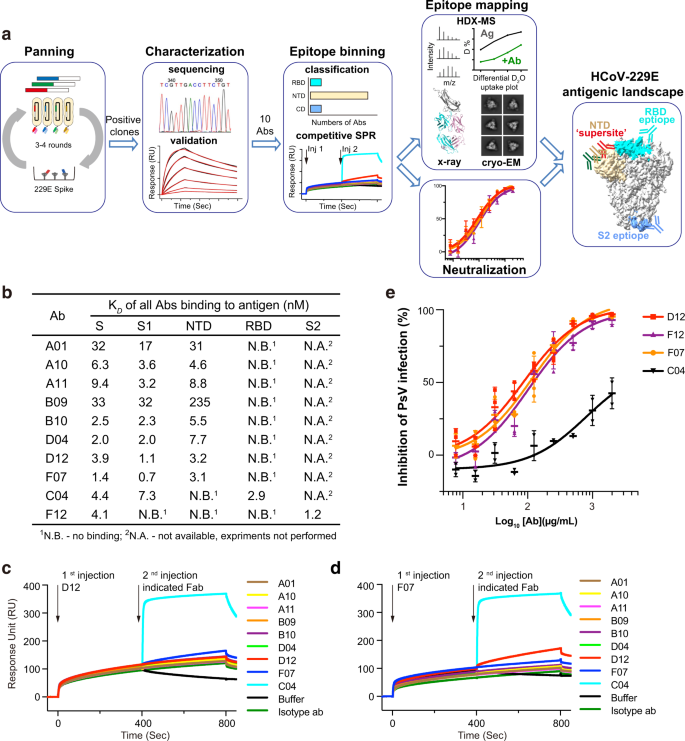
Choice and validation of antibodies towards 229E S trimer
We used a phage-displayed library (library F) of artificial, human antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) to pick out for antibodies that would acknowledge 229E S trimer (Fig. 1a, Supplementary Fig. 1a–c). Library F has a theoretical range of three × 1010, and has succeeded in picks towards quite a few proteins, together with a number of therapeutically vital targets, akin to IL-18, integrin, and Frizzled receptors40,41,42,43. 4 consecutive enrichment steps of panning have been carried out towards 229E S trimer, and single optimistic clones that sure to 229E S trimer however to not destructive management proteins in ELISA have been subjected to DNA sequencing. In whole, 13 Fabs with distinctive complementary-determining area (CDR) sequences have been recognized (Supplementary Fig. 1d). Recombinant Fabs have been then purified and examined for his or her binding to 229E S trimer through floor plasmon resonance (SPR). Ten of the 13 Fabs sure 229E S trimer with equilibrium disassociation fixed (OkayD) starting from 1–50 nM (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 1e). Three Fabs B03, B06, and E12 exhibited little or no binding to 229E S protein and thus have been excluded from subsequent investigations (Supplementary Fig. 1e).
a Schematic overview illustrating the antigenic panorama mapping strategy of 229E S trimer. b Interplay kinetics between every Fab and 229E S trimer, S1 or S2 subunit, NTD and RBD have been characterised by SPR. The outcomes point out that C04 is directed towards 229E RBD, F12 is directed towards the S2 subunit, whereas all the opposite Fabs particularly work together with 229E NTD. c, d Aggressive SPR outcomes present that the eight NTD-directed Fabs all compete for the same binding interface on 229E NTD. 229E S1 was immobilized onto the sensor, then blocked with saturating Fab D12 (c) or F07 (d), adopted by a second injection of buffer solely or the indicated Fabs. Fab C04 served as optimistic controls. e Neutralization profiles of IgG D12 (purple), F12 (purple), F07 (orange) and C04 (black) towards 229E PsV. Neutralizing actions are represented as particular person knowledge factors and imply ± SD (n = 3 biologically impartial experiments). Imply ± SD is indicated with  . Particular person knowledge factors are proven as stuffed purple squares (D12), purple triangles (F12), orange circles (F07) and black triangles (C04), respectively.
. Particular person knowledge factors are proven as stuffed purple squares (D12), purple triangles (F12), orange circles (F07) and black triangles (C04), respectively.
