticles have been comparatively comparable, these outcomes don’t permit us to say that floor binding and blocking of ligand binding are the main mechanism of antiviral motion of nano-CeO2 evidenced by us in antiviral assays. Due to this fact, the mode of motion driving the antiviral impact of CeO2 nanoparticles is to be elucidated in future research.
Schematics of the experiment (A), the place the higher half reveals SARS-CoV-2 binding to ACE2 receptor with out nanoparticles and decrease half demonstrates the theoretical inhibition of SARS-CoV2 binding to ACE2 receptor by of CeO2 nanoparticles. (B) Reveals the impact of nano-CeO2(+) and (C) the impact of nano-CeO2(−) particles on binding of SARS-CoV-2 onto ACE2 receptor in an ELISA assay, measured as optical density (OD450).
Bactericidal impact of CeO2 nanoparticles
In parallel to antiviral properties, antibacterial exercise in the direction of the Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus was analyzed. In keeping with our outcomes, neither nano-CeO2(+) nor nano-CeO2(−) as much as 2000 mg/l decreased the viable counts (expressed as colony-forming models, CFU) of E. coli or S. aureus by greater than 2 logs (99%) (Fig. 6, Desk 3), indicating that the antiviral impact of CeO2 nanoparticles was extra pronounced than their bactericidal efficacy. Comparability of smaller modifications than 2 log lower in CFU ranges in E. coli and S. aureus confirmed that Gram-negative E. coli was affected by nano- CeO2 to a better extent than Gram-positive S. aureus (Desk 3). Whereas nano-CeO2(−) concentrations of two, 20 and 200 mg/l decreased the variety of E. coli CFUs by 1.48–1.68 logs, no lower in viable counts of S. aureus in response to nano-CeO2 was noticed. Apparently, the response of E. coli was non-monotonous as additionally in case of non-enveloped bacteriophage MS2. The upper sensitivity of Gram-negative micro organism in contrast with Gram-positive micro organism towards nano-CeO2 particles has been proven additionally in earlier research and has been associated to redox exercise of nanoceria and the flexibility of a thicker peptidoglycan layer to alleviate this impact68. Within the literature, variable outcomes might be discovered on antibacterial results of CeO2 nanoparticles, each as a result of number of nanoparticles used in addition to as a result of totally different antibacterial assays utilized. The minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of nano-CeO2 in the direction of a sequence of Gram-positive and -negative micro organism has been proven to fluctuate between 20 and 140 mg/l69,70. One other research the place nanoparticles of CeO2 have been ready utilizing surfactant Tween-80, demonstrated MIC of 150 mg/l whereas with out the surfactant the MIC worth was 3000 mg/l71. In one other research, full inactivation of E. coli was achieved within the presence of 1000 mg/l of CeO2 nanoparticles72. Thus, our end result displaying no vital antibacterial exercise of CeO2 in the direction of Gram-positive S. aureus (Desk 2) and comparatively modest antibacterial impact in the direction of Gram-negative E. coli as much as 2000 mg/l, coincided with a number of the outcomes printed earlier however differed from others, respectively.
Bactericidal exercise after 1 h publicity to nano-CeO2, Ce(NO3)3, nanoparticles of SiO2 and Ag towards Gram-negative Escherichia coli (A) and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (B). Bactericidal exercise is expressed as log discount in viable counts in comparison with unexposed management after 1 h. Outcomes of three unbiased experiments with normal deviation are expressed as discount of log CFU/ml. The dotted line signifies a restrict of quantification.
In another way from nano-CeO2 that confirmed vital or comparatively modest antibacterial impact, nano-Ag particles demonstrated vital antibacterial impact already at 1.5 mg/l. Expectedly Gram-negative micro organism have been extra delicate in the direction of nano-Ag and at 1.5 mg/l, already greater than 4 logs lower in E. coli viable counts was noticed. Viability of Gram-positive S. aureus decreased by > 4 log from 15 mg nano-Ag/l (Fig. 6, Desk 3). These outcomes are in settlement with earlier research which have proven the efficacy of Ag nanoparticles ranging from low mg/l vary27. Certainly, silver nanoparticles which are proven to behave by way of silver ion launch and ROS formation73 and the next interplay between Ag ions and thiol teams of proteins in addition to permeabilization of bacterial membrane, have been usually considered the nanoparticles with highest antibacterial exercise. In January 2022, greater than 18,000 articles have been registered in ISI WoS on “nano* AND silver* AND antibacter*”.
Nanoparticles of SiO2, usually considered innocent, didn’t present any bacterial toxicity in our experiments. Inexistent antibacterial exercise of nano-SiO2 alone has been proven additionally in different research, nonetheless, a lot of the papers on SiO2 used silica nanoparticles as carriers of extra biologically energetic metallic ions or different nanoparticles and thus, aren’t an ample comparability for our objective.