Antibody classification and downselection
Subsequent, we expressed and purified 229E NTD, RBD, S1, and S2 subunits (Supplementary Fig. 2a, b) and evaluated their binding to the ten validated Fabs individually (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 2c–f). 9 of the ten Fabs sure the S1 subunit effectively, with OkayD values akin to their affinities for intact 229E S trimer (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 2c). In the meantime, Fab F12 confirmed no binding in any respect to both S1, NTD or RBD though it sure intact S trimer tightly (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 2c, d), suggesting that it might bind to S2 subunit or a structural epitope that solely exists in trimeric S. Certainly, F12 sure S2 and S trimer with comparable OkayD values (1.2 and 4.1 nM) (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 1e, Supplementary Fig. second), confirming that the epitope of F12 is confined to the S2 subunit. Among the many 9 Fabs that sure the S1 subunit, solely Fab C04 acknowledged RBD whereas the opposite eight antibodies all sure NTD (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 2e, f). Such phenomenon implies that the NTD of 229E is extra antigenic than its RBD, which is in sharp distinction to earlier observations on the three extremely pathogenic β-HCoVs whereby their RBDs reasonably than NTDs are immunodominant18,19.
Up to now, ten 229E S-reactive Fabs may very well be categorised into 3 main teams, every recognizing the NTD, RBD or S2 subunit of 229E S (Fig. 1b). In comparison with group 2 and group 3 which embody C04 and F12, respectively, the NTD-recognizing group 1 is a big group comprising eight totally different Fabs. To grasp if these Fabs bind to comparable or distinct epitopes on NTD, we then carried out aggressive SPR to verify for his or her reciprocal binding to 229E S1 subunit. Contemplating that antibody pairs focusing on comparable epitopes can manifest false mutual binding when the affinity of the second antibody is far larger than that of the primary one, we thus flowed the strongest NTD binder D12 (or F07) first to saturate the immobilized S1 proteins earlier than difficult with every of the opposite NTD Fabs (Fig. 1c, d). Second injection of RBD-binding C04 was used as a optimistic management and certainly induced a big shift within the interference sample, whereas second injection of D12 (or F07) was taken as management for efficient blockade (Fig. 1c, d). Second injection of some other NTD Fabs hardly elicited wavelength shift, indicating that their binding was blocked within the prior presence of D12 (or F07) (Fig. 1c, d). Furthermore, concurrent binding was not noticed between F07 and D12 both (Fig. 1c, d). Collectively, these outcomes implies that the eight NTD-directed Fabs, A01, A10, A11, B09, B10, D04, D12 and F07, all compete for comparable binding websites on NTD.
Epitopes and neutralizing potencies of dominant NTD-directed antibodies
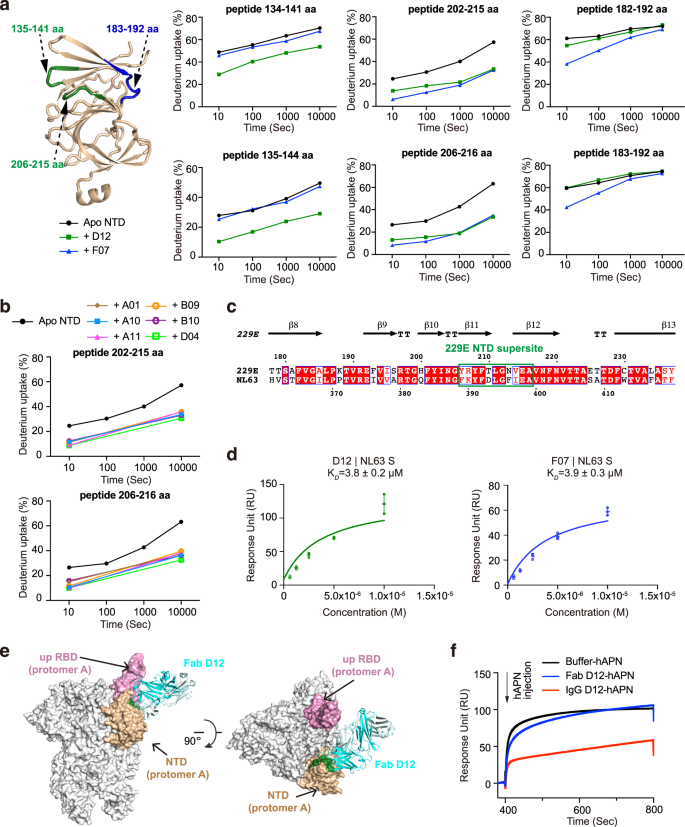
Earlier research of the β-HCoVs S proteins revealed the existence of ‘antigenic supersites’ within the NTDs of SARS-CoV-2 and OC4325,28,29. To grasp if the NTDs of α-CoVs exhibit comparable antigenic options, we got down to map the epitopes of the eight NTD-directed Fabs and assess their neutralizing potential. We first utilized HDX-MS39 to high quality map the epitope of D12 on the NTD of 229E (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Figs. 3a, 7a). In comparison with NTD alone, peptides 134–141 aa, 135–144 aa, 202–215 aa and 206–216 aa manifested markedly decreased HDX in any respect measured timepoints within the presence of Fab D12, suggesting that NTD areas encompassing 135–141 aa and 206–215 aa are possible concerned in D12 interactions (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. 3a). Subsequent, epitope mapping was carried out for all the opposite NTD antibodies utilizing HDX-MS (Supplementary Fig. 3). Of word, a number of the antibodies manifested comparable HDX safety profiles as seen with D12 (Supplementary Fig. 3a), whereas others, exemplified by F07, exhibited profound HDX safety in areas encompassing 183–192 aa and 206–215 aa as a substitute (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. 3b). As 135–141 aa, 183–192 aa and 206–215 aa are spatially shut to one another (Fig. 2a) and all antibodies manifested strongest HDX safety in 206–215 aa (Fig. 2a, b; Supplementary Fig. 3), the HDX-MS outcomes thus counsel that the NTD loop encompassing 206–215 aa possible performs determinant roles in participating all NTD antibodies. These antibodies, divided into two sub-groups and represented by F07 and D12 respectively, could method 206–215 aa from barely totally different angles, thereby resulting in totally different safety profiles on peripheral areas like 135–141 aa and 183–192 aa. Per the HDX-MS outcomes, Ala-mutations of single residues inside 206–215 aa induced as much as 96% lower in antibody binding, and the tetra-mutant (NTDT210A/L211A/N213A/V214A) barely sure D12 or F07 anymore (Supplementary Desk 1). Therefore, in keeping with the outcomes from aggressive SPR, the HDX-MS knowledge additionally signifies that the epitopes of the eight NTD-directed Fabs are extremely comparable and symbolize an ‘antigenic supersite’ within the 229E NTD (Supplementary Fig. 4b, close-up view).
a Antibody-dependent amide hydrogen safety signifies the potential interacting areas of D12 and F07 on 229E NTD. 229E NTD segments that manifested appreciable HDX lower in any respect measured timepoints within the presence of Fab D12 or F07 are highlighted on the cartoon illustration of NTD and labeled. Deuterium uptake plots of those segments within the absence (black) and presence of Fab D12 (darkish inexperienced) or F07 (blue) are plotted as p.c deuterium uptake versus time on a logarithmic scale for instance their HDX kinetics. b Deuterium uptake plots present that appreciable HDX decreases have been noticed for NTD peptides 202–215 aa and 206–216 aa at 10 s and 10,000 s within the presence of all different 229E NTD-directed antibodies, indicating that these antibodies additionally goal this area on 229E NTD. c Sequence alignment of 229E and NL63 NTDs. The antigenic supersite in 229E NTD is marked by inexperienced rectangle. d Equilibrium evaluation plots depicting the interactions between immobilized NL63 S protein and Fabs D12 (left) and F07 (proper). The OkayD values are proven as particular person knowledge factors and imply ± SD (n = 3 biologically impartial experiments). Imply ± SD is indicated with  and particular person knowledge factors are represented with open inexperienced (D12) or blue (F07) circles. e Mannequin of Fab D12 binding to 229E S trimer in one-RBD-up configuration. Fab D12 is depicted as ribbons (gentle and heavy chains in several shades of blue). 229E S trimer is proven as grey floor representations, with its RBD in ‘up’ configuration coloured pink and the intra-subunit NTD coloured wheat. NTD area 206–215 aa is coloured darkish inexperienced to focus on the consensus epitope focused by D12, F07 and all the opposite NTD-directed antibodies. f Pre-binding of D12 in IgG however not Fab format interferes with the binding of hAPN to the 229E S trimer. Immobilized 229E S trimer was saturated with D12 in both Fab or IgG format earlier than injection of recombinant hAPN protein (injection level indicated with arrow). All SPR experiments have been independently carried out at the very least twice and consultant profiles from one experiment are proven.
and particular person knowledge factors are represented with open inexperienced (D12) or blue (F07) circles. e Mannequin of Fab D12 binding to 229E S trimer in one-RBD-up configuration. Fab D12 is depicted as ribbons (gentle and heavy chains in several shades of blue). 229E S trimer is proven as grey floor representations, with its RBD in ‘up’ configuration coloured pink and the intra-subunit NTD coloured wheat. NTD area 206–215 aa is coloured darkish inexperienced to focus on the consensus epitope focused by D12, F07 and all the opposite NTD-directed antibodies. f Pre-binding of D12 in IgG however not Fab format interferes with the binding of hAPN to the 229E S trimer. Immobilized 229E S trimer was saturated with D12 in both Fab or IgG format earlier than injection of recombinant hAPN protein (injection level indicated with arrow). All SPR experiments have been independently carried out at the very least twice and consultant profiles from one experiment are proven.
Subsequent, we requested whether or not this antigenic supersite, 206–215 aa, is preserved in NL63, one other α-HCoV. Notably, curated prediction of the B cell epitopes on NL63 NTD signifies the presence of a robust B cell epitope on the similar place (Supplementary Fig. 4d, far proper panel, 393–397 aa). Furthermore, this NTD epitope manifested ~80% sequence similarity among the many varied isolates of α-HCoVs (Fig. 2c, boxed area and Supplementary Fig. 4e). Certainly, Fabs D12 and F07 might cross-react with NL63 S protein (Fig. second and Supplementary Fig. 4f) (albeit weakly), almost definitely pushed by their recognition of the same area in NL63 NTD (Fig. 2c, boxed area). The above outcomes collectively argue that, akin to earlier observations in β-HCoVs, ‘antigenic supersites’ additionally exist within the NTDs of α-HCoVs, though the areas of such ‘antigenic supersites’ are distinct between α-HCoVs and β-HCoVs (Supplementary Fig. 4d).
In contrast to the outward-facing antigenic supersites in β-HCoVs NTDs (Supplementary Fig. 4a)22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29, the recognized antigenic supersite within the NTD of 229E seems to be partially buried within the all-RBD-down conformation of the 229E S trimer (Supplementary Fig. 4b), though it might develop into totally accessible when the intra-subunit RBD is within the ‘up’ conformation (Supplementary Fig. 4c). We then docked D12 onto the one-RBD-up mannequin of 229E S trimer, utilizing 206–215 aa of NTD as interface constraints (Fig. 2e). Primarily based on the docking mannequin, the binding of D12, in its IgG format, would hinder the interplay between 229E RBD and its host receptor human aminopeptidase N (hAPN)44,45. Certainly, we discovered that pre-incubation of 229E S with IgG D12 diminished the binding of hAPN (Fig. 2f) and that IgG D12 inhibited the entry of 229E pseudovirus (PsV) with IC50 at 86 μg/mL (Fig. 1e). Likewise, IgG F07 additionally inhibited the entry of 229E PsV with IC50 at 115 μg/mL (Fig. 1e).
Collectively, these outcomes point out that every one the 229E NTD-directed antibodies acknowledge an analogous neutralizing epitope ranging 206–215 aa on 229E NTD. Given the excessive sequence conservation of this epitope throughout varied isolates of α-HCoVs (Supplementary Fig. 4e), it might even symbolize a hotspot of antigenic vulnerability on all α-HCoVs NTDs.
Epitope and neutralizing efficiency of the primary α-HCoV S2-directed antibody F12
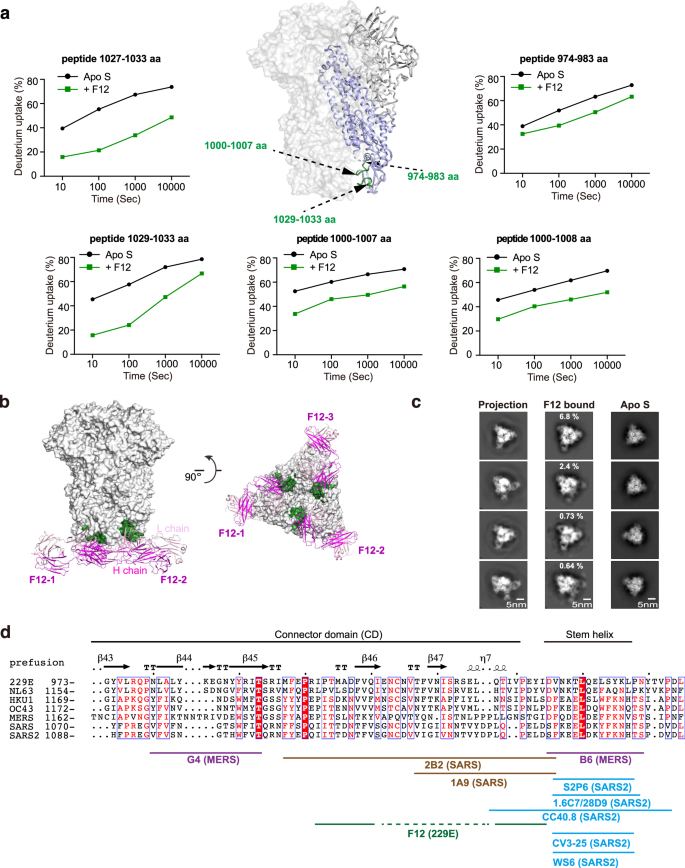
The stronger potential of S2 subunit over S1 subunit to function pan-HCoV intervention goal has spurred enthusiasm to seek for S2-directed antibodies46,47. Though a number of S2-directed antibodies have been reported for SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV and confirmed restricted broadness amongst them, no such antibody has been reported but for α-HCoVs till the identification of F12 on this research31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38 (Fig. 1b). We thus went on to high quality map the epitope of F12 on intact 229E S trimer and to characterize its breadth inside genus. Within the presence of F12, decreased HDX was noticed for peptides 974–983 aa, 1000–1007 aa, 1000–1008 aa, 1027–1033 aa and 1029–1033 aa in 229E S2 (Fig. 3a, Supplementary Figs. 5a, 7b), indicating a excessive likelihood for residues in these areas to work together with F12 straight or not directly. The HDX safety impact was most profound in areas ranging 1027–1033 aa, adopted by 1000–1007 aa, and was average in 974–983 aa (Fig. 3a; Supplementary Fig. 5a). Such statement, along with the truth that 1000–1007 aa and 1029–1033 aa are conformationally adjoining to one another (Fig. 3a), counsel that these two areas possible represent the genuine epitope for antibody F12, whereas the HDX lower in spatially extra distant 974–983 aa could originate from oblique stabilizing results. Per such notion, single residue mutagenesis in both 1000–1007 aa or 1029–1033 aa fully prevented the binding of F12 (Supplementary Desk 2).
a F12-dependent amide hydrogen safety signifies its potential interacting areas in 229E S2. S2 segments that manifested appreciable HDX lower in any respect measured timepoints within the presence of Fab F12 are highlighted with darkish inexperienced on the cartoon illustration of 1 229E S protomer (S2 coloured purple) within the context of 229E S trimer (gentle grey floor presentation). Deuterium uptake plots of those segments within the absence (black) and presence (darkish inexperienced) of Fab F12 are plotted as p.c deuterium uptake versus time on a logarithmic scale for instance their HDX kinetics. b Mannequin of Fab F12 binding to 229E S trimer within the all-RBD-down state. Fab F12 is depicted as ribbons (gentle and heavy chains in several shades of magenta). The genuine epitope of F12 as double-defined by HDX-MS outcomes and mutagenesis verification is highlighted with darkish inexperienced on the grey floor illustration of 229E S trimer. c To look at the correspondence between cryo-EM 2D class averages and the mannequin of F12-bound 229E S trimer, consultant 2D projections of the mannequin (left panels) is in comparison with reference-free averages of F12-bound 229E S trimer (center panels) or 229E S trimer alone (proper panels). d Sequence alignment of CD and stem helix area throughout the S2 subunits of α- and β-HCoVs. The structural epitope of F12 and the epitopes of different beforehand reported S2-directed antibodies are indicated with strong traces below the alignment.
Utilizing these findings as constraints, we then went on docking F12 onto the pre-fusion conformation of 229E S trimer (Fig. 3b)10. To additional affirm the docking outcomes, we additionally collected cryo-EM knowledge on F12-bound 229E S trimer. Though a high-resolution mannequin of this advanced was not obtained on account of sturdy orientation desire, we have been in a position to receive prime quality reference-free class averages of some views (Fig. 3c). Evaluating the reference-free class averages of F12-bound and F12-free 229E S trimer, stoichiometric binding of F12 may very well be clearly seen (Fig. 3c, evaluate the correct two panels). Furthermore, the reference-free class averages of F12-bound 229E S trimer matched very nicely to the 2D projections of the docking mannequin (Fig. 3c, evaluate the left two panels), additional corroborating the docking mannequin. Subsequent, we examined the neutralizing efficiency of F12. IgG F12 did inhibit the entry of 229E PsV with IC50 at 101 μg/mL (Fig. 1e), presumably by initiating untimely conformational change of S proteins or by blocking the formation of the 6-HB, similar to different S2-binding NAbs do35,38. Collectively, these outcomes point out that F12 acknowledges a structural epitope within the connector area (CD) of 229E S2 subunit and is certainly neutralizing (Fig. 3d).
Beforehand, a number of S2-directed NAbs have been reported31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38. Of the 2 NAbs that concentrate on MERS-CoV S2, G4 binds to a variable glycosylated loop throughout the CD and lacks cross-reactivity, whereas B6 acknowledges the comparatively conserved stem helix area instantly earlier than the HR2 and has been discovered to cross neutralize MERS-CoV and OC43 (Fig. 3d)35,38. In the meantime, 2B2 and 1A9 acknowledge comparable areas throughout the CD of SARS-CoV and the latter manifests restricted cross-reactivity to SARS-CoV-2 (Fig. 3d)37,48. For SARS-CoV-2, the epitopes of all of the S2-directed NAbs cluster throughout the stem helix area and certainly one of these NAbs, S2P6, has been discovered to harness broad neutralizing exercise towards almost all β-HCoVs31,32,33,34,35,36 (Fig. 3d). Taken collectively, these findings point out that the stem helix area inside S2 appears to be an epitope with higher pan-HCoV potential than the CD area. In additional assist of this, we discovered that CD-targeting F12 lacks cross-reactivity even to NL63 in the identical genus (Supplementary Fig. 5b).
Neutralizing epitopes within the distal finish of 229E RBD
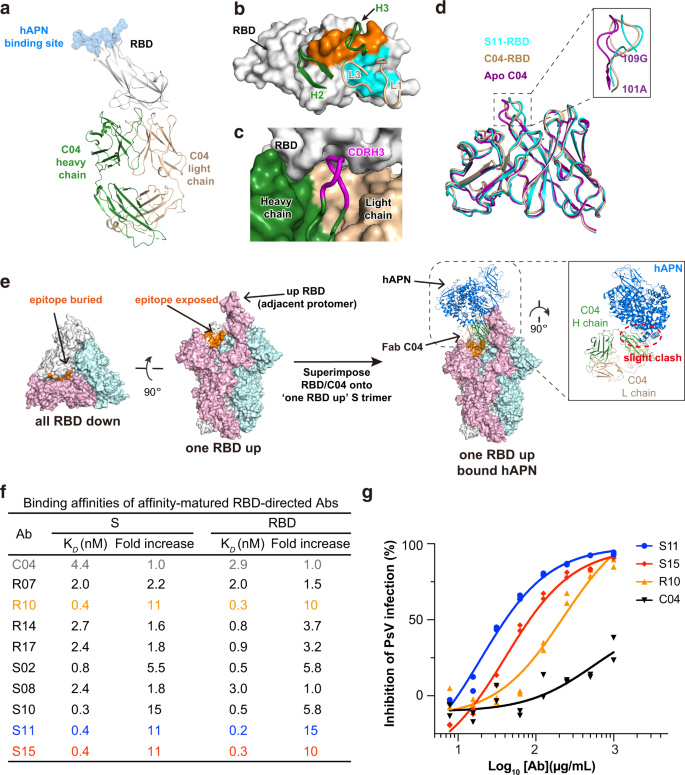
Within the case of SARS-CoV-2, it’s observed that essentially the most potent NAbs normally acknowledge epitopes inside RBD, adopted in efficiency by antibodies towards its NTD and S2 subunit20,49,50. Opposite to this statement, the RBD-directed C04 seems to be the least neutralizing in all recognized antibodies towards 229E S, with IC50 > 500 μg/mL (Fig. 1e). To grasp if its low neutralizing exercise correlates with its mode of motion, we then decided the crystal construction of Fab C04 alone and C04 in advanced with 229E RBD (Fig. 4a, Supplementary Fig. 6a and Desk 1). C04 buried 525 Å2 floor space on the RBD with its CDRL1 and CDRL3, and 462 Å2 with its CDRH2 and CDRH3 (Fig. 4b). Amongst these CDR loops, CDRH3 is of specific curiosity because it incorporates as many as 5 Gly residues throughout the CDRH3 loop (Supplementary Fig. 1d), which possible endows it with nice structural plasticity to neatly match itself right into a pocket on RBD floor (Fig. 4c), by largely spine pushed interactions (Supplementary Fig. 6g). The structural plasticity of CDRH3 can also be nicely demonstrated by its giant conformational change upon binding RBD (Fig. 4d). Whereas the RMSD of CDRH3 reached 1.51 Å upon RBD binding, the typical RMSD of CDRL1, CDRL3 and CDRH2 was solely 0.66 Å.
a Crystal construction of Fab C04 in advanced with 229E RBD in cartoon representations. The heavy and lightweight chain of C04 are coloured darkish inexperienced and wheat respectively, whereas 229E RBD are coloured grey. The binding web site of host receptor hAPN is depicted with blue spheres. b Contact residues are coloured orange (heavy chain) and blue (gentle chain) on floor illustration of 229E RBD. CDR loops participating 229E RBD are proven and labeled. c The heavy (darkish inexperienced) and lightweight chain (wheat) of C04 and the RBD (grey) are proven as floor representations. CDRH3 (magenta) is depicted in cartoon for instance its neat becoming into the floor pocket on 229E RBD. d Structural superimposition of free C04 (purple), RBD-bound C04 (wheat) and RBD-bound S11(blue) illustrating the conformational change of CDRH3 upon binding RBD. All buildings are proven as cartoon representations and the inset is the close-up view of CDRH3 area. e Left: The epitope of C04 seems buried in all-RBD-down conformation however turns into totally uncovered in one-RBD-up conformation. Proper: Binding of Fab C04 would barely intervene with the binding of hAPN to neighboring ‘up’ protomer (coloured pink, anti-clockwise). Construction of Fab C04-bound 229E S trimer was modeled by superimposing the construction of RBD-C04 onto the one-RBD-up 229E S trimer. Subsequent, this construction was aligned with hAPN-229E RBD advanced primarily based on the 229E RBD in ‘up’ place. f Binding affinities of parental C04 and affinity-matured antibodies towards 229E S trimer or RBD have been characterised by SPR. Of the affinity-matured antibodies, antibody S11 (blue) and S15 (purple) exhibited as much as 11-fold improve of their affinity for 229E S trimer and RBD. g Neutralization profiles for IgG S11 (blue), S15 (purple) and R10 (orange) are in comparison with that of parental IgG C04 (black) towards 229E PsV. Particular person knowledge factors are proven as stuffed blue circles (S11), purple diamonds (S15), orange triangles (R10) and black triangles (C04) respectively.
Notably, the epitope of C04 is distal to the hAPN receptor binding web site on 229E RBD (Fig. 4a), considerably analogous to the binding mode of a number of SARS-CoV-2 NAbs together with CR3022, EY6A, S304 and 553-49, which additionally goal the ‘cryptic’ epitopes within the distal finish of SARS-CoV-2 RBD20,51,52,53. Akin to those SARS-CoV-2 NAbs, the epitope of C04 additionally seems buried within the all-RBD-down conformation of 229E S trimer, but would develop into totally accessible when its anti-clockwise neighboring RBD is within the ‘up’ place (Fig. 4e, left panel). Structural alignment of the C04-229E RBD advanced with the one-RBD-up S trimer additional signifies that binding of Fab C04 would barely intervene with the binding of hAPN to the neighboring ‘up’ protomer (Fig. 4e, proper panel). Persistently, pre-incubation of 229E S with C04 in both Fab or IgG format certainly diminished the binding of hAPN (Supplementary Fig. 6b), though to an extent lower than that induced by IgG D12 pre-incubation (Fig. 2f). Of word, binding of CR3022 or 553-49 has been proven to induce the destruction of SARS-CoV-2 S protein53,54,55. As C04 additionally targets the ‘cryptic’ floor on 229E S protein, we puzzled if the binding of C04 would induce the disassembly of 229E S and thus visualized 229E S below negative-staining EM both within the absence or presence of C04 (Supplementary Fig. 6c). Within the presence of C04, a superb portion of the 229E S trimers disassembled into C04-bound 229E S protomer (Supplementary Fig. 6c, proper) by the top of the 1 h incubation whereas a lot of the 229E S trimers remained intact within the absence of C04 (Supplementary Fig. 6c, left). Due to this fact, moreover blocking the binding of APN by steric hinderance, C04 may also neutralize by inducing the disassembly of 229E S protein.
The place of C04 epitope explains its relative low neutralizing exercise. Within the case of distal-end binding antibodies like CR3022, neutralizing exercise is extremely correlated with their affinity for SARS-CoV-2 RBD56. Provided that C04 was chosen from a naïve artificial library, it clearly lacks the chance to enhance its affinity by somatic hypermutation. To boost the neutralizing efficiency of C04, we thus carried out in vitro affinity maturation utilizing a soft-randomized library primarily based on the parental clone and obtained a subset of optimistic clones which exhibit larger affinities for each 229E RBD and S trimer (Fig. 4f, Supplementary Fig. 6d, e). Of those affinity-matured antibodies, antibody S11 and S15 exhibited as much as an 11-fold improve of their affinities for 229E RBD and S trimer (Fig. 4f), largely on account of their a lot slower disassociation from targets (Supplementary Fig. 6d, e). Accordingly, IgG S11 and S15 manifested considerably enhanced neutralizing exercise towards 229E PsV infections as in comparison with IgG C04, with IC50 values at 19 and 40 μg/mL respectively (Fig. 4g). We additionally went additional to characterize the construction of S11-RBD advanced and located that the binding mode of S11 is identical to that of C04 (Supplementary Fig. 6f), with an general RMSD of 0.69 Å. The foremost distinction between S11 and C04 lies of their distinctive G-rich CDRH3 loops, whereby CDRH3 residues A109S110V111 matured into I109T110F111 in S11, thereby enabling further sidechain-to-sidechain hydrophobic packing with P393 and W419 of RBD (Supplementary Fig. 6g). Therefore, analogous to the ‘cryptic’ epitopes within the distal finish of SARS-CoV-2 RBD, a neutralizing epitope can also be situated within the distal finish of 229E RBD.